Risk ManagementThis particular report on risk management covers a lot of the dimensions of the Infosys Enterprise’s function of risk management. The information connected to risk that have been discussed under this particular portion might not be exhaustive in nature. The report might also comprise of the statements which are by nature forward – looking. The business is subject to a lot of uncertainties which might lead to real results to vary in material terms from the ones that are seen in those statements which are forward – looking in nature (Zhu & Fukushima, 2009). Considering if a few of the risks materialise, the prospects, the financial conditions and the business might be adversely and materially impacted. The prospects, the financial performance, the operating results as well as the business might also be adversely influenced as a result of the uncertainties as well as the risks which are not presently known or also those which are not presently thought to be practical. Discussed below is an overview of the Infosys Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) function which allows the fulfilment of the strategic goals by governing, monitoring, mitigating, assessing, analysing and identifying any potential threat or risk to the goals. Although the fulfilment of the strategic goals is the main driver, the commitment, the obligation, the culture and the values that the company holds towards its community, partners, regulatory bodies, investors, customers and employees are the basis upon which the Enterprise Risk Management framework of the company is grown (Ben-Tal et al., 1998). The proactive and the systematic identification of the mitigation and the risks thereof allow quick or effective decision – making as well as in boosting the organisation’s performance. The Enterprise Risk Management function is an enabler of decision that not just looks towards minimizing the influences of the risk however the same also allows proper allocation of the risks on the basis of the appetite of risk as well as on the ranking of the impacts of the risks. The strategic decisions are made once minute study has been made upon the residual risks, the tertiary risks, the secondary risks as well as the primary risks. The Enterprise Risk Management at Infosys covers all of the risks which is faced by the establishment under a variety of different sections which include the compliance risks, legal risks, operational risks as well as strategic risks. Any given section might possess external or internal dimensions. Therefore, the appropriate indicators of risks are made use of for the proactive identification of these risks (Föllmer & Schied, 2002). 3 Main Constituents of the ERM Framework at Infosys The Infosys enterprise makes use of the incorporated ERM framework which is being used throughout the establishment by the office of the risk – management. The framework is dependent upon the global standards and is tailor – suited to the needs of the business.
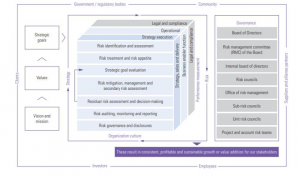
Figure 1: Integrated ERM Framework of Infosys. The risk management framework of the Infosys Enterprise is employed across a lot of different stages throughout the establishment. The main responsibilities as well as the risks involving the management of risks in the organisation have been described as under:
The Board of Directors have the responsibility of approving the main objectives of the business which are to be attained by the organisation. They must also have to ensure that the management is focusing upon mitigating the risks. Apart from these, they are also liable to review the performances of the risk and the strategy committee (Ruszczyski & Shapiro, 2006).
The company as well as the industry of Infosys Enterprise are transforming considerably and this has genuinely led to risks’ heightening which are connected to those choices which are strategic in nature, the strategy execution as well as conventional compliance and operational related risks. The objectives of the business have been written in a set of particular goals in the near – term and strategic goals in the long – term within a corporate score – card. The goals encompass the areas of continuous long – term sustainability of the establishment, retaining as well as attracting talent, initiatives of cost – optimisation, operational excellence as well as keeping the momentum of the services which are software – enabled. Moreover, the initiatives of progress include the reduction of the effects of the possible influences to the regulations of the labour and immigration in the US along with various other nations (Artzner et al., 1999). The framework of risk management thinks of the following wide sections of risk:
The risks that come out of the threats being directed to the organisational, financial or reputational standings of the company result from different elements such as non- conformity or violations of laws and regulations, contractual compliances, potential litigations, code of conduct or other prescribed practices of the organisation are taken into account in this category. It also incorporates the potential risks which emerge out important geopolitical/ regulatory changes or risks that arise out of business or strategic or operational decisions (Infosys, 2019). 7 The process of risk management The ERM framework of the organisation defines the steps in order to figure out, evaluate and assess the risk factor. Residual as well as secondary risks are applied as key ingredients for takings decisions upon the key strategies of risk mitigation. Risk governance The company has taken into account a structure of multi level governance in order to oversee and report the different sort of risks as well as their mitigations. Cross functional risks or critical risks at all the different levels are being enhanced to the next phase with respect to the governance structure. The critical risks falling under different risk classifications at the Group level are properly evaluated by the CEO (Chief Executive Officer), Chief Risk Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operating Officer as well as the General Counsels at different counsels. The critical risks emerging out of these councils are given to Internal Board of Directors and hence to the Board’s committee of risk management on quarterly basis (Infosys, 2019). Risk Library The risk management office has developed a multi level risk register. To consider about the highest level, the risks in order to achieve the strategic goals of the company for Scaling Agile digital and Energizing the Core. It has also been initiated in order to make sure organisational hygiene, which is concerned with efficiency, effectiveness, integrity, security, governance. To move further down into the hierarchy of the risk register includes the risks concerned with sub processes as well as controlled risks. The quantitative exposure of the company from the exposure of the risks at different levels are brought together in order to make an appraisal of the company’s risk exposure. This hierarchy guarantees that there exists a risk library which is common in the company (Infosys, 2017). The common risk register is being activated on the iGRC of the company, the technology portal of the company. RISC RISC360 is the Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) program of the company that brings together three layer defences within one ambit in order to stimulate the risk- based auditing and decision making. The company has incorporated a technology platform known as iGRC, to assist the initiative. This new platform provides a consolidated picture of the strategic goals as well as the relevant risks concerned with leadership in order to facilitate effective and quick form of decision making throughout the enterprise risk, in conformity with Sarbanes Oxley Act, corporate audit and internal audit. The very process of their integration while taking into account on platform which is common to the company makes sure that the audits rely upon the risks that are attached to the overall structure of the company and it gets the privilege synergies amongst the different defence lines (Infosys, 2019). 8 Risk management highlights for year 2019 In course of the period, the emphasis of the company was on consideration of the idea of adopting the ERM framework (integrated) throughout the organisation as well as bolstering the program of risk management: Considering it as a part of appraising the major risks, the office of the risk management:
Risk management in any company plays a very important role in mitigating or neutralising the elements which might otherwise turn out to be harmful for the concerned business. From the above analysis of the facts, it is evident that the Infosys had made serious efforts to effectively manage the risk. Among others, the risk management unit of the company assessed the business environment on a regular basis while taking into account the external indicators’ trend lines such as client technology spent and revenue bookings out of the huge outsourcing engagements. Furthermore, the elements of risks prior to business penetration are reviewed. These findings collectively proved the point that the company is capable of incorporating the risk management measures. Artzner, P., Delbaen, F., Eber, J.-M., Heath, D., 1999. Coherent risk measures. Mathematical Finance 9 (3), 203–228. Barvinok, A., 2002. A Course in Convexity. American Mathematical Society, Ann Arbor. Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A., 1998. Robust convex optimization. Mathematics of Operations Research 23 (4), 769–805. Föllmer, H., Schied, A., 2002. Convex measures of risk and trading constraints. Finance & Stochastics 6 (4), 429–447. Infosys. (2017). Infosys: Annual Report 2016- 17. Retrieved 14th October, 2019 from https://www.infosys.com/investors/reports-filings/annual-report/annual/Documents/AR-2017/financials/pdf/Infosys_AR17_Risk_Management_Report.pdf Infosys. (2019). Infosys: Annual Report 2018- 19. Retrieved 14th October, 2019 from https://www.infosys.com/investors/reports-filings/annual-report/annual/Documents/infosys-ar-19.pdf Jabbour, C., Peña, J., Vera, J., Zuluaga, L., 2008. An estimation-free robust cvar portfolio allocation model. Journal of Risk 11, 57–78. Lüthi, H.-J., Doege, J., 2005. Convex risk measures for portfolio optimization and concepts of flexibility. Mathematical Programming, Series B 104, 541–559. Ruszczyski, A., Shapiro, A., 2006. Optimization of convex risk functions. Mathematics of Operations Research 31, 433–452. Shapiro, A., Dentcheva, D., Ruszczyn´ ski, A., 2009. Lectures on Stochastic Programming: Modeling and Theory. SIAM, Philadelphia. Soyster, A.L., 1973. Convex programming with set-inclusive constraints and applications to inexact linear programming. Operations Research 21 (5), 1154–1157. Zhu, S., Fukushima, M., 2009. Worst-case conditional value-at-risk with application to robust portfolio management. Operation Research 57 (5) |