Short Report Global Economy Assignment Sample
Introduction
The current study emphasises on reflecting the inflation trends or trajectory in Germany, ranging from 2000-2020, and also the year 2021. Moreover, it also observes the factors which largely contribute in inflation trajectory in the nation.
Inflation Path
Annual rate of inflation in Germany increased to 4.5% in October 2021, which is the highest rate since August 1993. The inflation rate was 1.35% in 2019. The present rate matches the target rate of European Central Bank, which is below, however, close to 2%. Hence, Germans may risk deflation than high levels of inflation.
Factors contributing to the inflation trajectory in 2021
Demand factors
Increase in disposable income : Personal Disposable Income in Germany highlighted an average amount of 233.74 EUR Billion, from the year 1960 to 2021. It reached an all-time high amount of 920 EUR Billion within the first quarter of 2021 (Bobeica et. al. 2017). Also, it recorded low of 22.96 EUR Billion during the first quarter of the year 1960.
Increase in money supply: Money Supply M3 increased to approximately 3616.50 billion euros in September, as compared to 3602.80 billion euros in August 2021 (Israel and Schnabl, 2020). It is further estimated to trend around 3700 billion euros in 2022, as per the latest economic models.
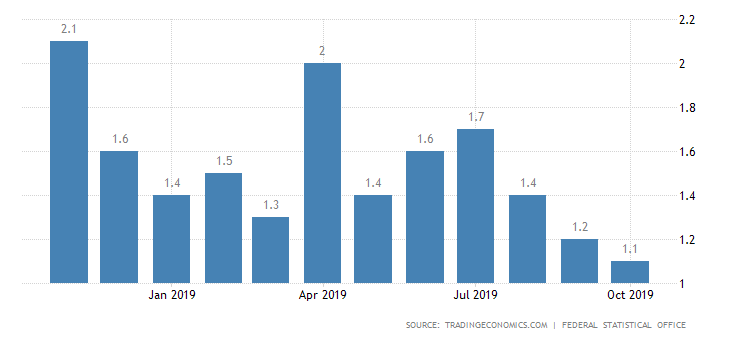
Figure 1 Inflation trends in Germany
(Source: Joana Ferreira, 2019)
Rise in exports: A strong increase in exports broadened the trade surplus amounting to 13.6 EUR Billion as compared to 12.8 EUR Billion in May 2021, with the growth rate of 0.4%.
Supply factors
Energy prices: Energy prices in Germany have been increasing faster as compared to the general average price level since months (Serletis and Liu, 2020). Also, consumers or people in the country burning fossil fuels had to pay €25 or $29.70 per ton of Carbon dioxide emitted since January 2021.
Tax cut: Six-month cut in sales tax in 2020 resulted in inflation in Germany. Falling consumer demand due to the pandemic outbreak, resulted in Germany government cutting the VAT rates to approximately 16% and 5% during the second half of 2020, as compared to the previous rates of 19% and also, 7%.
Natural calamity: The Ahr Valley flood in Germany resulted in increasing inflationary pressure within the economy (Howe, 2020). The country’s government highlighted an increase in inflation by 0.37%.
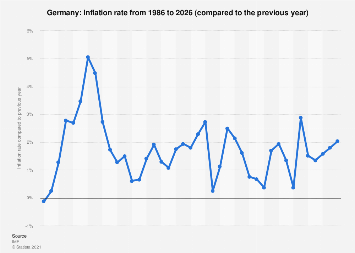
Figure 2 Rate of Inflation in Germany (1986-2026)
(Source: Aaron O’Neill, 2021)
Conclusion
Based on the data and statistical findings concerning inflation trends in Germany, it is estimated to trend around 1.80% in 2022 as well as 2% in 2023, as per the latest economic models in the country. The above study highlighted the inflation trends and trajectory in Germany.
References
Bobeica, E., Nickel, C., Lis, E. and Sun, Y., (2017). Demographics and inflation (No. 2006). ECB Working Paper.
Howe, G., (2020). The fight against inflation (pp. 45-60). Routledge.
Israel, K.F. and Schnabl, G., (2020). Alternative Measures of Price Inflation and the Perception of Real Income in Germany.
Serletis, A. and Liu, J., (2020). Inflation and economic activity in advanced and emerging economies. International Journal of Finance & Economics.
Online:
Joana Ferreira, 2019. German Inflation Rate Unchanged at 1-1/2-Year Low. [Online:]. Accessed through:< https://tradingeconomics.com/articles/11282019131047.htm >
Aaron O’Neill, 2021. Inflation rate in Germany 2026. [Online:]. Accessed through:< https://www.statista.com/statistics/375207/inflation-rate-in-germany/ >
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

