SOE11147 Global Logistics and Supply Chains
Module Code And Title – SOE11147 Global Logistics and Supply Chains
1. Statement of the purpose of the report
Several types of supply chain strategies are available in the market that is going to be evaluated in this study. Software change strategies to guide organizations to recommend the most effective supply chain management strategy for new product development. Usage of the latest technologies to utilize available capital resources of organizations are going to be discussed in this study. Improvement strategy to operate the supply chain is going to be discussed to identify appropriate measures that are to be taken into consideration for organizational performance development.
2. Key findings
2.1 Evaluation of supply chain strategy
Implement information technology in the warehouse
Organization supply implements information technology in the manufacturing area to increase efficiency of employees and productivity of an organization. Most of the companies I have taken help from information technology to build a digital supply chain that is sustainable in every uncertain situation. As cited by Mostafa, Hamdy & Alawady (2019), cost of production reduces for consideration of digital supply chain management strategy. Implementation cost is high however digital infrastructure reduces pressure from the management team and allows them to control the entire process efficiently. Infrastructure of the manufacturing area is reconstructed based on the supply chain management system and it is necessary for operational success.
Ensure optimum utilization of available resources
Utilization of available resources is necessary to maximize organizational profit and a new product development strategy requires several types of resources to collaborate with different market situations. As opined by Moktadir et al. (2018), organizations forecast the farm products available through supply chain management and their capacity of inventory management. In this way, supply channel strategy utilizes available resources based on organization’s capacity. Operation management is operated in a structured way and it is controlled by a centralized body and they are able to access real-time data of product position and entire management process.
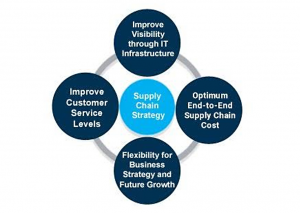 Figure 1: Supply chain strategy (Source: Moktadir et al. 2018)
Figure 1: Supply chain strategy (Source: Moktadir et al. 2018)
Improve customer care service
Supply chain management creates a path from manufacturer to consumer and it helps to collect consumer data directly. As cited by Hu et al. (2019), new product development strategy is based on customer needs and wants and the supply chain management strategy focuses on collecting their data to enhance the production process and mitigate sales risk for the upcoming period. Consumer data is essential to measure organizational capacity and new product development is enhanced by understanding different levels of customers and their affordability.
Implement flexible business management
Companies face several types of uncertain situations during dealing with new product development strategies because the market is unpredictable. Flexible making is necessary for every organization to maintain market competitiveness. As stated by Palandeng et al. (2018), supply chain management strategy allows organizations to take efficient initiatives to improve decision-making power by providing real-time data to managers. Success of an organization cannot arise in a single strategy and organizations must implement new innovative strategies to deal with the changing environment.
2.2 Review of supply chain concepts
Supply chain concepts involve different steps that are taken by an organisation to provide products and services to end-users and final consumers. These steps include the transmission of raw material and other resources for transmission to the final product and transfer of that product to different locations’ consumers. As argued by Chandak & Chandak (2021), an organisation’s productivity rate and performance depend on the effectiveness and performance of “supply chain management”. Thus it is necessary for a manufacturing or retail organisation to develop a “supply chain management” that has digital assistance and latte technology in order to develop a “digital supply chain”. The five key concepts that should be significantly considered by an organisation in order to increase their growth along with cash flow for better financial stability in the market.
Planning: an organisation should evaluate demand in the market and needs of consumers to manufacture products and services for consumers. As cited by Frederico et al. (2019), therefore, organisations should develop strategies for long term demand along with short term demand in the market. The supply chain leader should develop integrated “supply chain strategies” that consider feedback of consumers to produce consumers’ demanded products. The above-mentioned steps improve an effective supply chain along with consumer satisfaction level which is a key factor for an “effective supply chain”.
Procurement: after properly evaluating market demand and developing planning for demand, product organisation is required to acquire sufficient “raw material, components and resources” to manufacture the final product that is provided to final consumers. Procurement process is also affected by an organisation’s supply chain along with the whole supply chain strategy. As opined by Frederico et al. (2019), thus an organisation should have a “digital logistic system” that is suitable to acquire ray material from the global market. As a result, it is able to acquire ray material and manufacturing components at a low price and improve future business sustainability.
Production: production is a process that is involved to give a shape of the finished product through produce with raw material and manufacturing components. As argued by Linardatos & Papastefanopoulos (2021), effective supply chain management ensured an organisation reduces operation costs along with improving productivity through improved availability of raw materials and resources. Besides that, an effective supply chain also consists automation production line that improves an organisation’s production process that is boost performance of an organisation’s global logistic system.
Distribution: distribution process includes transmission of final product to demand at different business locations. As opined by Black & Wiliam (2018), a digital supply chain supports an organisation to identify and observe supply processes at different locations through a real-time evaluation process. It is necessary for an organisation to improve safety of the final product and boost the supply process to develop an effective global logistic chain.
Customer Interface: consumers’ interface refers to providing required products along with facility through that they provide feedback after consuming goods. As argued by Sousa et al. (2019), a supply chain should have a return facility to improve the satisfaction level of consumers. It is noticed that sometimes and consumers are not interested in consuming a product after buying. The organisation should provide replacement and return faculty to ensure a high level of consumer satisfaction.
The above-mentioned concepts should be followed step by step by a global organisation to ensure better consumer satisfaction along with engagement. As cited by Shackleton & Shackleton (2019), these two factors should be given the most preference by a global manufacturing or retailing organisation that ensures better coordination between demand and supply of product. Better coordination between “demand and supply” ensured an organisation’s better consumer satisfaction along with better revenue that plays a significant role to ensure an organisation’s future sustainability and growth.
2.3 Evaluation of how they could improve the way they operate
Resource-Based View theory (RBV)
Resource-based theory suggests an organisation develop better relationships between different types of resources of an organisation through better supply chain management. As argued by Valaeiet al. (2018), an organisation mainly has physical resources, human resources along organisational capital resources. An organisation is required to consider these resources to operate their manufacturing along with distribution process effectively to ensure effectiveness of supply chain.
Physical resources: Physical resources include organisational plant and machinery along with raw material and equipment that are used in the manufacturing process. An organisation should have an effective supply chain that should develop through considering different concepts of supply chain to ensure better operational management along with productivity rate. As cited by Arbelo &Arbelo (2021), an organisation should provide raw material and manufacturing components on-demand in the production process to ensure “better utilisation” of physical resources that also improve the organisation’s profitabilityalong with productivity in the global market. If an organisation fails to consider these steps then face loss along with reduced competitive advantage in the global market.
Human capital: Human capital refers to manpower such as employees and leaders of an organisation. Skilled employees and workers play a prime role to ensure an effective “supply chain process” along with productivity of the organisation. As argued by Kamble & Gunasekaran (2020), thus it is necessary for an organisation to provide training on latest technology and tools that are used by another organisation to develop a “digital supply chain”. As a result, organisations have access to an effective supply process that maintained better relations between the “demand and supply” of products. If an organisation fails to provide training to employees that fail to improve “productivity and better utilisation” of physical resources in the global market.
Organisational capital resource: capital refers to developing better coordination between “organising, controlling and coordinating systems”. Therefore an organisation is required to make an investment to develop a “digital supply chain”. As argued by Drury (2004), these steps may assist an organisation to ensure a better competitive advantage in the global market through an effective global logistic system. These steps assist organisations to improve competitive advantage or fail to improve competitive advantage.
Network Perspective (NP) theory
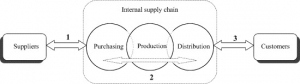 Figure 2: Network Perspective (Source: Yu & Xue, 2018)
Figure 2: Network Perspective (Source: Yu & Xue, 2018)
Network theory helps an organisation to develop an effective network between different stakeholders of the organisation; they are directly or indirectly affected by the organisation’s supply chain process. The supply chain is performed on the basis of demand consumers and consumers depend have affected organisations production process along with suppliers steps to supply raw material and different resources for manufacturing. Thus it is necessary for an organisation to develop better coordination between consumers, organisation and their suppliers. As argued by Yu & Xue (2018), neither organisation fails to improve production rate along with the better performance of the supply chain network. Therefore organisations should evaluate market demand to ensure optimum utilisation of resources and maintain a supply of raw materials material. The evaluation of consumers’ demand is to assist organisations to acquire sufficient raw material along with steps for the manufacturing process. After taking these steps, the organisation needs to provide finished products at different locations on demand of consumers within the required period. These steps ensured a better network between these stakeholders of the organisation and improved productivity rate along with better competitive advantage.
3. Recommendations
- Monitor demand and supply: organisations should monitor demand for products and services at different locations to produce products and consider optimum utilisation of resources. As argued by Cole & Stevenson (2019), these steps of organisation support organisation to improve productivity along with business growth in the global market. Required demand and supply for that demand are significant variables for global logistic chains. These steps of organisation support organisations to improve their position with a competitive advantage and compete with their competitors in the global logistic process.
- Implement latest technology: organisation should implement digital technology along with the latest supply tools that support organisation to evaluate demand in market and feedback after consuming product. The latest technology not only supports organisations to evaluate actual demand in the market nevertheless but also improves their operating performance in the global market. As stated by Rostamzadeh et al. (2018), further, organisations may access other raw materials along with minimum prices that support the reduction of operating costs. These steps also access them to future business sustainability along with better financial stability.
Conclusion
It is concluded that this assignment is a support organisation to develop an effective “supply chain management” through the consideration of concepts of supply chain along with the process of developing the supply chain that is discussed in theoretical analysis. The study also reviewed global logistic challenges and issues to operate the supply chain process in the global market. Besides that, it is observed that different global organisations ensure their productivity along with business sustainability through the concept of a “global logistic system”. Further, organisations should consider theoretical analysis that is discussed in above paragraphs to take steps along with properly developing a “digital supply chain” that is suitable for e value demand in the global market and maintaining supply for that demand through supply products at global level.
Reference
Books
Drury C, (2004), Management and Cost Accounting, 6e, London, Thomson
Journals
Arbelo, A., Arbelo-Pérez, M., & Pérez-Gómez, P. (2021). Profit efficiency as a measure of performance and frontier models: a resource-based view. BRQ Business Research Quarterly, 24(2), 143-159.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0149206321993576
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (2018). Classroom assessment and pedagogy. Assessment in education: Principles, policy & practice, 25(6), 551-575. Available at: https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/files/83523952/Classroom_assessment_and_pedagogy_BLACK_Published2018_GREEN_AAM.pdf
Chandak, A., Chandak, S., & Dalpati, A. (2021). Evaluation of Impact of Success Factors of Supply Chain Strategy and Flexibility on Supply Chain Performance. Pakistan Journal of Statistics and Operation Research, 185-194. Available at: https://pjsor.com/pjsor/article/download/2874/1110
Cole, R., Stevenson, M., & Aitken, J. (2019). Blockchain technology: implications for operations and supply chain management. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal. Available at: https://eprints.lancs.ac.uk/id/eprint/131605/1/PDF_Proof.pdf
Frederico, G. F., Garza-Reyes, J. A., Anosike, A., & Kumar, V. (2019). Supply Chain 4.0: concepts, maturity and research agenda. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal. Available at: https://ir.xjtlu.edu.cn/upload/source/2020-12-14/1607925584_pxnhc.pdf
Frederico, G. F., Garza-Reyes, J. A., Anosike, A., & Kumar, V. (2019). Supply Chain 4.0: concepts, maturity and research agenda. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal. Available at: https://derby.openrepository.com/bitstream/handle/10545/624168/Accepted%20Version.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Hu, J., Liu, Y. L., Yuen, T. W. W., Lim, M. K., & Hu, J. (2019). Do green practices really attract customers? The sharing economy from the sustainable supply chain management perspective. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 149, 177-187. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921344919302617
Kamble, S. S., Gunasekaran, A., & Gawankar, S. A. (2020). Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. International Journal of Production Economics, 219, 179-194. Available at: http://agri.ckcest.cn/file1/M00/0F/A7/Csgk0F4oCMeAbz3xABM8_eyy10o901.pdf
Linardatos, P., Papastefanopoulos, V., & Kotsiantis, S. (2021). Explainable ai: A review of machine learning interpretability methods. Entropy, 23(1), 18. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/23/1/18/pdf
Moktadir, M. A., Rahman, T., Rahman, M. H., Ali, S. M., & Paul, S. K. (2018). Drivers to sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy: A perspective of leather industries in Bangladesh. Journal of Cleaner Production, 174, 1366-1380. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095965261732721X
Mostafa, N., Hamdy, W., & Alawady, H. (2019). Impacts of internet of things on supply chains: a framework for warehousing. Social sciences, 8(3), 84. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/423316
Palandeng, I. D., Kindangen, P., Tumbel, A., & Massie, J. (2018). Influence analysis of supply chain management and supply chain flexibility to competitive advantage and impact on company performance of fish processing in Bitung city. Journal of research in business, economics and management, 10(1), 1783-1802. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/267833343.pdf
Rostamzadeh, R., Ghorabaee, M. K., Govindan, K., Esmaeili, A., & Nobar, H. B. K. (2018). Evaluation of sustainable supply chain risk management using an integrated fuzzy TOPSIS-CRITIC approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 175, 651-669. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/download/55393895/Paper.pdf
Shackleton, R. T., Shackleton, C. M., & Kull, C. A. (2019). The role of invasive alien species in shaping local livelihoods and human well-being: A review. Journal of environmental management, 229, 145-157. Available at: https://scholar.sun.ac.za/bitstream/handle/10019.1/122761/Shackleton_JEnvironManage_2019.pdf?sequence=2
Sousa, T., Soares, T., Pinson, P., Moret, F., Baroche, T., & Sorin, E. (2019). Peer-to-peer and community-based markets: A comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 104, 367-378. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/am/pii/S1364032119300462
Valaei, N., Rezaei, S., Bressolles, G., & Dent, M. M. (2021). Indispensable components of creativity, innovation, and FMCG companies’ competitive performance: a resource-based view (RBV) of the firm. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration. https://researchonline.ljmu.ac.uk/id/eprint/15287/1/APJBA-11-2020-0420.pdf
Yu, R., Xue, G., & Zhang, X. (2018, April). Application provisioning in fog computing-enabled internet-of-things: A network perspective. In IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (pp. 783-791). IEEE.https://par.nsf.gov/servlets/purl/10095999
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

