STUDENT RESEARCH FINDING AND SCHOLARSHIP
Introduction
The present study will provide an outline of creating funding opportunities to carry out research at universities. A Project Initiation Document (PID) will be done by providing the aims and objectives of the project. A summary of project justification and anticipated outcomes will be given. Product descriptions and product breakdown structure will be done along with the project activity plan. Risk analysis and contingency plans of the project will be done. Explanation of the MOSCOW technique will be provided with sprint planning or time box planning. A comparison and discussion about the strengths and limitations of Prince 2 and Agile will be discussed.
PART A
Aims and Objectives of this project
Aim
The aim of the project is to create funding opportunities for research at universities by implementing innovative ideas and venture capitalists.
Objectives
- To create funding and scholarships
- To minimize the risk of conducting the project
- To reduce the impact of ethical and legal issues
- To build a better application for the project
Deliverables and sustainable benefits
The primary deliverable of this project is to raise scholarships and fundings for students. The expected sustainable benefit of conducting this project is to provide better education to all students in the country. As per the opinion of Austin et al. (2018), it is required for project managers to focus on different sustainable benefits to complete it properly. Scholarships will help students of the UK to get good knowledge and ideas about different things (Niesz et al. 2018).
Assumptions
The assumption of this project is to complete it within time and will be completed within the given budget.
Measures
Ethical, legal and social
Students from various backgrounds will share their information for conducting this project. As per the opinion of Luft and Roughley (2016), in order to conduct research, it is necessary for all participants to provide the required help to a certain extent. The Government of the UK has made a Charities Act, 2016, to demonstrate their commitment to protecting the public and donors in a charity.
It is required to identify proper students that require funds and scholarships to get a better quality of education. As per the study of Barrett et al. (2019), students coming from a poor background are required to get help to complete their future studies. A scholarship program will help a lot of students in the UK to continue their education properly (Robinson, J.A. and Hawthorne, 2018).
Ethical measures that are being taken for the project is to include members that really want to help students that require this money. According to Sicat (2017), to complete a project it is necessary to include group members that have better ideas in the past. It is required to take proper ethical measures in order to restrict the project from getting affected.
Summary of justification for the project and anticipated outcomes
Reference
The development of an application that is used for gathering information about different people. As per the opinion of Gouseti (2017), it is required to get an idea about relevant data from prior tasks to complete the task in better ways.
Outline
The number of students that require fundings and scholarships for future study has increased immensely in the UK. Hence, it is required to conduct a project that will help this kind of student. As per the study of Sevim and Sarıkaya (2020), funds are required to be raised for poor students in order to give them a better future. After completing this project successfully it will help to provide a good view about the requirement of raising money for needy people (Prijayanti et al. 2020).
Description of methods used
Prince 2 will be used for completing this project since it is easy to use and helps to provide specified work for every member of the team. As cited by Rassias and Witkowski (2019), assigning tasks to proper team members is an important factor for the success of a project.
Total requested budget
The total requested budget for conducting this overall project is £100,000. The whole project is required to be completed within this budget.
Detailed costs and its benefit
| Expenses | Costs (£) | Cost Type |
| Rooms | 9000 | Fixed |
| Books | 5000 | Variable |
| Transportation | 7000 | Variable |
| Utilities (Electric bills, internet, gas) | 150 | Direct |
| Groceries | 250 | Indirect |
| Savings | 300 | Variable |
| Dining Out | 200 | Indirect |
| Entertainment (Music or Television Subscriptions) | 120 | Indirect |
| Healthcare | 1000 | Direct |
| Clothing and Laundry | 60 | Fixed |
| Abroad Studying | 20000 | Variable |
| Furnishing (Tables, Chairs, Beds) | 2000 | Indirect |
| Total | 45080 |
Table 1: Cost and benefit analysis
(Source: Created by Learner)
The Total Cost Allocated for the Project is £100,000
The Required Cost for a Single Student is £45080
Hence, Benefit from the Project = (100,000 – 45,080) = £54,920
Therefore, The Cost-Benefit Ratio is = 1.12
Project Breakdown Structure
The project of student research and scholarship can be broken down into different parts. It includes project mandate, directing project, monitoring and control, managing boundaries and management of project delivery. Identification of various necessities for the project is required and then the project brief will be submitted. As per the opinion of Li et al. (2020), it is important to select proper manpower for a project after which it can be initiated. Work packages are then broken by recovering different mistakes. A quality assurance check will be done after this step and a final review and reviewing the progress of the project will be done.
WBS
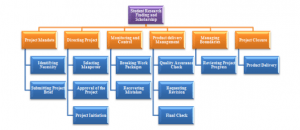
Figure 1: WBS of the project
(Source: Created by Learner)
Top Level Breakdown Project (Project Deliverable)
 Figure 2: Top Level Breakdown Project
Figure 2: Top Level Breakdown Project
(Source: Created by Learner)
Project Activities Plan
The first activity of the project is to identify different requirements of the project by submitting a project brief. Selection of proper members for the project will be done after this process then approval will be taken for further project. Control and monitoring will be done after this by breaking the work packages properly and recovering mistakes. As per the opinion of Rassias and Witkowski (2019), it is necessary for the manager of a project to check the quality of the project which will help to complete it more effectively. After this, the review of the project will be done.
Product Flow Diagram
Figure 3: Product Flow Diagram
(Source: Created by Learner)
Gantt Chart
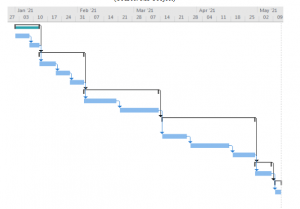
Figure 4: Gantt chart
(Source: MS Project)
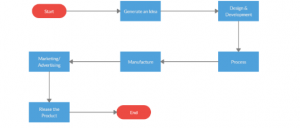
Figure 5: Timeline of the project
(Source: MS Project)
Network Diagram
Figure 6: Network Diagram
(Source: MS Project)
Critical Path
Figure 7: Critical Path
(Source: MS Project)
Risk Analysis and Contingency plan
Risk
The major risk of the project is that there might exist several problems of communication among team members. Different requirements for conducting this project might not be available which may create several issues. Social and illness issues are major factors that might happen during this project. As per the opinion of Barrett et al. (2019), it is required for the manager of a project to find out different risks during this project to have better control of the overall project. Valuable members might quit during this project which will create problems in future. Low motivation level and technological problems are huge issues during this project. Scheduling and documentation issues are factors that might affect the project.
Risk Management Plan
| Risks | Severity | Frequency | Impact | Mitigation |
| Communication Problems | Medium | Low | Low | Self-Development
Active Listening |
| Ineffective Requirements | High | Low | High | Educational Policies Enhancement |
| Illness and Social Issues | Low | Medium | Medium | Mediclaim
Healthcare Practices |
| Quitting Members | High | Medium | High | Collaborative Approach |
| Processing Problem | Medium | Low | High | Following Rules and Regulations
Guidance |
| Low Motivation Level | Medium | Medium | High | Positive Interaction
Being Supportive |
| Technological Problem | High | Low | Medium | Innovation
Technological Influences |
| Documentation Issues | High | Medium | High | Proper Legislation
|
| Scheduling Issues | Low | Low | Medium | Time Management |
| Work and Study During Project Work | High | High | Medium | Self-Assessment
Time-Management |
| Client Related Issues | Low | Medium | Low | Interactive Communication |
| Third-Party Components | Medium | Low | Low | Social Enhancements |
| Group-Work Related Issues | High | Medium | Low | Collaborative Learning Methods
Group Motivation |
Table 2: Risk management table
(Source: Created by Learner)
Contingency plan
Communication problems in the project can be controlled by self-development and active listening to different views of members. Ineffective requirements can be met by the enhancement of educational policies and illness, social issues can be managed by practices of mediclaim activities. As per the study of Luft and Roughley (2016), it is required to decide various alternatives of risks that might happen while conducting a project. Following regulations and rules will effectively help to reduce the chance of processing problems. The low motivation level of project members can be controlled by interacting with them properly.
A good collaborative approach would be beneficial to restrict members of the team from quitting the project. Implementing new technologies for the project will be helpful to control the issue of technological problems. According to Ferdiansyah et al. (2016), issues related to group work can be minimized by the methods of collaborative learning. The social enhancement will help to control different third party components and interactive communications are required to reduce client-related issues. Documentation issues and scheduling issues can be minimized by implementing proper legislation and management of time.
PART B
MOSCOW Technique
The major intention of selecting the Moscow technique for this project management method is to provide an overall interdepartmental agreement regarding project priorities (Long et al. 2019). A defined direction of project work is destined to be finished within a proper time as well as meeting its objectives. The technique is adequately suitable for developing the project management plan to successfully implement project work (Burkholder, 2019). Identification of must have stages is conducted through this technique as well as it is hugely appreciated for high and low-level project works. Breaking the entire project work into smaller structures will be more appropriate in this technique. A worked out and the soluble process is maintained through applying proper resources and manpower according to the project needs (Clifton, 2016).
The major perspective for using the Moscow technique in this project is to prioritize the resource management ability of the project work. Unnecessary items are removed from the project plan and this technique helped the project manager to remove such processes (Farah and Barack, 2019). The items removed from the project work will be added in the category as well as the necessary items required for the project work is added in could’ and should categories (Hancock and Szalma, 2019). These above-mentioned items are distributed within the percentage category of project work and it is useful for ensuring positivity in resource management strategy for the selected project work (Gillis et al. 2020).
| Must-Have
❖ Academic Requirements ❖ Financial Requirements ❖ General Knowledge |
Should Have
❖ Contact Details ❖ Educational Qualifications ❖ Appropriate Documentation ❖ Identity Proof |
| Could Have
❖ Technological Enhancements ❖ Adaptive Technology Coherent ❖ Positive Attitude ❖ Enhanced Communication |
Won’t Have
❖ Irregularity ❖ Less Attention ❖ Inappropriate Guidance |
Table 3: MOSCOW Framework
(Source: Created by Learner)
| Activity | Description | Days |
| Collecting Information | Gathering information of students regarding the project | 15 |
| Resource Analysis | Analyzing financial capabilities and manpower | 50 |
| Selecting Project Objectives | Selection of goals | 12 |
| Planning | Resource implication, manpower implication, budget allocation, risk management | 40 |
| Monitoring and Controlling | Procurement, Risk Analysis, Reviewing project tools | 15 |
| Final Check | Quality assurance, product check | 21 |
| Project Closure | Preparing for delivery, Deadline, Project Deliverables | 15 |
| Product Delivery | Logistics, Customer Relations | 12 |
Table 4: PRL of Project
(Source: Created by Learner)
Use Case 1
Figure 8: Use Case 1
(Source: MS Visio)
As a <Student>, I want to visit <Educational Fund Raisers> so that I can raise <funds> donated by <Teachers and support staffs>
Use case 2
Figure 9: Use Case 2
(Source: MS Visio)
As a <Student> I want to attend <College and Educational Events> so that, I can raise <funds> donated by <Teachers> and <Alumnus>
Use Case 3
Figure 10: Use Case 3
(Source: MS Visio)
As a <Student> I want to approach <College management> so that I can raise <funds> through <Online Alumni Portal> donated by <Alumni>
Use Case 4
Figure 11: Use Case 4
(Source: MS Visio)
As a <Student> I will approach <Group of Students> to raise <Collective funds> from the <Teacher> to complete my project
Prototype 1 (UC1)
Figure 12: Prototype 1 based on Use Case 1
(Source: MS Visio)
Prototype 2 (UC2)
Figure 13: Prototype 2 based on Use Case 2
(Source: MS Visio)
Time Box Planning
| Processes | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun |
| Identifying Necessity | ||||||
| Submitting Project Brief | ||||||
| Selecting Manpower | ||||||
| Approval of the Project | ||||||
| Project Initiation | ||||||
| Breaking Work Packages | ||||||
| Recovering Mistakes | ||||||
| Quality Assurance Check | ||||||
| Requesting Revision | ||||||
| Final Check | ||||||
| Reviewing Project Progress | ||||||
| Product Delivery |
Table 5: Timebox Planning
(Source: Created by Learner)
Final Prototype
Figure 14: Final Prototype based on user feedback on Prototype 1
(Source: MS Visio)
Class Diagram
Figure 15: First cut class diagram
(Source: MS Visio)
First, the cut class diagram of the project is responsible for describing the different entities and attributes present in the project (Alto et al. 2018). As seen in the above diagram, five separate entities can be seen which consist of more than four attributes. These attributes are responsible in defining the major functions of the website through which the student can request funds for their research. Stream, Teacher, Admin, Research Topic, Students are the five major entities present in the website (Morrison et al. 2018). Each of the entities carries a unique primary key function which allows it to communicate with other entities through foreign key functions (Asarta et al. 2018).
PART C
Prince 2
Strengths
The primary focus of Prince 2 is to provide better output and work on continuous progress. It helps to promote better communication among members of a team since it provides a vocabulary that is common to everyone. As per the opinion of Li et al. (2020), it is important for members of a group to communicate with each other for better completion of a project. Prince 2 is generic in nature since it can be used in any sector or industry.
Prince 2 makes members more accountable by defining the best possible responsibilities and roles to every individual. It encourages stakeholder involvement to make certain decisions. As per the study of Rubleske et al. (2020), it is necessary for a company to assign proper roles to every member to get the best outcome from a task. It is considered to be easy to use for everyone as it can be adapted in order to suit the requirements of any project. The major benefit of using Prince 2 is it helps to save time for managers in a project since meetings are arranged on a regular basis.
PRINCE2 methodology is effective for this project which is divided into six stages of project management. Project Mandate, Directing Project, Monitoring and Control, Product Delivery Management, Managing Boundaries and Project Closure are the crucial stages of a project management plan. The stages are used to fulfil the requirements of this particular project as well as bring out the best possible outcome from it.
Limitations
The weakness of using Prince 2 is it has only two techniques and tools. It creates several problems for conducting various projects. Prince 2 does not cover soft skills which is the main disadvantage of using this. As cited by Ferdiansyah et al. (2016), managers of a project are required to implement different techniques in order to complete a task much effectively. The major limitation of Prince 2 is it requires good knowledge for a person to run it.
Figure 16: Comparison between Agile and Prince 2
(Source: Martinez et al. 2017)
Agile
Strengths
Customers will be able to get value sooner and are not required to wait for later since the software can be deployed quicker. The strength of Agile Project Management is fewer resources get wasted because managers work on tasks that are mostly updated. As per the opinion of Martinez et al. (2017), it is required to update the status of a project on a regular basis to get a better idea about it. Agile can be adapted better if any kind of change occurs and it responds much faster in comparison to Prince 2. It has a huge community with whom knowledge can be shared.
Agile helps to complete a project much properly and immediate feedback can be received. There is a great scope for developers to improve their skills based on this feedback. As per the study of Minton (2019), in order to complete a project properly, it is necessary to receive different views from other people to get a better chance of improvement.
Limitations
The disadvantage of using Agile Project Management is some projects can become everlasting since there is no clear end to them. As per the study of Rassias and Witkowski (2019), it is important for project managers to create a proper plan for completing a project within a certain time and budget. Scope creep is a factor that is a great limitation in comparison to Prince 2. Teams can easily get sidetracked due to a lack of different processes while conducting the project. Projects might get suffered if it takes more time than required and long term projects face problems from incremental delivery.
Pince 2 will be used for completing this project.
Conclusion
Based on the above discussion it can be concluded that Prince 2 Project Management method will help to complete the project much effectively. It is necessary to develop a better project plan in order to complete the project within a certain time. The major criteria of the project are to create a proper plan for completing it within £100. A good analysis of different risks that may affect while conducting this project is necessary to be done properly. The project is considered to be completed within £54,920 hence it will help to save a lot of money which can be used for other purposes. A proper work breakdown is done in order to complete the project and different contingency plans for restricting various risks have been given. Communication problem is one of the most common issues in this project hence it can be controlled by self-development and active listening.
References
Alto, K.M., McCullough, K.M. and Levant, R.F., 2018. Who is on Craigslist? A novel approach to participant recruitment for masculinities scholarship. Psychology of Men & Masculinity, 19(2), p.319.
Asarta, C.J., Bento, R., Fornaciari, C.J., Lund Dean, K., Arbaugh, J.B. and Hwang, A., 2018. The Scholarship of Teaching and Learning: changing the dominant narrative about (and in) research institutions. Journal of Management Education, 42(6), pp.731-748.
Austin, A.L., Vincent, S.K. and Kirby, A., 2018. Protective factors among postsecondary students enrolled in a first-generation program. Journal of Research in Technical Careers, 2(2), p.45.
Barrett, C.A., Newman, D.S., Lords, P.O., Ritter, C. and Cottrell, J.M., 2019. Coding communication in the consultation: Accurate, reliable, and efficient analysis. School Psychology, 34(4), p.341.
Burkholder, J.M., 2019. Interpreting the conventions of scholarship: rhetorical implications of the ACRL Framework. portal: Libraries and the Academy, 19(2), pp.295-314.
Clifton, G., 2016. Does one size fit all? Using scholarship to enhance the student learning experience. Practice and Evidence of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, pp.57-65.
Farah, A.O. and Barack, C.O., 2019. The quest for Turkish scholarships: African students, transformation and hopefulness. African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development, 11(7), pp.883-892.
Ferdiansyah, I., Purwanto, E. and Windarko, N.A., 2016. Fuzzy gain scheduling of PID (FGS-PID) for speed control three-phase induction motor based on indirect field-oriented control (IFOC). EMITTER International Journal of Engineering Technology, 4(2), pp.237-258.
Gillis, M., Lemus‐Martinez, S. and DeBaets, A.M., 2020. Toward a Scholarship of Teaching and Learning: Addressing Ethics and Humanities in Health Professions Education. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 2020(162), pp.157-166.
Gouseti, A., 2017. Exploring doctoral students’ use of digital technologies: what do they use them for and why?. Educational Review, 69(5), pp.638-654.
Hancock, P.A. and Szalma, J.L., 2019. Sustained attention to science: a tribute to the life and scholarship of Joel Warm. Human factors, 61(3), pp.365-373.
Li, M., Wu, W. and Yang, X., 2020. Research on Fuzzy Fractional Order PID Control of Liquid Temperature in Displacement Digester. Journal of Korea TAPPI, 52(5), pp.15-30p.
Long, M.C., Goldhaber, D. and Gratz, T., 2019. Washington’s College Bound Scholarship Program and its Effect on College Entry, Persistence, and Completion. Education Finance and Policy, pp.1-52.
Luft, T. and Roughley, R., 2016. Self: The Role of Reflective Practice for Supporting Professional Identity Development in Graduate Students. SUPPORTING, p.53.
Martinez, D.C., Morales, P.Z. and Aldana, U.S., 2017. Leveraging students’ communicative repertoires as a tool for equitable learning. Review of Research in Education, 41(1), pp.477-499.
Minton, C.A.B., 2019. Counselor Education and Supervision: 2017 inaugural review. Counselor Education and Supervision, 58(1), pp.4-17.
Morrison, J.A., Berner, N.J., Manske, J.M., Jones, R.M., Davis, S.N. and Garner, P.W., 2018. Surveying Faculty Perspectives on Undergraduate Research, Scholarship, and Creative Activity: A Three-Institution Study. Scholarship and Practice of Undergraduate Research, 2(1), pp.43-54.
Niesz, T., Korora, A.M., Walkuski, C.B. and Foot, R.E., 2018. Social movements and educational research: Toward a united field of scholarship. Teachers College Record, 120(3), pp.1-41.
Prijayanti, D., Artha, E.U. and Arumi, E.R., 2020, May. Web-Based Monitoring Information System for Scholarship Holder. In 1st Borobudur International Symposium on Humanities, Economics and Social Sciences (BIS-HESS 2019) (pp. 1222-1226). Atlantis Press.
Rassias, M.T. and Witkowski, O., 2019. The Program in Interdisciplinary Studies of the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton. EMS Newsletter, 6(112), pp.40-42.
Robinson, J.A. and Hawthorne, T.L., 2018. Making space for community-engaged scholarship in geography. The Professional Geographer, 70(2), pp.277-283.
Rubleske, J., Fletcher, T. and Westerfeld, B., 2020. E-Sports Analytics: A Primer and Resource for Student Research Projects and Lesson Plans. Journal of Instructional Pedagogies, 23.
Sevim, Ö.M. and Sarıkaya, E.E., 2020. How to be productive in PhD Level: A needs assessment study for doctoral students’ research productivity. International Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 12(2), pp.75-94.
Sicat, G.P., 2017. Birth of a Think Tank: The founding of PIDS. Philippine Institute for Development Studies.


