Assignment Sample The Integration of Autonomous Robots into Farming
1.0: Introduction
Autonomous robots have been implicated within farming sector for killing weeds so that fresh crops are commercially available in market. This chapter focuses on issues that are faced by farmers due to poor innovations and its mitigation through application of autonomous robots.
1.1: Background
Application of autonomous robots (AR) within farming activity is support in treatment of crops through detection of pathogenic actions of weeds. Weed-mapping service has become a major action of this innovative technology that offers environmental benefits (Fwi.co.uk, 2021). On the other hand, implication cost of this technology is high that may create barriers but it involves in declining manual errors of farmers.
1.2: Rationale
Lack of technical skill of farmers may generate issues in assessing that innovation within AR. Poor knowledge regarding soil health among farmers generates issues in production of crop through maintaining biodiversity (Fwi.co.uk, 2021). Soil erosion has become another challenge faced by farmers in recent times that provokes incorporation of discussed type of robot.
1.3: Aims
The aim of the study is to investigate how AR get integrated into farming for increasing efficiency and mitigates workload
1.4: Research significance
AR is included under artificial intelligence that provides an opportunity to perform tasks in an efficient manner by elimination of errors.
Chapter 2: Literature review
2.0 Introduction
Issues that are faced by farmer in current times support in determination of requirement of innovation within technology. In addition, improvement that is conducted within AR will be determined from this chapter. In addition, this study ensures benefits achieved by farmer after application of mentioned robots.
2.1: Conceptual framework
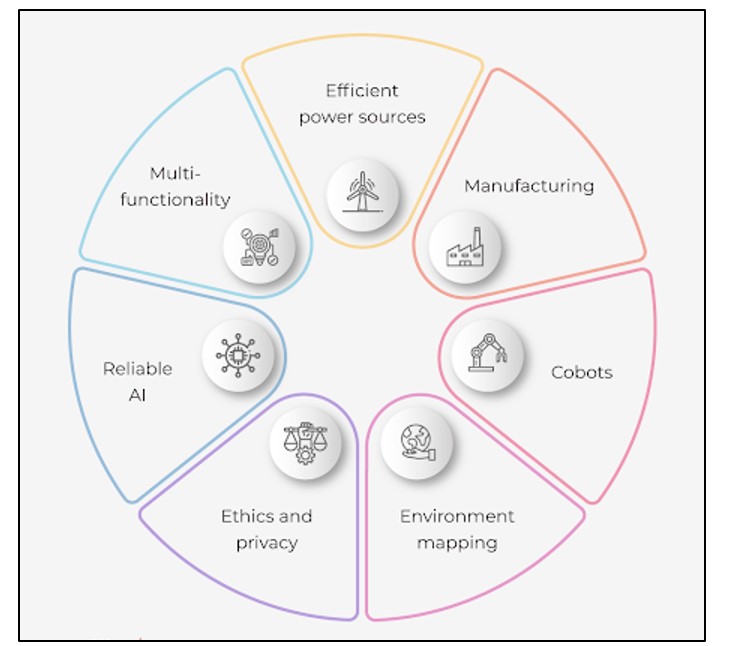
Figure 2.1: Conceptual framework
(Sources: Created by author)
2.2: Determination of different issues faced by farmer in current times
2.2.1: Rapid climate change
Farmers fail to grow crops during growing season due to appearances of volatile weathers for huge pollution. In addition, agricultural limitations for improper weather within suitable season for extending production of crops may create barriers in maintaining product availability based on demands. As opined by Ntshangase et al. (2018), presence of poor knowledge regarding soil management practice makes barriers in conservation of water. In this particular context, water scarcity is another issue faced by farmers while production of crops due to changing of season. Crop pollination gets affected for appearances of weeds and pests for not getting sufficient water. Unavailability of fertile soil makes barriers in execution of proper pollination of crops.
2.2.2: Alternation of consumer needs
Quality of crop has become a major priority of farmers and that is fulfilled through proper application of insecticides and pesticides so that devastating impacts of pests are avoided. Changes in expectation of society create additional work pressures over farmers in production of crops within all seasons. Quality may be declined due to frequent applying chemicals so that growth rate of crop increases rapidly. As mentioned by Al-Kodmany (2018),the urban population focuses on food security which is fulfilled through offering food according to needs. Poor application of resources, farmers failed to meet demands of urban community who makes investment through analysing quality of food at best price.
2.2.3: Insufficient mechanism
Workload of farmers increases frequent due to frequent alternation of requirements of customers. Important decisions are generated by a farmer regarding execution of farming activity that may lose food value of product due to appearances of soil erosion. As reported by Benke and Tomkins (2017), mechanisms have an opportunity to boost productivity rate so that food standards have been maintained. In addition, poor application of technology makes issues in extending time for conduction of agricultural operations.
2.3: Exploring recent technical improvement within AR
Advanced solutions have been provided by AR through developing artificial intelligence (AI) that involves making advancement of problem-solving aspects. In addition, AI provides scope to deliver quick responses to human feedback by implication of learning analytics. In addition, facial recognition software has been developed within AR so that detection movement has been conducted in an easy manner. As explained by Schuster et al. (2019), self-localization opportunities are also included within AR so that crop mapping is conducted in an efficient manner. Supporting this fact, actions are modified which are estimated before through detection of urgency.
2.4: Critical analysis of various advantages of AR
Risk rates are declined through detection of unpredicted risk while production of crop through checking quality of soil. Moreover, productivity level increases through fulfilling needs of buyers through analysis of their needs so that product plans are constructed efficiently. Moreover, safety of farmers is also maintained by using these approaches through maintaining a safe working environment. Performance can be conducted at a lower value through implication of automatic that discard human efforts. As suggested by Shockley et al. (2019), farmer gets a scope to invest in large equipment for storing crops for overcoming crop diseases occurred for unfavourable weather. Moreover, investment has been conducted through saving money from checking labour cost by allowing AR within agricultural actions.
2.5: Critical evaluation of multiple challenges faced while application of AR
A complication with manufacturing procedures is leading to issues for farmers regarding using this mentioned technology. In addition, multiple functions have been conducted by AR that introduces confusion for farmers in overcoming specific framing issues. Moreover, a decline of human interaction makes limitation in conduction of agricultural industry in an efficient manner. Presence of efficiency of robots to conduct in agricultural industry reduces needs for labour that provides barriers in managing employability. As reported by Angelopoulos et al. (2021), software has been implicated for storing data that may be done in improper manner for poor technical knowledge of farmers. Absence of re-learning scope of this type of robots creates issues in making further improvement of devices while facing complications due to accidents. Thus, mapping challenges may introduce issues execution of tasks within real-life scenarios.
2.6: Analysis of theories or strategies applied to improve AR
Structuring of information-processing by implication of external intelligence is support in offering external power supplies. In addition, adaptability of intelligence is required so that further actions are rectified by evaluation of previous issues. Allocation of unsupervised learning provides an opportunity to use natural languages that support in maintaining recognition patterns. Gunderson et al. (2017) discussed in article that challenging tasks are performed through allocation of efficient effort so that responding capacity to external stimulation gets enhanced.
2.6: Literature gap
AR optimises productivity through controlling plant disease in terms of identification of risk that appeared for pollution or soil erosion. Multi-functionality provides scope to handle multiple tasks but generates issues in accessibility of AR for lack of technical ideas among farmers. Thus, interrelationship between multifunctional scopes with workload minimization is not linked up properly and creates limitations of this literature.
2.7: Summary
Complications that arise in producing crops for supplying foods would be determined from these chapters. Requirement of AR in agricultural industry for declining work pressures through using efficiency would be estimated in this literature.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.0: Research Onion
3.1: Research Philosophy
Understanding objectives that are generated within research is help in conduction of research in a scientific method. Science is included for maintaining validity of knowledge so positivism philosophy would be incorporated for making specifications of knowledge.
3.2: Research Approach
Existing theories will be applied for maintaining authenticity within data so deductive approach would be followed in this study. Absences of proper knowledge regarding versatile intelligence within AR creates issues in acquiring data from farmers
3.3: Research Design
Research question would be answered in an efficient manner through linking between identified variables from research topic. Descriptive design would be included so that data regarding AR and its utility for generation of crops are not generalised.
3.4: Sampling technique and sample size
Snowball sampling techniques would be implicated as it requires no candidates for offering their perception which support in allocation of primary data. About 6 journal articles will be selected as a sample for construction of authentic themes by connecting with objectives.
3.5: Data collection method
Secondary qualitative method would be implicated for incorporation of descriptive information availed within journals as well as books.
3.6: Data collection tools and techniques
Information would be recorded in Ms Word for better analysing issues and benefits availed by a farmer after installation of AR. Moreover, relevance within data is maintaining through an investigation regarding choosing articles within a database like Google scholar.
3.7: Data analysis techniques
Text is structured for generation of themes which ensures research regarding analysing evidence. Thematic technique will be beneficial for evaluation of and depth understanding of secondary data.
3.8: Ethical considerations
Copyright act 1988 will be used for elimination of copyright issues whale application of a journal that is grabbed from Google scholar.
Chapter 4: Data
4.1: Sources type
Secondary sources would be implicated for saving costs that are allocated for research work. Moreover, efforts will be discarded which may appear while arranging surveys or interviews for conduction of primary quantitative and qualitative research. Previous information will be utilized so that information is identified in a short time.
4.2: Depth of data
Articles that are published within last 5 years ensure the inclusion of recent data. Inductive approach would be avoided as it focuses on gathering evidence from participants for building new theories for future learners. Inclusion and exclusion criteria will be followed so that developing processes of AR are identified and its further benefits within action of farmers are evaluated. Sources will be investigated based on year of publication and details of authors who involved in other research workers.
4.3: Confidentiality issues
Improper implication of regulation that is established within the country may reduce interest of future readers to focus on this research. Moreover, privacy needs to be maintained while inclusion of articles.
Chapter 5: Discussion
5.1 Research question
- What challenges are faced by farmers in recent times?
- What are recent technological developments within AR?
- How AR provide benefits to farming in terms of extending efficient and resolving workload issues?
5.2: Objectives
- To identify issues that are faced by farmer in current times
- To estimate recent technological development in AR
- To evaluates advantages of autonomous robots in farming such as mitigating workload and extension of efficiency
5.2: Research guidance
Research questions are identified from objectives that are structured through following aims of research. In addition, determination of problems of farmers will be estimated in research problems. Requirements of changes with research question will be distinguished from there. In this context, further changes in question will not be required.
References
Angelopoulos, G., Baras, N. and Dasygenis, M., (2021). Secure Autonomous Cloud Brained Humanoid Robot Assisting Rescuers in Hazardous Environments. Electronics, 10(2), p.124.
Benke, K. and Tomkins, B., (2017). Future food-production systems: vertical farming and controlled-environment agriculture. Sustainability: Science, Practice and Policy, 13(1), pp.13-26.
Fwi.co.uk (2021) World’s first autonomous farm robot fleet ready for 2022. Available at: https://www.fwi.co.uk/arable/crop-management/worlds-first-autonomous-farm-robot-fleet-ready-for-2022#:~:text=The%20world’s%20first%20fleet%20of,farmers%20in%20just%20two%20years [Accessed on: 28th March, 2021]
Gunderson, E.A., Hamdan, N., Sorhagen, N.S. and D’Esterre, A.P., (2017). Who needs innate ability to succeed in math and literacy? Academic-domain-specific theories of intelligence about peers versus adults. Developmental Psychology, 53(6), p.1188.
Legislation.gov.uk (2021) Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.Available at: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1988/48/contents [Accessed on: 28th March, 2021]
Ntshangase, N.L., Muroyiwa, B. and Sibanda, M., (2018). Farmers’ perceptions and factors influencing the adoption of no-till conservation agriculture by small-scale farmers in Zashuke, KwaZulu-Natal Province. Sustainability, 10(2), p.555.
Saunders, M.N., Lewis, P., Thornhill, A. and Bristow, A., (2015). Understanding research philosophy and approaches to theory development.
Schuster, M.J., Brunner, S.G., Bussmann, K., Büttner, S., Dömel, A., Hellerer, M., Lehner, H., Lehner, P., Porges, O., Reill, J. and Riedel, S., (2019). Towards autonomous planetary exploration. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 93(3), pp.461-494.
Shockley, J.M., Dillon, C.R. and Shearer, S.A., (2019). An economic feasibility assessment of autonomous field machinery in grain crop production. Precision agriculture, 20(5), pp.1068-1085.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

