The Strategy of International Business
Part A: Critical reflection
Introduction
International business strategy can be defined as the plans that guide various conventional transactions that take place among various factors in different countries. The term international business strategy is a set of actions and plans of a private or public multinational company to enhance profits. This type of business is known as different other terms such as global business, multinational business, international firms, and so on. International business strategy can assist to expand and diversify a business. Economic globalization is a process by which a business can rapidly expand its markets to international clients.
The institution-based view of a business suggests that foreign clients and customers are required to build strong rules skill of the business in both informal and formal entertainer countries. It helps to visualize the competitiveness degree in the business and calculates the performance of the company. It has been observed from the article that international business and institutional-based view are two closely related fields. In this context, the researcher is going to critically reflect on an article based on an institution-based view of international business strategy in comparison with resource-based and industry-based views. The main topics of this critical reflection are various areas of substantive research.
Body paragraph 1
In this section, the researcher wants to critically reflect on the article based on the institutional view of international business strategy. It has been observed from the article that there are three legs of a strategy tripod. The legs are institution-based view, resource-based view, and industry-based view. This article argues that the institution-based view is the third leg in the strategic management of international business (Peng, Wang & Jiang, 2008). It has been also noticed that several other researchers agree with this topic in their research and stated that the first two legs are resource-based views, and industry-based views. The researcher reviews the roots of the institution-based view and identifies two important theories. After properly analyzing the views the other researcher suggests that the institution-based view indicates the third leg of a strategy tripod and controls the criticisms of resource-based views, and industry-based views (Gokalp, Lee, & Peng, 2017).
The institutional-based view is considered as a main theoretical paradigm and lens in the research of international business management. Peng et al., (2017) explain institutions as constraints devised by humans that help to structure interactions between humans. As per the definition of this researcher, institutions can be defined as the rule of the game and classified into two categories such as informal camps, and formal camps. Another researcher Lamb et al. (2018), have stated that institutions are cognitive, regulative, and normative activities and structures that give meaning and stability to the social character.
Two main theories develop the pillars of the institution-based view and they are as follows. The bounded rational perspective of choices business owners and managers sensibly follows their interested areas and develops strategic choices in the provided framework of the institution. This framework helps the business owner to decrease the uncertainty and provide proper meaning to the decision-makers of an international business (Peng et al., 2017).
The second theory is the combination of informal and formal institutions to observe the behavior and performance of the company. It has been observed that sometimes informal constraints are playing a crucial role in decreasing uncertainty while formal constraints are failed. The informal constraints help to identify legitimacy and provide rewards to the company and managers (Peng et al., 2018).
In recent days, it has been observed that most researchers and scholars are now using these two theories to provide an interdisciplinary and integrating view to international business-related questions. These theories also help the scholars to provide answers for various topics like family control and ownership, informal economies, development of entrepreneurship, venture partner selection, compensation of executives, and so on (Gokalp et al., 2017).
From the body paragraph one of the critical reflections, it can be observed that institutional-based view is the third leg of the strategic tripod and can help to provide answers related to international business strategy. In the next paragraph, the researcher is going to discuss the first point of argument that is based on the entry barriers of international business.
Body paragraph 2
`Entry barriers of international business
In this section, the researcher is going to critically reflect on the first topic of the argument that is the entry barriers of international business. According to Peng et al. (2008), various international business strategies can be applied in emerging economies. The important international business strategy for an emerging economy is using antidumping as an entry barrier.
Various other researchers state that different forces can govern the competitiveness of an industry and it is considered as the important entry barrier for an international business. In international business, the entry barriers are always significant and can give rise to various terms such as responsibility for foreignness (Ugalde Azpiazu, 2021).
Antidumping policies can be defined as the policies implemented by governments on overseas imports at the time when products are going to be dumped by using low prices in the local market of a country. The duty related to antidumping is implemented in a country to save the local markets and businesses from this disloyal competition with foreign companies. Firme & Vasconcelos (2020) have stated that in recent days, most of the researches of entry barriers are based on the different variables of the market such as differentiation of products, economic scales, and so on. Bagayev et al. (2017) argued, and stated that very rare institution-based views are considered as an entry barrier in international business. These researchers also state that one of the important institutional and non-market-based variables is laws of anti-dumping and can be considered as the entry barriers for international business. Evidence related to antidumping has been observed after properly investigating IB. Discrimination is a piece of important evidence for antidumping. After critical reflection of this institution-based view of international business, it can be observed that the researchers are arguing about the entry barriers for the IB. From this paragraph, it can be concluded that antidumping is an important barrier. In the next section, the researcher is going to critically review further institution-based views related to IB strategy.
Body paragraph 3
International business strategy regarding competing in and out of India
Within this context the researcher has reflected on the impact of Indian politics and the economic system within the business company coming within India. India is one of the rising economic countries and Different aspects like political, social as well as legal ways in India impacts the businesses which are going to be taking place within India in a profound manner. Different companies which are doing business with India are also impacted due to the changes within social, financial and socio ecological structure in India (Verbeke & Yuan., 2021). The IT sector among other sectors has shown an amazing development and only is second to the United States. The main USP of the IT sector within the market is that the Indian IT market provides a good quality of work within relatively lower amounts of costs. In case of establishing businesses related to IT pharms within India, companies from outside are going to generate a high amount of revenue for themselves along with an amazing quality of work while paying not much. The less capital consumption within the current Indian economy has been influencing big Multinational Companies (MNC) to open their branches within India (Doh et al., 2017). Not only the IT farms but also outsourced business processes are being raised within India which is better known as BPO as well. The raise of these companies are beneficial for both India as well as the outside countries as well. The differentiation of the economic levels within different countries impacts within the economic situation of both the countries in a positive manner. Multinational companies increasing their businesses in India not only help India to generate a higher amount of revenue but also help the country to employ a higher amount of youth in different organizations as well. For having a high level of population the situation of Indian youth regarding different jobs is critical and it is required that these people get employment. With increased number of multinational companies within India the business is going to increase both of the company as well as within India as well. The success of some firms of India along with change within the politics has raised insecurities within the countries of the west. Different American states have been noticed to pass different laws which ban firms of India to avail official contracts. This can impact in both positive as well as adverse manner in case of both the countries (Rehman & Anwar, 2019). Not allowing India to have contracts is going to impact the project managers to cost a higher fortune in order to get the projects done while Indian people involved within the process might face unemployment and poverty as well.
Body paragraph 4
Growing a firm in china for improving international business
Within this part the researcher has focused on the impact of growing a farm within china in order to increase international business. China has a poorly regulated economical system and string growth is generally not being observed much in the economical levels which are poor enough. Despite having a poorly balanced economic situation, China has been portraying an amazing rate of economic growth within the country. This phenomenon has been searched by many researchers who came up with some interesting answers. According to the researchers, the interpersonal networks which can be seen within different managers of different organizations in china, has been impacting within the growth of the Chinese pharms (McAdam, Bititci & Galbraith., 2017). Financial help and monetary help are being provided by the different managers of different companies in order to ensure that the growth of the other companies does not stop. Having an interconnected chain like this is going to help the forms in a proper manner while required. The financial fluidity among different organizations in china has been highly helpful for the performances which are being portrayed by the companies of china in recent times helping the different Chinese companies to generate the monetary revenue. The researcher has found that the current relationship within the different managers of the Chinese firms provides them with an institutional key in order to solve any kind of difficult monetary situation which might have arisen within the country. It has been noticed that not only the managers of Chinese companies but also different organizational leaders of outstanding MNCs have tied their knot with the managers of the Chinese organizations in order to understand the situation of china if they can expand their business within china. The recent improvements of Chinese economics have reduced the possibilities of performing low cost based joint ventures within the Chinese organizations (Yuan et al., 2020). In order to establish a form in China to increase and improve businesses it is highly required for those companies to form an alliance with the managers of Chinese organizations so that expansion of outstanding companies within China becomes easier.
Conclusion
It is highly important to determine a specific strategy in order to expand a company within different sectors. The business expansion strategy is required to be dependent on the countries where an organization is looking to increase its business. Different countries have different people, different interests as well as different financial situations. A company is required to analyses those aspects before they decide to expand their business. Proper analysis not only helps the company to look into the current situation of different countries in a proper manner but also helps to understand which strategy they are required to apply or what are the choices often people within the country or whether the product being produced by the company is going to be accepted within the other country. After the analysis, the companies are required to determine a business expansion strategy so that getting into other countries to expand their business becomes easier for the countries. Business expansion is highly required for every business organization and along with globalization; expanding business has become relatively easier. Different business expanding methods are available among which a company is required to look into the expansion strategy which are going to match the criteria’s of that company in a most perfect manner so that they can implement that business expansion strategy within their business and can expand in different countries.
Part B: Report
Executive Summary
This report is based on institution-based view of international business strategy. In this report part of the researcher is going to select two themes of the strategy of international business. In order to prepare this report, the researcher has been selecting a retail company from United Kingdom namely Unilever and discuss the international business strategy of this company. In order to prepare this report, the first theme that is going to select is internalization path. The researcher in this theme the internationalization path of Unilever is going to discuss. In order to enter a marker an organisation is required to look into the different aspects of the market which are financial stability, buyer power as well as preferences of the people regarding different products as well. Different market entering strategies are available which are going to be applied in order to look into the proper strategy of entering in a market. Within this study different market entry schemes availed by the company and their application has been focused in a detailed manner.
Introduction
The era of globalization and digitalization has paved the path for international business conducted by the organizations. Unilever is a multinational company headquartered in London and Rotterdam founded in 1929. Unilever has various types of products which include food, energy drinks, confections, soft drinks, baby foods, cleaning agents, pet food, bottled water, pregnancy tests, and margarine. The product of Unilever is available in 190 countries across the world. This giant manufacturer owns more than 400 brands with turnover of 53.7 billion Euros in the year of 2017. This company is arranged into three main divisions. They are home care, beauty and personal, foods and refreshments. In the year of 2010 Unilever has shifted its centre of attention to the healthy and beauty products. This company has listed itself on the London stock exchange and it is a constituent of FTSE 100 index. Unilever has total revenue of 50.724 billion Euros and an operating income of 8.303 billion Euros in 2020. It has the total assets of 67.659 billion Euros with a total equity of 17.655 billion Euros. The two themes are going to be presented in this part are the internationalism path and market entry package.
Theme 1: Internationalism path
This theme describes the business scenario of Unilever more clearly. Unilever is regarded as one of the most transnational companies across the world for its impeccable transition from the very first day of business operations (Dow, 2018). This organization has diversified its business operations world widely. In 1930 at time of foundation it only produced sop and produced food. And after that the Unilever has evolved through the Darwinian system which retains the useful things and rejects those which do not work for this organization.
Internationalization pattern of company
Unilever emphasizes on the practice of which responds to the market place well (Hokinson, 2017). This company has secured its internationalism through a continuous transition process which evolved globally as well as locally. The nature of products of any company needs proximity to the local as well as the global markets and Unilever is not the exception manufacturing its product in this regard. The matrix of every manager of this company across the world shares a common vision and understands the corporate strategy very well which helps this company in its internationalism pathway. The major products of Unilever are solely responsible for business profits in North America and Europe and some of the products like lox soap, Lipton tea are known even in Cambodia or Albania where the unlevel has no industrial operations (Sahara, 2018). In the 75 countries across the world Unilever does its business through various operating companies with a total of 500 companies in the business group. Unilever groups believe in informal types of cooperation with self-sufficient unit’s world widely. To this day the organizational structure of Unilever has been extended to a certain point but still they have a long term policy and they are very consistent with it. The two parent companies of Unilever have a long tradition of doing and expanding their business. Unilever is a good example of far-flung units which shares a common vision.
Over the years the company has weathered numerous changes to evolve with the international trends in business operations. During the Second World War all the food industry faced various problems to get the raw materials. The unlevel is not the exception. But after that when the source of raw materials gets less important the primary focus of this industry has been shifted to distribution systems and preservation technology. This company has so many competitive advantages and as a result of this they developed frozen products. In the year of 1966 the product group of this company became responsible for business profits and the national management started working with an advisory role. But in time of industrial negotiations local finance and their advice determined the decisions. In time of new reorganization this company created three board directors. In terms of product Unilever has numerously improved its position as the new groups were more concerned for the consumer need.
Application of Uppsala model
The Uppsala model is very relevant in explaining the business pathway of Unilever towards its internationalism. The Uppsala model emphasizes on the process which sets up various subsidiaries in the foreign countries (John, 2018). Unilever followed the model to make their business international (Abouts, 2021). The Uppsala model tells about the strategic goals which a company wants to achieve in their business operations in the foreign countries. Unilever set up my strategic goals in foe gin countries with their subsidiaries. The Uppsala model proved itself to be very close to the business environment so many organizations use this model to compare themselves with their competitors.
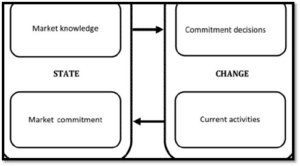
Figure 1: Aspects of Uppsala model
(Source: Cooley, 2019)
The Uppsala model was originated from the empirical observations from various Swedish manufacturers. This international model differentiates between four steps to enter into the international market. It cannot be observed independently. The four steps are no regular activities of exporting, establishing foreign subsidiaries, exporting through independent representatives and foreign manufacturing (Cooley, 2019). Following the Uppsala model, Unilever has started their expansion with nearby markets. After this they enhanced their knowledge about the market and got control of the market and resources to expand their business in the distance market with different cultures, languages as well as geographical regions. It can be said that the organization has identified different opportunities in the market to invest in the parameters which has helped the company to progress in a steady manner. The market commitment of the company has been retained through the production of quality products in a low price range (Abouts, 2021). It has helped the company to gain brand recognition. On the other hand, involvement in corporate social responsibilities has helped the company to draw investors’ attention to their current activities. Thus diverse notions of the business have been maintained in a synchronized manner.
Theme 4: market entry packages
Entering in the international markets generates wide opportunities of growth and development but it also does consist of considerable risks. Hypothetical or exaggerated demands of consumers that have to be met in a saturated market, or even alternating partnerships to meet business goals which may result in multiple failures can form huge challenges for a new business to flourish (Ahi et al.,2017). These risk factors can be dealt with proper market intelligence information during any concerned decision making. The comprehensive study of Market entry package analysis develops research about the existing global businesses. In-sites scrutiny, search study about the partners, consulting about strategies and elaborate business planning.
International market entry requires the knowledge about cultural Idiosyncrasies, expansion strategies and legal preconditions (Blackburne & Buckley, 2019).Market entry analysis develops reports about the organisation potentials, reality feedbacks, business model and strategic planning for the business.
Assessment of foreign entry modes
There are several factors before a business enters the international markets. For instance the Unilever companies have decided to expand its business and share their facilities globally. Their expansion of their business will require importing, exporting, documentation of licenses, partnership protocols, strategic alliance in both the bases, acquisitions, establishments of the new and entirely owned subsidiaries (Greenfield ventures), these are few modes through which the organisation can step their foot into the global markets (Buckley et al.,2018)
| Types of entry | Advantages ( Pros) | Disadvantages ( Cons) |
| Acquisition | Quick entry, renowned, substantiated operations | Higher costing, issues with home office integration |
| Franchising and Licensing | Risks are low, quick entry and low costings | Lacks control, Competitor licensee may be developed, regulatory and legal environment must be heard |
| Greenfield Venture( new Subsidiary) | Acquirement of local markets, will become one of the insider and employment within local people | Very risky, risks of the unknown people, growth sinks as for the set-up time. |
| Exporting | Entries are quick, risks are even low | Controlling lacks, rare knowledge of the locals, high impact of transportation |
| Partnership and strategic alliances | Investments are reduced due to sharing of cost, risk taken are reduced, grants to be a local entity | High in cost than of exporting, integration issues among different corporation cultures, licensing or franchising may be impacted |
Table 1: Aspects of market entry
(Source: self-Created)
After scrutinising the facts and figures through which companies like Unilever can step to the global markets, there must be comparative analysis that must be conducted with the strategies and goals of the organisation. Exporting is one of the most typical and easy ways to the global markets (Del et al.2017). The home country sources their companies’ products sales and foreign services through exporting.
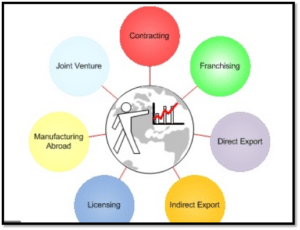
Figure 2: Types of foreign entry modes
(Source: Surdu et al.,2018)
The perks to entry through such mode that it reduces the firm’s expenses on the establishments of operations in a new country. Franchising in a new country is difficult without any licensing, if the business is licensed with accordance with the new countries legal authorization the risks reduces and costing of the business are minimized, On the other hand the local turns to become a competitor and the business must exercise legal regulatory resources within their business (Surdu et al.,2018). If the Unilever company chooses such a mode of market entry strategy the business will be legalized in particular with few local legal norms.
Usage of foreign entry modes by Unilever
Various approaches regarding global market entry modes allows companies to take part in international markets without any investments in the foreign facilities and plants. As to the expansion of the market an organisation may decide to improve their competitive trump cards through investing on the operations that are conducted in that particular country.
The FDI offers the formal accomplishment of operations regarding the business on the grounds of foreign soils (Shen et al.,2017). The factories, networks that are distributed that serve the local markets of the country and the sales departments. This Is known to be the most expensive commitment that an organisation serves to an oversea market which is driven typically by the attractiveness and enlarged size of the market targets.
The concerned organization has different types of subsidiaries all over the world. It must be said that the company has planned for expansion in a structured manner to register economic benefits. On the other hand, it must be mentioned that subsidiaries offer less debt aspects as individual entities are responsible for their conducts which ultimately supports the growth of the organization (Jamontaite et al.,2017). The market opportunities can also be addressed through this approach and significance of its selection lies here. Market opportunities can also be shed light upon through such prospects. For example, Asia has a big market for packaged food products. Owning a subsidiary in the region is beneficial for growing the market share at a stable rate.
Conclusion
Most business eventually ventures themselves to globalize among its own industry, from which most of the organisation misses their analysis regarding the strategic planning against their internationalization ways, operations that can determine the growth of the business in that particular country, critical evaluation of corporate strategies that are analyzed with the comparative study of the existing businesses in the local areas and the most important path to enter the international markets through the analytics of modes of expansion In the foreign markets. The recommendation that can be suggested with the thorough analysis is that an organisation such as that of Unilever must generate a plan of action that can channel the resources of the business effectively to compete among the global businesses. Unique and reliable goals and strategic goals can accomplish global dominance.
References
Ahi, A., Baronchelli, G., Kuivalainen, O., & Piantoni, M. (2017). International market entry: how do small and medium-sized enterprises make decisions?. Journal of International Marketing, 25(1), 1-21.DOI: 10.1509/jim.15.0130
Bagayev, I., Davies, R. B., Hatzipanayotou, P., Konstantinou, P., & Rau, M. (2017). Non-tariff barriers, enforcement, and revenues: The use of anti-dumping as a revenue generating trade policy (No. 17/06). Working Paper Series.https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/175485/1/WP17_06.pdf
Blackburne, G. D., & Buckley, P. J. (2019). The international business incubator as a foreign market entry mode. Long Range Planning, 52(1), 32-50.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2017.10.005
Buckley, P. J., Chen, L., Clegg, L. J., & Voss, H. (2018). Risk propensity in the foreign direct investment location decision of emerging multinationals. Journal of International Business Studies, 49(2), 153-171. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41267-017-0126-4
Cooley, A. (2019). Ordering Eurasia: The rise and decline of liberal internationalism in the post-communist space. Security Studies, 28(3), 588-613. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14747731.2020.174190
Del Giudice, M., Arslan, A., Scuotto, V., & Caputo, F. (2017). Influences of cognitive dimensions on the collaborative entry mode choice of small-and medium-sized enterprises. International Marketing Review. DOI 10.1108/IMR-05-2016-0098
Doh, J., Rodrigues, S., Saka-Helmhout, A., & Makhija, M. (2017). International business responses to institutional voids.https://doi.org/10.1057/s41267-017-0074-z
Dow, D., Leech, P., & Welch, L. (2018). Inertia and managerial intentionality: Extending the Uppsala model. Management International Review, 58(3), 465-493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00482-018-0331-5
Firme, V. D. A. C., & Vasconcelos, C. R. F. (2020). Main Determinants of Opening Antidumping Cases: A Poisson Analysis Using Panel Data. The International Trade Journal, 34(4), 387-414.DOI: 10.1080/08853908.2020.1727385
Gokalp, O.N., Lee, S.H. & Peng, M.W., 2017. Competition and corporate tax evasion: An institution-based view. Journal of World Business, 52(2), pp.258-269.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2016.12.006
Gurkaynak, G., Yıldız, C., & Kinalp, S. (2018). The Relationship between Trade Policy and Competition Policy: The Interface Between Predatory Pricing and Anti-Dumping Regulations. Gönenç Gürkaynak, THE ACADEMIC GIFT BOOK OF ELIG, ATTORNEYS-AT-LAW IN HONOR OF THE 20TH ANNIVERSARY OF COMPETITION LAW PRACTICE IN TURKEY, 177-204.https://www.gurkaynak.av.tr/docs/b5e8e-academic-gift-book-of-elig.pdf#page=187
Hokinson, L., & Happen, P. (2017). The ‘casino model ‘of internationalization: An alternative Uppsala paradigm. Journal of International Business Studies, 48(9), 1103-1113. DOI: 10.1057/s41267-017-0113-9
Jahn, B. (2018). Liberal internationalism: historical trajectory and current prospects. International Affairs, 94(1), 43-61 https://doi.org/10.1093/ia/iix231
Jamontaite, K., Ahmedova, S., Okumus, A., & Ozturk, S. (2017). An Analysis on Turkish market entry opportunities: the case of Lithuanian dairy companies. Ekonomika, 96, 79-101.DOI: https://doi.org/10.15388/Ekon.2017.2.11000
Lamb, N. H., & Roundy, P. T. (2018). Institutional, stakeholder, and cultural influences on corporate social performance: an institution-based view. International Journal of Comparative Management, 1(1), 4-18.DOI:10.1504/IJCM.2018.10012494
McAdam, R., Bititci, U., & Galbraith, B. (2017). Technology alignment and business strategy: a performance measurement and Dynamic Capability perspective. International Journal of Production Research, 55(23), 7168-7186.https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1351633
Peng, M., Wang, D. & Jiang, Y. An institution-based view of international business strategy: a focus on emerging economies. J Int Bus Stud 39, 920–936 (2008).https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400377
Peng, M.W., Ahlstrom, D., Carraher, S.M. & Shi, W.S., 2017. An institution-based view of global IPR History. Journal of International Business Studies, 48(7), pp.893-907.DOI: 10.1177/1042258717749234
Peng, M.W., Sun, W., Vlas, C., Minichilli, A. and Corbetta, G., 2018. An institution-based view of large family firms: A recap and overview. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 42(2), pp.187-205.DOI 10.1108/IMR-03-2018-0108
Rehman, A. U., & Anwar, M. (2019). Mediating role of enterprise risk management practices between business strategy and SME performance. Small Enterprise Research, 26(2), 207-227.https://doi.org/10.1080/13215906.2019.1624385
Sahara, K., & Sansei, S. (2018). Effectuation, Causation and the Revised Uppsala Model: A Behavioral Analysis of Iranian SMEs’ Internationalization. In Entrepreneurship Ecosystem in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) (pp. 567-590). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75913-5
Shen, Z; Puig, F. & Paul, J. (2017): Foreign market entry mode research: A review and research agenda. The International Trade Journal, https://doi.org/10.1080/08853908.2017.1361368.
Surdu, I., Mellahi, K., & Glaister, K. (2018). Emerging market multinationals’ international equity-based entry mode strategies. International Marketing Review. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR102015 0228
Ugalde Azpiazu, I. (2021). Anti-dumping measures: a step back in international trade or a legitimate reaction against unfair practices?. https://academica-e.unavarra.es/bitstream/handle/2454/39105/Memoria_TFG_Ugalde_Azpiazu%2C%20I%C3%B1aki%20..pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Verbeke, A., & Yuan, W. (2021). A few implications of the covid‐19 pandemic for international business strategy research. Journal of Management Studies, 58(2), 597-601.https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12665
Yuan, Y., Lu, L. Y., Tian, G., & Yu, Y. (2020). Business strategy and corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics, 162(2), 359-377.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-018-3952-9
Abouts, 2021. Overview of the organization. https://www.unilever.co.uk/

