TIME AND COST CONTROL USING BIM
Literature Review
Introduction
BIM or Building Information Modelling can be defined as a process that has an intelligent three-dimensional model which provides many tools and features to do more efficient planning, designing, constructions and management of infrastructures and buildings. BIM software is mainly used for architecture, engineering and construction projects. It is mainly a digital representation of a building or architecture that has physical and functional characteristics. BIM is used to create advanced drawings and models for construction projects, and in addition, it has features of sharing, collaborating and visualizing. Main function of BIM is to control time and cost of a project, and it has additional features that help to control time and cost of a construction project. This assignment has a brief description of BIM tools and its features, problem statement of research and questions of research. In addition, there is a brief description of implementing BIM in construction projects, advantages of BIM to control time and cost of a project and challenges faced while implementing BIM for construction projects. There is a brief description of current market statics of Architecture, engineering and construction industry of U.K. that is using BIM as their mandatory tool.
Problem Statement
BIM can be described as one of the greatest innovations of architecture, engineering and construction industry. The model comes with its various virtues opening up opportunities for construction firms in major developed nations like the U.K. Incorporation, and implementation of the model have brought together various advantages and challenges for the firms. The assignment constitutes of the various factors of B.M.I. and their contributions to the industry.
Research Questions
- How can be BIM implemented in an architecture, engineering and construction projects?
- What are major gains in controlling cost and time with implementation of B.M.I. in construction projects?
- What are the major challenges faced by project management and construction firms while implementing BIM in their projects?
- What are the current trends of the U.K. construction industry, and what are the contributions of BIM for its flourishment and efficient performance?
Concept of BIM
BIM is a short form of Building Information Modelling, and this can be described as a process to create information of a construction project. In addition, it manages information of a construction project and manages the life cycle of a project. According to Alnaggar and Pitt (2019), BIM can be defined as a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. As such, it serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life cycle from inception onward. Main aspect of this process is a model of building information that contains a digital description of every particular area of construction and build an asset in project. It works by collecting information for project, assembling that information, making collaboration of that information and update that information when needed for project. Information assembled and collaborated by this model is implemented in key stages of project to have effective project management for construction. BIM is mainly used for construction projects, where architecture, design and engineering are main aspects of a project. BIM is mainly a digital model for assembling building information and this model helps to support those people, who are having interactions for doing project, who have authorities to take actions for project and who are engaged in this project to do work collaboratively (Bhatija et al. 2017). This BIM process helps to add value for project, which is a lifetime value for asset. Hence, BIM can be deduced as a series of techniques that helps to enable practice and process of designing virtually and doing construction of the life cycle of a project.
Basic function and task of BIM is to bring together all of information for a project. The model should contain information about all components of a building in project and assemble that information in one place to help project management and individuals of project. BIM helps every individual in that project to make it possible to access that information for any purpose and stage when it’s necessary for the project. There are many parts of a construction project such as design, construction, architecture and many more and BIM helps to manage all these aspects of a project to have effective project management and work functions. In addition, it helps to reduce risks and mitigations for project, minimize costs of project and manage time of project. BIM data can be used to manage construction of a building and entire project cycle of that building (Biagini et al. 2016). In every step of project, BIM can be a significant factor to use and this is because it has all data of design, demolition, materials used, spaces, products, systems and sequences. All of these aspects are connected with each other for Construction and BIM helps to resolve conflicts by signalling conflict detection. In addition, it prevents errors in different stages of project to prevent development or construction of project. According to Charehzehi et al. (2017), BIM is mainly a digital presentation of a building, which is three dimensional or 3D and this model contains single information of actual building components in three-dimensional animation. In addition, this model contains physical locations of components, structures of building, manufacturers, fire rating, materials used and many more.
BIM cannot be defined as software; it can be simply defined as a model that helps to improve the efficiency and quality of a construction project by saving time and costs of projects. BIM model helps to share its information among designers, engineers, architects, contractors, subcontractors and with other project officials to inform them about design, operation, construction and ownership of project. Main application of project is to control time and cost of project and visualize the entire project by a monitoring system. However, Chen and Nguyen (2019), stated that the main function of this tool is to represent three-dimensional representations for project needs. BIM provides a great number of tools to project management to visualize and manage project works and project functions.
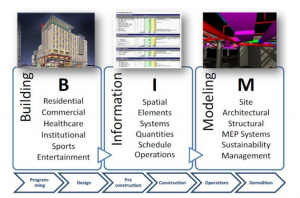
Figure 1: Concept of BIM
(Source: Chen and Nguyen, 2019)
Implementation of BIM
Main aspect of implementing BIM to a project is to have cooperation and collaboration of every individual and group in project. BIM can be implemented by project management at every stage of a project for designing purpose, construction purpose, operations and visualization. However, the main aspect of implementing BIM to a project is to save time and cost of project in an effective manner (Fadeyi, 2017). BIM provides a great number of tools to project management that helps to save time and cost of projects such as
| Name of Product | Manufacturer | Function |
| Digital Project Suit | Gehry Technologies | It is a suite of BIM that has all the features of designing, information management and review. |
| Navisworks Manage | AutoDesk | It mainly helps to do a three-dimensional design of buildings and do clash detection. |
| Vico Office | Vico Software | It is a tool that helps to do coordination by various 3D model analyses. In addition, it has features of estimating and scheduling. |
| Bentley Navigator | Bentley | It helps to dynamic coordination between disciplines and models. |
| Tekla Structures | Tekla | It is a tool that helps to do the three-dimensional structure of buildings. In addition, it has features of modelling and detailing those structures. |
| Solibri Model Checker | Solibri | It is a tool that looks over quality control and quality assurance of project. |
| Synchro Professional | Synchro Limited | This tool helps to schedule systems of project, and in addition, it helps to plan simulations of project. |
Table 1: Tools and Features of BIM
(Source: Fadeyi, 2017)
Implementing BIM in a construction project is necessary for project management and for implementing BIM in their project, project management should follow some steps such as
Step 1: Senior management of an organization or a project should be involved while implementing BIM in their project. Staff, employees and team members of a project have maximum needs of implementing BIM in project (Fan et al. 2015). However, there should be a support of leaders to achieve success in implementing BIM to their project. Implementing BIM contains a good amount of money, and if there is no support of leaders or higher authority, implementation process of BIM will be unsuccessful.
Step 2: Choosing appropriate software for project needs is the most significant step of implementing BIM. There are so many companies in the market that offers various BIM tools and software for project management and while choosing project management have to look over functions and features of the software that suits their organization and project (Jeong et al. 2016). While choosing BIM software for project, project management should not take cost as a significant factor for purchasing. Purchasing a high cost and high-quality BIM software that provides many features and tools and suits the needs of project can save plenty of time and high cost of project. Project managers have to be careful while choosing their tools of BIM, and they should look over the design and features of their tool that suits their company and industry. In addition, employees of project and company should be well trained to use tools in their project.
Step 3:Implementing BIM in projects can bring changes in processes and procedures of project and for this reason; project management should set their project goals and objectives to achieve success. Having meetings, communicating with employees and taking suggestions from senior employees can help to determine goals and changes needed according to the goals of the project (Khaja et al. 2016). Setting time goals and cost goals is a significant process for construction project and project management should look over these factors while implementing BIM.
Step 4: Employing skilled employees and staff and assembling the best team for a project is very much significant for implementing BIM in a project. BIM process needs skilled and experienced employees to control functions and procedures of model. Team members of project should be motivated, inspires and appraised for their work to make decisions, control temper and provide training for implementing necessary changes for project needs (GhaffarianHoseini et al. 2017). There are needs of encouragement provided to employees to avoid delays and faults of them.
Step 5: BIM tools provide many features that allow collaborating and implementing changes in the system. It is very much significant to set up needed processes and features that will help project management to make efficient progress in project work. Setting up standards for using objects and templates is one of the major tasks of project management while implementing BIM. Every group member and employee of project should collaborate and cooperate in implementing the process of BIM in their project (Kushwaha, 2016). Model templates can make the process work quicker than previous, and in addition, it will help to understand system to users. There is a need of content library that will help project teams and team members to collaborate.
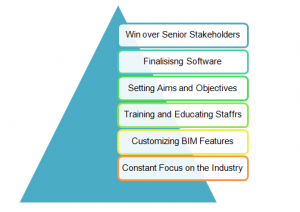
Figure 2: Implementation of BIM
(Source: Li et al. 2016)
Step 6: BIM can be defined as technical progress of construction industry, and there are lots of changes made after innovation of BIM in the industry. Previously A.U.T.O.C.A.D., CAD, Rebit and other software are used for designing process, and innovation of BIM has brought effective changes in industry (Li et al. 2016). So, project management should look over innovations, new features provided in BIM and new updates of BIM for keeping a close eye on innovations and progress of industry.
Advantages of BIM in Time and Cost Controlling
There are many advantages of BIM in time and cost controlling of a project. BIM software provides many tools and features to users that helps to control time and cost of project (Mesároš and Mandičák, 2017). Using BIM in construction projects can provide many advantages such as
Better level of Collaboration and Communication: BIM software hasdigital features that help to collaborate, visualize and share sets of construction drawings to every group members. Project members can share project models and do planning and designing by the help of BIM tools. In addition, project members can review drawings and models of project on-site by using their mobile devices (Martinez-Aires, 2018). Every project members can be updated by information shared into BIM, and this could save a lot of time of employees and project members of project.
Estimation of Cost According to Model: BIM software has features that allow users and estimators to work on factors that have higher values. In addition, it identifies factoring risks and assemblies of construction that helps to estimate cost of project and save costs for project (Menon and Varghese, 2018).
Visualization of Construction: Plan and visualization of an entire project can be done before construction of project using BIM tool. It helps to do 3d visualization by the help of simulations, and it helps to calculate time needed for doing construction of project.
Reduce Risks and Cost: According to recent statics maximum number of companies have adopted BIM and have positive returns of their investment (Matthews et al. 2015). It helps to reduce risks of construction by previewing designs and architectures of project.

Figure 3: Advantages of BIM
(Source: Menon and Varghese, 2018)
Challenges faced while Implementing BIM
Advantages and disadvantages of implementing BIM have been highlighted by various authors in the last decade leading to a wide variety of academic literature. Each of such academic knowledge shelves provides a unique perspective of BIM implementation and its effectiveness in terms of cost and time. Zou et al. (2017) states that a considerable number of researches establish the advantages of using BIM in the construction industry yet it fails to highlight critical issues related to incurring high cost of implementation. He suggested that design-stage development and a check of illustrations and blueprints is generally conducted prior to a construction project leads to less expenditure and overall impact on the stakeholders. In the process of building projects’ productivity assessment in terms of expenses and planning assumptions, it is necessary to highlight time and cost control measures as main area focus for internal and external stakeholders.
Tahir et al. 2018 state that high-cost expenses relating to BIM implementation have been a significant issue for organisations with a low budget and lack of technological infrastructure. Most multinational companies involved in construction and building industry has access to a high level of technology due to their full availability of resources. Due to high financial efficiency through economies of scale and high turnover rates, such companies find it easier to allocate resources towards implementing BIM software strategies in construction projects. However, companies with low access to financial support, especially in the case of emerging companies, find it challenging to apply BIM technologies.
Sun et al. (2017) further verifies the notion highlighted by Tahir et al. 2018 and states that low financial asset companies have a lesser amount of funding capability for investing in BIM technologies. The author further adds that, although initial stages of BIM implementation has significantly high costs, in the long-run return on investment from BIM implementation is exceptionally high. Companies understand the massive boost in profit that BIM allows to grab, yet fails to introduce such technologies in the short run. High-cost requirements for BIM is mainly due to the demand of high skilled labour capable of handling BIM software and applying Computer-Aided Design models to real-life construction projects.
According to Smith (2016), high expenditure for applying BIM technologies in construction sector arise mainly from acquiring high skilled labour, expensive software, hardware, and cost required for building prototypes. He adds that implementing formulated 3D designs from BIM software also requires highly skilled engineers capable of converting prototype models into real-life designs. Further, according to him, skilled civil engineers and CAD designers are scarce in the labour market and hence have a high cost of procurement. In the initial stages, especially for emerging corporations, building prototypes also require a significant amount of expenses. In addition, hardware requirements for performing high graphic designing tasks are high and also require additional expenses.
Sarkar et al. (2015) state engineers face several problems while implementing BIM models as well. He says that 3D CAD models are very close to real-life building structures and portrays a feasible solution to several needs that is theoretically accurate. Moreover, according to him, CAD models are theoretically and mathematically feasible, developing such structures in real life are difficult for engineers owing to the limitation of availability of raw materials, technological infrastructure and external environmental conditions.
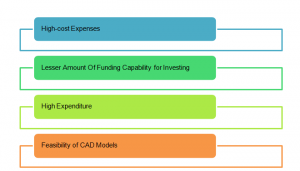
Figure 4: Challenges of Implementing BIM
(Source: Sarkar et al.2015)
BIM and Current Construction Industry of U.K
B.M.I. can be described as one of the greatest innovations of architecture, engineering and construction industry, and efficiency of this software has a vast effect on the construction industry (Nguyen et al. 2018). Major leading countries of the construction industry such as U.K. are using this software in their construction business in a heavy basis. According to recent statistics, 75% of construction companies in the U.K. use BIM software as the major tool of their business (Patil and Khandare, 2017). Redland, Balfour Beatty Plc, Morgan Sindall, Mace Ltd. and many more big construction companies in the U.K. use B.M.I. Software in their business. According to Rokooei, (2015) recent construction industry is completely digitalized and BIM is the biggest reason of this change. Current construction industry of the U.K. is having the maximum growth and using BIM and tools and features of BIM is helping the industry to achieve success and have more growth in their business. Advanced BIM tools have features of faster delivery, lower costs, improvements and lower emissions and that no other software provides so many benefits to a construction business. These are the reasons why the recent construction industry has a tendency to use BIM in their projects and business of construction.
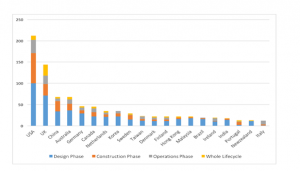
Figure 5: Graph of Current Construction Industry
(Source: Patil and Khandare, 2017)
Summary
Time and cost control is a very significant factor of architect, construction and engineering industry. Controlling time and cost of a project can bring maximum benefits for a project. In this assignment, time and cost control by using BIM in architect, Construction and engineering industry has been deduced. General description of BIM and implement process of BIM has been described in this assignment in a greater context. BIM is an efficient software for controlling cost and time of construction projects. BIM provides many features and tools to their users that help project management to manage their works and functions of project. This assignment has a clear description of various tools, and features that is provided by BIM software and advantages of using these tools and features are described in this assignment. This report shed lights on challenges that are faced by engineers, architects, project managers and project members while implementing BIM in their projects. In addition, there is a clear description of BIM and current construction industry of U.K. that describes massive use of BIM in construction industry of U.K. In conclusion, it can be said, that this assignment has its main focus on architecture, engineering and construction industry of U.K. There are so many problems of implementation of BIM in industry and those problems and solutions of those problems have been deduced briefly in this assignment.
Reference List
Alnaggar, A. and Pitt, M., 2019. Towards a conceptual framework to manage BIM/COBie asset data using a standard project management methodology. Journal of Facilities Management, 17(2), pp.175-187.
Bhatija, V.P., Thomas, N. and Dawood, N., 2017. A Preliminary Approach towards Integrating Knowledge Management with Building Information Modeling (K BIM) for the Construction Industry. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 8(1), pp.64-70.
Biagini, C., Capone, P., Donato, V. and Facchini, N., 2016. Towards the BIM implementation for historical building restoration sites. Automation in construction, 71, pp.74-86.
Charehzehi, A., Chai, C., Md Yusof, A., Chong, H.Y. and Loo, S.C., 2017. Building information modeling in construction conflict management. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 9, p.1847979017746257.
Chen, P.H. and Nguyen, T.C., 2019. A BIM-WMS integrated decision support tool for supply chain management in construction. Automation in construction, 98, pp.289-301.
Fadeyi, M.O., 2017. The role of building information modeling (BIM) in delivering the sustainable building value. International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment, 6(2), pp.711-722.
Fan, S.L., Wu, C.H. and Hun, C.C., 2015. Integration of cost and schedule using BIM. 淡江理工學刊, 18(3), pp.223-232.
GhaffarianHoseini, A., Zhang, T., Nwadigo, O., GhaffarianHoseini, A., Naismith, N., Tookey, J. and Raahemifar, K., 2017. Application of nD BIM Integrated Knowledge-based Building Management System (BIM-IKBMS) for inspecting post-construction energy efficiency. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, pp.935-949.
Jeong, W., Chang, S., Son, J. and Yi, J.S., 2016. BIM-integrated construction operation simulation for just-in-time production management. Sustainability, 8(11), p.1106.
Khaja, M., Seo, J.D. and McArthur, J.J., 2016. Optimizing BIM metadata manipulation using parametric tools. Procedia Engineering, 145, pp.259-266.
Kushwaha, V., 2016. Contribution of building information modeling (BIM) to solve problems in architecture, engineering and construction (A.E.C.) industry and addressing barriers to implementation of BIM. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol, 3(1), pp.100-105.
Li, X., Wu, P., Shen, G.Q., Wang, X. and Teng, Y., 2017. Mapping the knowledge domains of Building Information Modeling (BIM): A bibliometric approach. Automation in construction, 84, pp.195-206.
Martinez-Aires, M.D., Lopez-Alonso, M. and Martinez-Rojas, M., 2018. Building information modeling and safety management: A systematic review. Safety science, 101, pp.11-18.
Matthews, J., Love, P.E., Heinemann, S., Chandler, R., Rumsey, C. and Olatunj, O., 2015. Real time progress management: Re-engineering processes for cloud-based BIM in Construction. Automation in construction, 58, pp.38-47.
Menon, M.A. and Varghese, S., 2018. Labour productivity measurement method using 3D BIM of a commercial project. Labour, 5(05).
Mesároš, P. and Mandičák, T., 2017, October. Exploitation and benefits of BIM in construction project management. In I.O.P. Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 245, No. 6, p. 062056). I.O.P. Publishing.
Nguyen, P.T., Vo, K.D., Phan, P.T., Nguyen, T.A., Cao, T.M., Huynh, V.D.B., Nguyen, Q.L.H.T.T. and Le, L.P., 2018. Construction Project Quality Management using Building Information Modeling 360 Field. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 9(10), pp.228-233.
Patil, S. and Khandare, M., 2017. Application of BIM for Scheduling and Costing of Construction Project. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(12), pp.1644-1647.
Rokooei, S., 2015. Building information modeling in project management: necessities, challenges and outcomes. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 210, pp.87-95.
Sarkar, D., Raghavendra, H.B. and Ruparelia, M., 2015. Role of key performance indicators for evaluating the usage of BIM as tool for facility management of construction projects. International Journal of Civil and Structural Engineering, 5(4), p.370.
Smith, P., 2016. Project cost management with 5D BIM. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 226, pp.193-200.
Sun, C., Jiang, S., Skibniewski, M.J., Man, Q. and Shen, L., 2017. A literature review of the factors limiting the application of BIM in the construction industry. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 23(5), pp.764-779.
Tahir, M.M., Haron, N.A., Alias, A.H., Harun, A.N., Muhammad, I.B. and Baba, D.L., 2018. Improving Cost and Time Control in Construction Using Building Information Model (BIM): A Review. Pertanika Journal of Science & Technology, 26(1).
Zou, Y., Kiviniemi, A. and Jones, S.W., 2017. A review of risk management through BIM and BIM-related technologies. Safety science, 97, pp.88-98.


