U25189 M452 Operations Management Coursework
Problem 1
Problem 1 (a)
Apple is the most innovative manufacturing industry. The most innovative product of Apple is the IPhone that created a revolution in mobile technology (Wang et al., 2020). These were the first devices that were used to surf the “real interest”. This was various people’s introduction to the marketplace of digital content such as the app store. Apple’s business plan was to eliminate competition and open up new markets through disruptive innovation. By reinventing products, it creates from destruction as well as gains a competitive advantage. Apple’s competitive strategy for their manufacturing product emphasizes a continuous improvement process that results in the release of continuously improved versions in order to profit from the wave of reinvention (Zhang et al., 2020). Empathy, technological economies of scale, scale and network externalities, and a globally distributed as well as vertically integrated ecosystem are among the many factors that have contributed to Apple’s innovation strategy’s success increase.
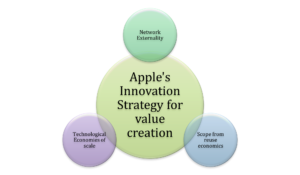
Figure 1: Apple’s innovation strategy for value creation
(Source: Self-created on Word)
Apple has become a disruptor as a result of a violent wave of reinventing empathy, architecture, technology, as well as vendor specialization in order to achieve exclusive market power (Reid and Sanders, 2019). Empathy is used to derive economies of scale, economies of scope, as well as network externality effects from design, technology, and the capabilities of their global suppliers in Apple’s approach to innovation as well as creativity. It helped Apple develop its sophisticated organizational culture as well as global ecosystem in order to establish a monopoly on new markets for creative destruction a successful method Apple’s high brand value as well as innovative nature are due to this (Tiedemann, 2020). Apple’s innovations’ success inspires their imagination. However, a disruptive innovation strategy of reinvention for creation as well as exclusivity emerges from Steve’s compassion as well as drive for perfection.
Problem 1 (b)
(i) The “Material Requirements Planning”, for short, is a method for figuring out about the materials as well as parts needed to make a product. There are three main steps that are to make a list of the components as well as materials that are already in use, figure out what else is needed, as well as plan to make or buy more of them. In order to reduce costs as well as improve labor efficiency, lot size is used to standardize the calculated net requirements to a specific unit. Lots can be sized in one of two ways. The first is to unify by quantity, as well as the second is to unify by time (Olsen and Tomlin, 2020). A generalization of the “economic order quantity model”, the “dynamic lot-sizing model in inventory theory” takes into account the fact that a product’s demand fluctuates over time.
(ii) The “dynamic lot-sizing model” is based on the premise that the total demand for a given period must be satisfied within that period (Merigó et al., 2019). Demand for a given period cannot be delivered earlier or later than that period if this assumption allows for no backlog. Demand for a specific time period cannot be fulfilled prior to its expiration if a backlog is allowed, but it can be fulfilled later at the backorder cost. The “dynamic lot size model”, like most mathematical models, is a simplified representation of how things actually work in practice. Customers provide a grace period, also known as a demand window, in the majority of “real-world applications” (Meredith and Shafer, 2023). The corresponding time frames are denoted by the requirements earliest as well as most recent delivery dates. The managers mostly used this analysis for the economical quantity costs analysis for their business.
Problem 2
Problem 2 (a)
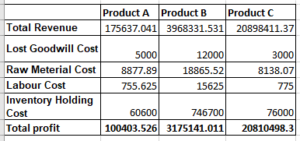
Figure 2: Total profit of the company
(Source: Self-created on Excel)
Objective: The main objective of using the “Integer programming model” is to analyses the profit of the company with their peach product basis.
Function: The Function of this model to analyses the accurate profit on the basis of lost goodwill, Raw material, Labor cost as well as the inventory holding cost.
Decision Variables: The main decision variables are Total Revenue, Lost goodwill, Raw material, Labor cost as well as the inventory holding cost.
Constraints and sign Restriction: The main constraints is to restrict the few or all the variables within the organization problem that includes the integer values (Mahmoudi and Parviziomran, 2020). This will enable the accurate modelling problems that include the discrete quantities.
Problem 2 (b)
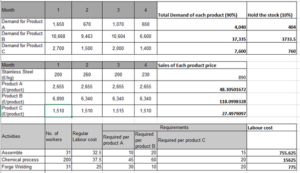
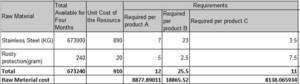
Figure 3: Optimal Solution for different products
(Source: Self-created on Excel)
The Above figure represents the Total revenue of the three activities that are Assemble, Chemical Process as well as the Forge Welding (Iris and Lam, 2019). These include the raw metals of stainless steel as well as the Rusty protection. This raw material includes the total available for the four months with the units cost of the resources with product A, product B as well as product C. The Demand is based on the product category. This demand includes the total sales of the product (Kumar, 2022). That gives the total revenue with the category of products. After all the analysis there is an analysis of the total profit of the company.
Problem 2 (c)
Sensitivity analysis report
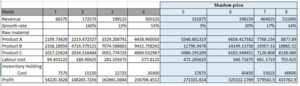
Figure 4: Sensitivity analysis with shadow price
(Source: Self-created on Excel)
Using a financial model as well as a set of assumptions, we use sensitivity analysis to see the different values of an independent variable affect a particular dependent variable. It is also known as “what-if” analysis or simulation analysis to us. Based on a variety of variables, carrying out such analysis enables us to make a more accurate prediction of a decision’s outcome. There is an examination of the variables move as well as one affects the other by analyzing both the target as well as input variables. They are able to develop improved ranges for the sensitivity analysis of those variables on the basis of this. If the most limited resource that changes is product A (Ikramov et al., 2019). There is also the use of the shadow price for the analysis of the changes in the range of the prices with the different raw materials with different product categories. This analysis is most useful for the availability of the most limiting changes in the resources of profit. This affected the profit of the company as well.
Problem 2 (d)
There are following limitations as well as the assumption of this Model are as follows.
Limitations
- Focus on optimizing for a single objective. In fact, there may be multiple objectives.
- It is not entirely true that the input and output variables are directly proportional. When production goes up, the average cost usually goes down because of economies of scale.
- The assumption of linearity of variables is that the resources needed for multiple activities equal the total of the resources needed for each activity (Hill, 2020). However, product mix synergies typically indicate that total demand exceeds total.
- Numerous decision variables, in practice, accept integer values. The number of employees Variables with continuous values are the focus of L.P.
Assumptions
Proportional: The fundamental premise of linear programming is that as the constraint inequalities change, so does the objective function.
Additivity: According to the additivity assumption, the sum of the profits contributed by each product is what determines the objective function’s total profit (Grover et al., 2022). Similarly, each product’s individual use of resources determines the total amount of resources used.
Continuity: The continuous nature of the decision variables is yet another assumption of linear programming. As a result, integer values can be used with any combination of output and fractional values.
Certainty: Certainty is another assumption of linear programming. Both the coefficients of the constraint inequalities as well as the parameters of the coefficients of the objective function are known with absolute certainty (Benjaafar and Hu, 2020). The “linear programming problem” provides information on material availability per unit, product profit per unit, as well as material demand per unit.
Limited Options: In light of this assumption, the decision variables cannot have negative values as well as the decision maker has specific options. In the sense that the production problem’s output cannot be negative, the nonnegative assumption holds true. As a result, this assumption is thought to be reasonable.
Problem 3
Problem 3 (a)
The low level coded bill of materials as under
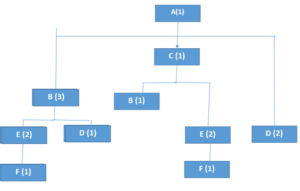
Figure 5: low level coded bill of materials
(Source: Self-created on Excel)
Problem 3 (b)
The MRP planning schedule for all product A, B, C, D, E and F items is developed as under
Figure 6: MRP planning schedule for all product A, B, C, D, E and F items
(Source: Self-created on Excel)
Reference list
Journals
Benjaafar, S. and Hu, M., 2020. Operations management in the age of the sharing economy: What is old and what is new?. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 22(1), pp.93-101.
Grover, P., Kar, A.K. and Dwivedi, Y.K., 2022. Understanding artificial intelligence adoption in operations management: insights from the review of academic literature and social media discussions. Annals of Operations Research, 308(1-2), pp.177-213.
Grover, P., Kar, A.K. and Dwivedi, Y.K., 2022. Understanding artificial intelligence adoption in operations management: insights from the review of academic literature and social media discussions. Annals of Operations Research, 308(1-2), pp.177-213.
Hill, A., 2020. Manufacturing Operations Strategy: Texts and Cases. Bloomsbury Publishing.
Ikramov, M.A., Mamajonov, H.N. and Toshpulatov, I.A., 2019. Improvement of light industry enterprises and competitiveness of management system. In Управление инновационными и инвестиционными процессами и изменениями в условиях цифровой экономики (pp. 118-124).
Iris, Ç. and Lam, J.S.L., 2019. A review of energy efficiency in ports: Operational strategies, technologies and energy management systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 112, pp.170-182.
Kumar, R., 2022. Operations management. Jyothis Publishers.
Mahmoudi, M. and Parviziomran, I., 2020. Reusable packaging in supply chains: A review of environmental and economic impacts, logistics system designs, and operations management. International Journal of Production Economics, 228, p.107730.
Meredith, J.R. and Shafer, S.M., 2023. Operations Management MBAs. John Wiley & Sons.
Merigó, J.M., Muller, C., Modak, N.M. and Laengle, S., 2019. Research in production and operations management: A university-based bibliometric analysis. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 20(1), pp.1-29.
Olsen, T.L. and Tomlin, B., 2020. Industry 4.0: Opportunities and challenges for operations management. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 22(1), pp.113-122.
Reid, R.D. and Sanders, N.R., 2019. Operations management: an integrated approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Tiedemann, F., 2020. Demand-driven supply chain operations management strategies–a literature review and conceptual model. Production & Manufacturing Research, 8(1), pp.427-485.
Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Lin, F., An, X., Zhou, H. and Fang, X., 2020. A hybrid energy management strategy based on line prediction and condition analysis for the hybrid energy storage system of tram. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 56(2), pp.1793-1803.
Zhang, F., Wu, X., Tang, C.S., Feng, T. and Dai, Y., 2020. Evolution of operations management research: from managing flows to building capabilities. Production and Operations Management, 29(10), pp.2219-2229.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

