Working on International Terms Assignment
1. Working International Team
In the increasingly globalized world, people are working in diverse cultural and social teams. International networking, mobility and changing demographics have forced most of the organizations to go through a change. The organizational change has contributed to an intensifying need to manage and recognize socio-cultural differences within a team. As cited by Silva et al. (2016), teamwork under a diverse atmosphere is extremely important to draw up full ranges of skills, educational backgrounds, abilities and experiences offered by cross-cultural workforces.
Besides, teamwork in the international market is crucial for encouraging innovation, decision making and flexibility. However, a massive challenge posed by cross-cultural teamwork is the conflicts of decision making and creative thinking. As discussed by Beaudry and Szalvai (2018), a team norm is required to be developed by the leaders to ensure harmony among members. Developing and running a team has become differently endeavoured than past due to the emergence of cross-cultural teams. The usual challenges regarding team building have increased significantly due to cross-cultural differences. Issues of the language barrier and remote team management have made the situation tough for leaders. In order to develop a strong and successful cross-cultural team, following factors are needed to be considered:
- First of all, it is important for leaders or managers to respect and acknowledge cultural differences. As per Gafni and Goldstein (2020), cultural diversity can be manifested in different ways such as language, behaviour and cultural differences. Hence it is important to learn about those cultural differences and prevent disrespectful behaviour.
- Secondly, uniform norms and regulations should be established, which needs to be followed by everyone. However, the issues and expectations of each member are required to be considered before the development of such norms.
- Thirdly, the approach of over-communication can be used to reduce the differences among the team members. An electronic communication tool can be effective in establishing positive and strong communication between employees (Silva et al. 2016).
- Fourthly, in order to deal with cross-cultural conflicts, team identity needs to be developed. Along with this, roles and responsibilities should be outlined by the managers or leaders. A shared or common goal is essential to bind a team together and reduces personal issues.
- Finally, cultural diversity should be leveraged within a team to create a sense of uniformity. It is not enough to learn the process of navigating cultural diversity within a team. Leaders should leverage cultural differences by embracing differences, new ideas and perspectives. It is necessary to develop a framework that makes it easier to understand each other and develop collaboration.
Theories of working in international team
The Lewis Model of Cross Culture
Development of a team in international terms requires prior knowledge of cultural differences. The four-player model has shed light on the effective process of team building; however, it rarely focused on cross-cultural issues. In order to understand the cultural differences, Richard Lewis has developed three categories of humans based on their behaviours. These three categories of humans are Linear-active, Multi-active and Reactive (Usova, 2018).A clear understanding of the behavioural differences is essential for promoting cultural diversity within the workplace.
.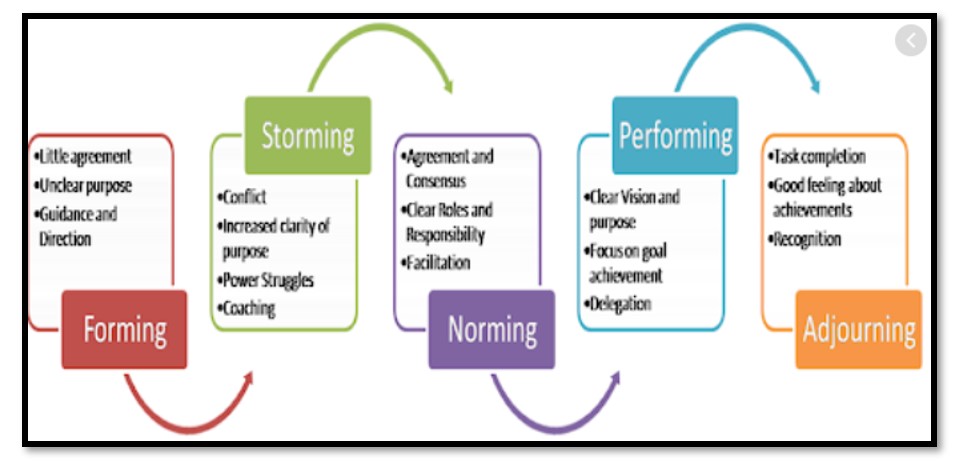
Figure 1: The Lewis Model of Cross Culture
(Source: Lewis and Bairatchnyi, 2017)
-
Linear-active
Linear active groups of people can easily be identified based on their English speaking ability. As per Niemi (2019), linear active people are usually less emotional, task-oriented and private in nature. This group of people are mostly found in North America, Britain, Australia and New Zealand, and Northern Europe.
-
Multi-active
Multi-active groups of people are scattered all around the world including regions such as Africa, South America, Middle East and Indian Subcontinent. These cultures are highly influenced by the geographic, linguistic and religious values (Usova, 2018). Some of the major characteristics of this culture are emotions, eloquences, drama, expressive body language, collectivism and compassion.
-
Reactive
The reactive people are found in all major countries of Asia except the Indian subcontinent. These groups of people have personal traits such as politeness, sensitivity and subtle attitude. As per Lewis and Bairatchnyi (2017), non-verbal communication is mostly followed by this group of culture.
Working with multiple cultures and international terms and conditions in business organisation has concerned several issues that greatly affect decision making process and teamwork. Group thinking processes are controlled by several elements of international business terms and multicultural environments affecting communication, food habits and business perspective.
Tuckman’s Teamwork Theory
Tuckman’s theory of the work can be considered as an appropriate theory that can help to illustrate different dimensions of working with the International team. As per the view of Kosmützky, (2018), this theory is associated with explaining five specific stages of developing organisational teams that help succeeding in managing a successful International team for organisational growth and development. The five specific stages that has been mention in this theory are the following:
Forming In the initial stage, the selection of team members based on their ability and capabilities is performed for developing an International team for maintaining organisational growth and development. According to the view of Irianto and Kartikasari, (2020), the most potential activities and elements considered are employees skills, project goals, interest and background, timelines, ground and individual roles. Evaluation of employee skill is necessary for understanding capabilities and experiences of the employees to justify whether they are fit for the team or not. Consideration of project goals and necessary for developing appropriate criteria for selection of team members in order to ensure their survival and positive outcomes of the International team development process. According to the view of Irianto and Kartikasari, (2020), evaluating employees interests and backgrounds in a forming process is necessary for developing appropriate assessment and Team Management strategies based on positive and negative situations. Organisational timelines and ground rules help to explain the importance of International team management for ensuring organisational growth and development by establishing a relationship and communications among all the team members.
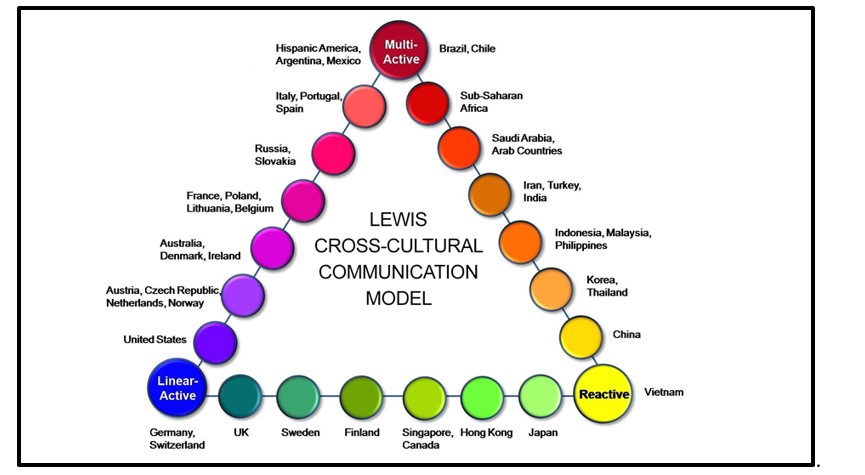
Figure 2: Tuckman Team Theory
(Source: Collings et al, 2018)
Storming Storing is associated with providing practical tasks to the team that has been created after forming for real examination of their abilities and capabilities in order to contribute in organisational growth and development. According to the view of Soni, (2020), the storming process started observing personality issues due to differences in background and communication habits of the team members. In this stage, several conflicts among International teams can be observed due to differences in beliefs and working style based on community and place of origin.
Norming: Norming stages are associated with appreciating each other’s strength and capabilities of working in an International team regarding their experiences and skills of contribution in business. In this stage, conflict between team members slowly decreases due to incensement of understanding and respect towards each other.
Performing: Performing stage is an important part of teamwork and working with an International team because it enhances the ability of contributing towards achieving goals and objectives of the company by increasing confidence and motivation. According to the view of Collings et al, (2018), In this stage, the eligible member survives in the difficult situation and others get eliminated from the international team due to lack of skills and unable to manage with the team.
Adjourning: The final stages of this theory are termed as adjoining that is associated with distributing the team after completion of project into different parts based on their ability and performances. In this stage, all the members of the International team experience learn a new assessment and leadership style by going through several difficulties and completing the team management process.
Cross-cultural training for working with international team
The cross cultural training process has to deal with several issues of International team development due to differences in interest and background of the people. Some of the most potential issues of working with international team and communication and training process are the following:
-
Different communication style
Differentiation in communication style is an important issue associated with working with an International team due to the gap in accent and language issues. In addition, the people coming from different geographical and social backgrounds use different strategies of speaking and communication in teamwork. According to the view of Browne et al, (2016), maintaining proper balance among International teams due to differences in communication style is a huge problem.
-
Different attitude towards conflict
Significant issues associated with working with the international team are federation in attitude towards conflict management and establishing relationships with team members. As for example, Japanese people are closely attached with the traditional ethics and behaviour and they prefer to use traditional culture in the workplace. According to the view of Collings et al, (2018), American employees are very opening minded and they prefer to follow modernisation principles in business and organisational belief. These differences in create drive attitudes of International team members towards conflict management.
-
Variation in a process of completing tasks
International team members that have belonged from different communities and geographical areas have also different approaches to completing their tasks and fulfilling organisational goals. According to the view of Browne et al, (2016), variations in working approach create issues in the process of decision making and problem solving by disagreeing off team members.
In order to overcome the major issues of international working process all the elements and associated component must of consider appropriately. In addition, adaptation of cross cultural training process can be considered as a profitable approach for minimising cross cultural issues in International team management for ensuring business growth and development accurately. It helps in ensuring a good relationship between different members of an International team by respecting differences in customs, traditions, verbal and nonverbal communication process. According to the view of Yates et al, (2020), cross cultural training programs played a great role in developing brainstorming ideas by ensuring proper flow of knowledge and information among all the team members positively. This process also helps in improving the situation and environment of the workplace and encourages people towards adjusting with socio economic and cultural differences with team workers. Development of common organisational goals by considering general interest of the International team can help in improving team bonding and works performances respectively. According to the view of Yates et al, (2020), consideration of important elements associated with leadership strategy such as assertive communication and advanced business knowledge greatly help in identifying characteristics that lead groups think for minimising the negative impact on team roles and team progress.
Moorhead et al, (1991), has developed important findings that has positively contributed in developing knowledge and information regarding groupthink hypothesis and way of minimising organisational challenges and barriers by controlling diversity in the workplace. As per the view of Bravo Gallart and Team, (2018), the most potential elements for cross cultural training are the importance of identifying appropriate leadership style, focus on minimising cross cultural issues and developing common goals based on common interest for controlling negative impact of groupthink. The author has highlighted that identification of appropriate leadership style based on organisational situation and resource management process is necessary for establishing good relationships among International teams. In addition, it is also necessary for ensuring a proper flow of knowledge and information amongst team members for completing their tasks and responsibilities in the given time frame.
External issues of working in international team
Apart from internal issues of working with international team there are several external issues such as social discrimination, groupthink and political issues. The social discrimination based on caste, community and genders in the workplace of foreign land and common issues. Most of the employees have to face social discrimination in the workplace. In addition, the boundary dispute of trade and comers and others political issues also greatly influences working process with international team.
Group thinks greatly influences the development of defective decision making process by influencing intellectual knowledge and information. Moreover, it negatively affects the logical reasoning abilities and thinking process. As for examples Flight Readiness Review for NASA, Jesse Moore has trapped in groupthinks and results as defective decision making.
The findings of the previous study have made a great contribution in the developing the knowledge and ideas of cross cultural issues and its impact on group thinking. It has identified that human nature and group thinning processes are positively controlled and managed by cultural surroundings and socio-economic factors. Most of the people intensify their decision making skills based on their hearing and observation from the social environments. Financial troubles and economic crises are important driving factors of group thinking processes in society and create external issues in international team. According to the view of Randall et al, (2020), most of the people avoid authentically and legal frameworks due to financial troubles and show negative response towards organizational works and decision making processes. Moreover, social and culture norm across several communities put negative impact of international team working (Kosmützky, 2018).
The presence of groupthink also restricted development of innovative ideas and brainstorming creativity in the social and business environment due to improper management of human capital. According to the view of Waizenegge et al, (2020), the stereotype mindset of the people of the International team also had a negative impact on organisational growth and development by affecting the relationship between team workers and lack of proper communication for project development. Other symptoms of the groupthink are self censorships that the negative affect of organisational growth and development by controlling human resource management (Bengtson et al, 2017).
According to the view of Park (1990), several important elements fails to maintain quality and standard by providing less focus on quantitative analysis of human behaviour and development groupthink. The more interest and evaluating the negative impact of group decisions for the workplace development and International team management and associated alternative options enhance its positive impact. This process could help in understand different perspectives and elements associated with group thinking processes for team management in business environments as well as social relations (Hidayah et al, 2020).
Process of rising issues in international team work
Opportunities: Opportunities represent the changes of believing and adapting illogical concepts and tradition regarding others cultures and team works. The wise utilization of groupthink opportunities can help in reducing its negative impact of decision making process respectively.
Decisions: Decision must be taken towards the opportunities of participating in groupthink chains based on own intelligences and ideas of logical reasoning towards accurate facts. According to the view of Waizenegge et al, (2020), this process helps in maintaining organizational growth and development by respecting cultural aspects as well.
Reality: Evaluation of the new era reality by using common senses and logical reasoning is important elements of groupthinks participation and observations. Connecting with reality of new era and factors of international team associated with cultural differentiation help in controlling negative impact of groupthink.
Assessment: Assessment is associated with analysis and evaluation of the several fact of groupthink before believing and forwarding it to the next generation. Analysing needs and the role of leadership style help in developing qualitative research findings and improvement in the discussion process of the article. As per the view of Matthew, (2017), focus on discussing different elements that control and drive group decision making process and group attitudes towards international teamwork can help to improve cross-cultural issues are important assessment.
2. Article 1 (Kantor’s four-way system)
The major focus area of the study is the four-way system of policy making process involving different cross cultural teams for developing appropriate approaches and policies for controlling and managing the social perspective of the society. This study has used quantitative research methods by collecting numerical data, coded statements and investigated results of human behavior changes and impact on thinking capabilities. The objectives of the articles were intended towards identifying different elements of team works and associated challenges. In addition, Esser and Lindoerfer (1989), has focused on identifying key elements of behavioral decision making and its impact on international teams in the workplace and social surroundings.
The model is significantly important to understand an effective team-building process. As mentioned by Adams and Daniel (2020), David Kantor has developed this model in the context of family systems. However, Ancona and Isaacs have transferred this model in the team building reams of organizations. As discussed by Champion and Gunnlaugson (2018), the concept of this model is based on the ideas of selecting the right team members, developing effective decision-making processes, and creating an attractive incentive scheme. In order to meet the organizational objectives, teams should be focused on completing the tasks, but also to create new ideas to move the organization forward. In order to enhance the efficiency of the team-building process, there are four core acts that have been identified.
- Move
A person initiates an action when they move forward, which identifies a direction and sets a team in motion. The initiation of team members is crucial for bringing positive change. Moreover, move intended towards advocacy of the of team building by implementing positive changes in the workplaces.
- Follow
It is the act that supports the actions taken by a person to create a positive change in the team. The support of followers is crucial for completing all the activities associated with a change (Adams and Daniel, 2020). In addition, it enhances the organizational revised or restructure by focusing on positive changes.
- Oppose
Oppose refers to the questions and concerns initiated by certain people of a team regarding the change. Every team has certain people who play the role of critiques in the development process.
- Bystand
Bystand is the act of providing perspectives on the change and inviting members to be reflective. Leaders can use bystanders to collect essential information and data that can be useful for a change.
These four aspects of the theory are significant for direction, momentum and energy to the working activities of teams. As mentioned by Champion and Gunnlaugson (2018), a wide range of alternatives are opened with the help of these acts, which leads to the formation of new ideas. Direction focuses in identifying and exploring associated areas for team building in order to manages the areas properly. In addition, momentum is concerned with managing organizational dynamic changing process of incorporating with new ideas and philosophy of team building. Energy represents the strengths and capabilities of the associated team members in order to developed new ideas.
3. Article 2 (Groupthink)
Group Think of Irving Janis
This article has focused on addressing different dimensions of the decision making process and the procedure is influenced by groupthinks capabilities. The major focus area of the study is the historical policy making process involving different cross cultural teams for developing appropriate approaches and policies for controlling and managing the social perspective of the society. The objectives of the articles were intended towards identifying different elements of groupthinks and associated challenges.
Symptoms of Group Thinks
There are several symptoms of group thinks as identify by Report of the Presidential Commission on the Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster
- Illusion of Invulnerability
- Inherent Morality
- Collective Rationalization
- Out-group Stereotype
- Self-Censorship
- Illusion of Unanimity
- Direct Pressure
- Self-Appointed Mindguar
The article has addressed major findings associated with development of group thinks process and its dynamic impact on organisational business practices based on international areas. Park (1990), has highlighted that groupthink is a phenomenon that occurs when a group of people develop certain concepts and consensus without appropriate logical reasoning and critical reasoning. It mainly focuses on developing alternatives for cultural issues in the workplace without conducting proper research based on mathematical evidence. Park (1990), has identified several symptoms of groupthink in the articles such as invulnerability, mind guards, stereotype and self-censorship. The article has identified an increase of invulnerability that encourages people towards taking up normal risk that has higher possibilities of creating periods between International teams while working. In addition, presence of arrogance and disrespectful towards others culture in the workplace degrades team relationships and put negative impact on organisational growth and development. As per the view of Zuofa and Ochieng, (2017), due to huge cultural differences, most of the people develop mind guards that become a barrier for exchanging knowledge and information among International teams in the workplace.
Groupthink and Doublethink
Groupthink and doublethink are not always negative for the growth and development of the society. In some perspective its greatly help in managing social and cultural issues in the international team working process in order to resolve the traditional beliefs and custom by developing a views logically. According to the view of Waizenegge et al, (2020), focusing on reviewing group thinking capabilities and procedures associated with the International team, decision making process help in supporting the groupthink is not bad always. Analyse extensive use of groupthink models for representing social circumstances and empirical knowledge across national and international boundaries are needed to understand its perspective. Moreover, addressing of major criticism towards the groupthink model and its relationship with International team work help in developing organizational team management approaches.
Space Shuttle Challenger
Space shuttle Challenger has focused on addressing major challenges and groupthink framework and its impact on group’s decision making process. Review of the decision making process from a new perspective in order to understand different factors that control group decision making and their contribution on International team works. Moorhead et al, (1991), has addressed different circumstances and phenomena of launching shuttle Challenger in the year 1986 for developing groupthink hypothesis. In addition, it has also focus on contribution in social and cultural behavioral understanding of human nature. The objective of the study is to develop revised framework for presenting leadership style and processing time needed for managing cross cultural differences in international teams.
References
Adams, S.B. and Daniel, S.M., 2020. The role of Team-based leadership in averting groupthink and enhancing institutional productivity: A Study of Federal Tertiary Institutions in Adamawa and Taraba States of Nigeria, 41-49
Bengtson, C., Ahlkvist, M., Ekeroth, W., Nilsen-Moe, A., Vedin, N.P., Rodiuchkina, K., Ye, S. and Lundberg, M., 2017. Working as Partners: Course Development by a Student–Teacher Team. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 11(2), p.n2.
Bravo Gallart, S. and Team, I.T.F., 2018. Diversity, Inclusion, and Mentoring: opportunities and challenges of working with an international research collaboration. APS, 2018, pp.C17-006.
Champion, K. and Gunnlaugson, O., 2018. Fostering generative conversation in higher education course discussion boards. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 55(6), pp.704-712.
Esser, J.K. and Lindoerfer, J.S., 1989. Groupthink and the space shuttle Challenger accident: Toward a quantitative case analysis. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 2(3), pp.167-177.
Gafni, R. and Goldstein, A., 2020. Effects of Multicultural Teamwork on Individual Procrastination. Interdisciplinary Journal of e-Skills and Lifelong Learning, 16, pp.043-063.
Hidayah, N., Widodo, S.E. and Abdullah, T., 2020. The Effect of Group Cohesivity, Working Satisfaction, And Team Effectivity Toward Senior High School Teachers’ Working Productivity. International Journal for Educational and Vocational Studies, 2(6).
Kosmützky, A., 2018. International Team Reseach in Comparative Higher Education. Journal of Comparative & International Higher Education, 10(Fall), pp.14-23.
Matthew, B., 2017. International team working in research–reflection by a student. OPTIMAX , p.17.
Moorhead, G., Ference, R. and Neck, C.P., 1991. Group decision fiascoes continue: Space shuttle Challenger and a revised groupthink framework. Human Relations, 44(6), pp.539-550.
Niemi, R., 2019. With regard to programmatic advertising, are Lewis’ findings on cultural dimensions still valid for millennials in the 21st century, 43-50.
Park, W.W., 1990. A review of research on groupthink. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 3(4), pp.229-245.
Randall, S., Crawford, T. and River, J., 2020. Us and them: The experience of international nursing students engaged in team based learning: A qualitative descriptive study. Nurse Education Today, 92, p.104527.
Silva, M.C., Peduzzi, M., Sangaleti, C.T., Silva, D.D., Agreli, H.F., West, M.A. and Anderson, N.R., 2016. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the teamwork climate scale. Revista de saude publica, 50, p.52.
Usova, M., 2018. Multi-cultural negotiations. In Language. Culture. Translation (pp. 154-155).
Waizenegger, L., McKenna, B., Cai, W. and Bendz, T., 2020. An affordance perspective of team collaboration and enforced working from home during COVID-19. European Journal of Information Systems, pp.1-14.
Yates, H., Wentz, B. and DasMajumder, S., 2020. Initial Student Perception of the Benefits of Participation on an International ASC Competition Team.
Zuofa, T. and Ochieng, E.G., 2017. Working separately but together: appraising virtual project team challenges. Team Performance Management: An International Journal.
Collings, D.G., Wood, G.T. and Szamosi, L.T. eds., 2018. Human resource management: A critical approach. Routledge.
Soni, V.D., 2020. Importance and Strategic Planning of Team Management. International Journal of Innovative Research in Technology, 7(2), pp.47-50.
Irianto, D. and Kartikasari, D., 2020. Fan Loyalty toward International Football Team: The Role of Brand Image. International Journal of Applied Business Research, 2(01), pp.58-72.
Kosmützky, A., 2018. International Team Reseach in Comparative Higher Education. Journal of Comparative & International Higher Education, 10(Fall), pp.14-23.
Browne, W., Dreitlein, S., Ha, M., Manzoni, J. and Mere, A., 2016. Two Key Success Factors for Global Project Team Leadership: Communications and Human Resource Management. Journal of Information Technology & Economic Development, 7(2).
Lewis, R.D. and Bairatchnyi, I.P., 2017. 12 Richard Lewis Communications-cross-cultural management consulting. Management Consultancy Insights and Real Consultancy Projects, p.161.
Beaudry, S. and Szalvai, E.T., 2018, March. Global Teamwork to Promote Cultural Understanding and Communication. In Developments in Business Simulation and Experiential Learning: Proceedings of the Annual ABSEL conference (Vol. 45).
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

