ATMC BUS502 Principles of Economics for Accountants
Article Title:
“What is the Soda Tax and which cities have one”by Beverly Birdfrom The Balance from 25th November 2018. Available at:
https://www.thebalance.com/soda-tax-and-which-cities-have-one-4151209
Instructions:
Access the article at the URL given above and read it carefully. Answer the questions and complete the diagrams in the spaces provided below. Use full sentences. If you use any references, please list at least the URL of your source. Possible total for this assessment task is 15 marks.
Question 1
According to the article, ‘the tax should reduce consumer demand for unhealthy food and beverages’.Use the supply and demand diagram below to illustrate and explain how the imposition of a tax affect consumers.
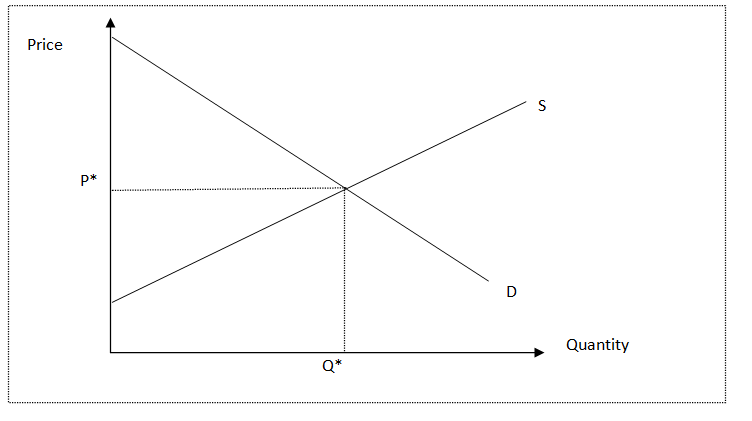
The consumption of the unhealthy food and beverages can be said elastic at moderate extent because on the increase in price of these goods, the consumption or demand of these goods can be reduced. Increasing price of these goods can reduce their demand among the consumers.
If the government imposes the tax on the unhealthy food and beverages, it will increase the price of the goods of these products as the suppliers or producers will impose this extra burden on the consumers. In such situation, the demand of these products will decline among the consumers.
Without tax, the equilibrium price and quantity will be on intersection point of the supply and demand curves as per the above graph. It is because the demand curve reflects the willingness to pay of the buyers. Due to tax, the price paid by the consumers will increase from P* that will reduce the demand. Increasing tax will decline the demand or the quantity sold from Q*.
Question 2
The article claims that “resulting revenues are an important part of the equation”. Use the demand and supply diagram below to illustrate and explain the Government revenues and the changes in consumer surplus and producer surplus, and the dead weight loss, due to an imposition of a tax.
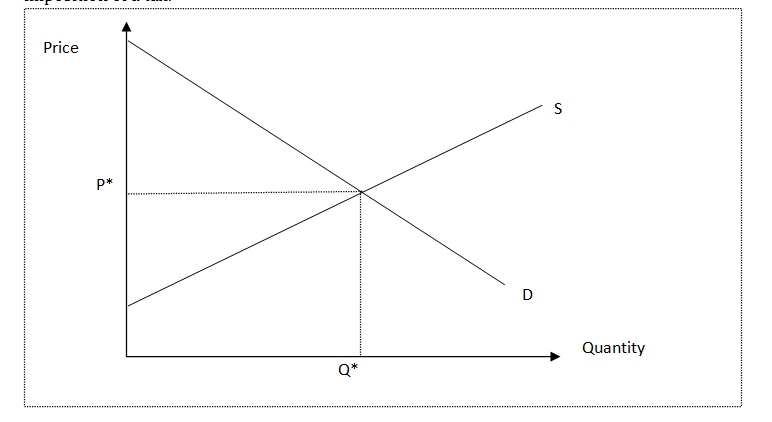
If there is no tax then the equilibrium price and quantity will be on intersection point of the supply and demand curves. The reason is that the buyers are willing to pay for the product showing their demand. In this situation, the consumer surplus is the area between the demand curve and price i.e. A+B+C.
In addition, the supply curve shows the sellers’ costs as producer surplus is the area between supply curve and the price i.e. D+E+F. So, if there is no tax then total surplus will be total of consumer surplus and producer surplus i.e. A+B+C+D+E+F. In such situation, the government cannot generate any tax revenue (See: Below Figure)
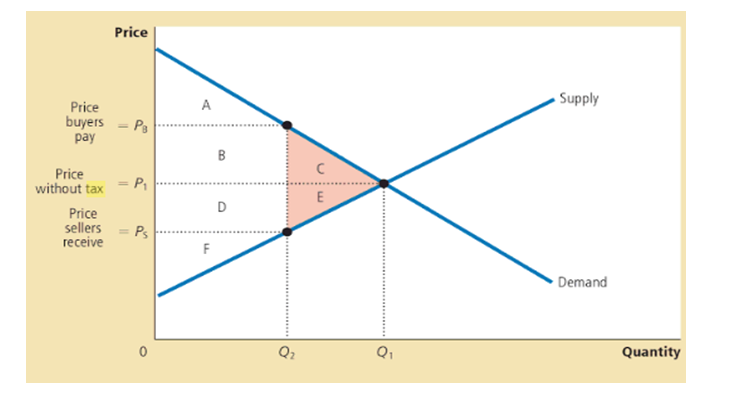
The article claims that “resulting revenues are an important part of the equation”. Use the demand and supply diagram below to illustrate and explain the Government revenues and the changes in consumer surplus and producer surplus, and the dead weight loss, due to an imposition of a tax.
If the tax is applied by the government, welfare can be enacted. Because of tax imposition, the price paid by the consumers will increase from P1 to PB that will decrease the consumer surplus to the area A showing the area below the demand curve and above the buyer’s price.
Apart from this, the price obtained by the producers will decrease from P1 to PS because there will be a decline in the producer surplus to the area F showing the area above the supply curve and below the seller’s price. In addition, there will be a decline in demand or the quantity sold from Q1 to Q2 due to tax.
So, government will collect tax revenue similar to the area of B+D. In such situation, total surplus with tax will be total of consumer surplus, producer surplus and tax revenue i.e. A+B+D+F.
| Without Tax | With Tax | Change | |
| Consumer Surplus | A+B+C | A | -(B+C) |
| Producer Surplus | D+E+F | F | -(D+E) |
| Tax Revenue | None | B+D | +(B+D) |
| Total Surplus | A+B+C+D+E+F | A+B+D+F | -(C+E) |
So, tax imposition will increase tax revenue by the area B+D as it will impact both the consumers and producers and also generates tax revenues for the government. But at the same time, total surplus will decline by the area C+E showing the losses from the consumers and producers because of tax imposition.
Thus, losses are higher than the revenue generated for the government. This loss from the consumer surplus as well as producer surplus is known as the deadweight loss because of tax imposition. It is extra tax burden that would be higher than the tax revenue generated by the government for social welfare showing from the below graph:
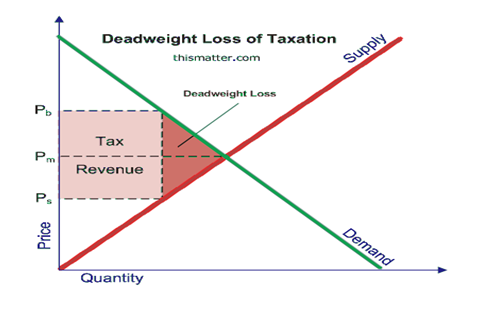
In the case of unhealthy food and beverages, some consumers will not buy due to higher prices than their willingness to pay price that will also reduce the demand and cause deadweight loss of taxation highlighted in dark red colour in the above graph
Question 3
According to the article residents of Philadelphia and Cook County “are not drinking less soda” following the imposition ofthe tax on sugary drinks.
- Explain in your own words what this means in terms of elasticity.
Elasticity shows the changes in quantity demanded on the changes in the prices of the goods and services. It shows the degree to which the demand changes with the change in price. Even imposing tax on sugary drinks, residents of Philadelphia and Cook County are not drinking less soda.
It means the demand has not changed even on increasing price due to tax imposition. It shows that the demand of sugary drinks is inelastic as the people of these cities are fond of or addicted to drink soda as they are willing to pay even higher prices after tax for consuming soda. So, this demand for the soda in these cities can be said inelastic.
- Complete the diagrams below to explain and illustrate the effect of the imposition of a tax on sugary drinks onequilibrium price and quantity in two cases: when the elasticity of demand for sugary drinks is
- relatively inelastic.
- relatively elastic.
- Relatively inelastic: Relatively inelastic demand is related to the less change in the demand proportionately than the changes in price. It means the change in prices brings fewer changes in the demand of the product. If the product price increases by 10% then the demand will decrease by 5%. It shows the demand is relatively inelastic. When the elasticity of demand for sugary drinks is relative inelastic, the imposition of the tax on surgery drinks on equilibrium price and quantity will decrease demand in less ratio. There will be low impact of tax on the demand of sugary drinks however, it will decline.
- Relatively elastic: In relative elastic demand, there is greater change in demand proportionately than the produce price. Means a specific change in price brings more changes in the quantity demanded. For instance, if the price of the produce increases by 10% then the demand of product will decline by 20%. It shows the relatively elastic demand. In the given case, imposition of a tax on sugary drinks on equilibrium price and quantity will bring more decrease in the demand of the sugary drinks. People will less prefer to consume these drinks on the imposition of tax.
References
http://web.uvic.ca/~aahoque/VIU/Chapter%204.pdf


