Business Analytics For Project Management Assignment Sample
Introduction
Businesses in 21st-century mainly depend on projects they undertake in improving their efficiency in analyzing their business operations and customer demands. Project management in organizations has been one of most vital sections where initiatives and innovation are taken into consideration therefore leading to widespread achievements. Take in case of John Lewis, a UK retail brand, it can be stated that In 2017, this retail brand has taken initiative in overcoming economic turbulence by coming up with a cloud platform approach known as John Lewis digital platform (JLDP). This project was initially started by a group of engineers with an aim of empowering their internal, organic experiments in order to increase their volume of production and services. An engineering team with technologies have made an attempt in bringing digital transformation in John Lewis in partnership thereby leading to success of this project. However, John Lewis treats its JLDP as a product that can be easily customers with a project or initiative. Focusing on this recent project, study focuses on risk management plans project managers undertake along with project management theories.
Risk forecasting
Risk forecasting refers to the process of predicting potential outcomes of a project. As opined by Daniel and Daniel (2018), project managers are assigned with the task of analyzing “historical project data” so that possible risks of a project could be determined. For instance, a fixed budget is allocated for projects and there is a constant risk of exceeding it. In 2017 John Lewis decided to introduce a cloud based “micro service architecture” which would facilitate organizations to offer digital propositions to customers in an agile manner (Hornby, 2019). This project was subjected to a number of risks and foremost risk was scope to exceed allocated budget. Project managers utilize quantitative budget forecasting tools namely, “Straight-line, Moving average, Simple linear regression and multiple linear regression”. These methods facilitated a project manager to ensure that a budget does not exceed permissible limits otherwise return on investment could be affected.
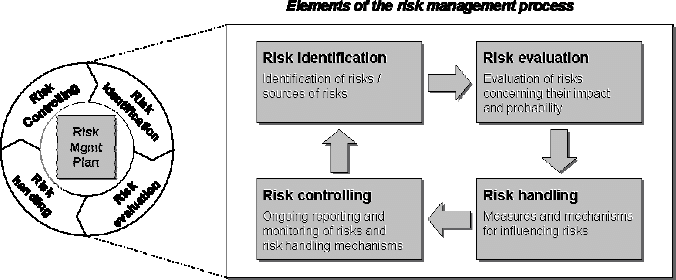
Figure 1: Risk management process
(Source: Ullah et al. 2021)
A systematic risk management process is conducted by project managers to ensure a risk free environment for the project. Based on opinions of Ullah et al. (2021), risk management is an “iterative process” and each stage of risk management needs to be planned systematically to ensure expected outcomes. A risk management process comprises four distinct stages namely, “Risk identification, Risk evaluation, Risk Handling and Risk controlling”. First step is to identify risks or sources which can lead to a poor outcome in a project. In the case of John Lewis, budget was a primary source of risk and since a database was needed it needed incorporation of appropriate technology and software which constituted a substantial share of budget. In addition to this, employees lacked digital literacy and required a comprehensive training programmer which would require further investment. Second stage is “Risk evaluation” which determines the probability of a negative outcome and their impact. Probability of exceeding the allocated budget for John Lewis was high as the database would expand in size and new features would be added to it. Subsidiary risk for this project was data privacy which did not have a high probability. A plethora of consumer data would be analyzed and stored in a digital database which would be prone to cyber-attacks. Third stage is to evaluate specialized measures to reduce probability of a risk. Suitable measures were taken by the IT department of John Lewis to ensure that the database could be accessed through two layered verification processes. It reduced the probability of this risk from taking place in the first place. Lastly risk controlling is concerned about reporting and monitoring risk handling mechanisms so that performance of the risk management process is sustained. It is crucial to perform a risk identification process continuously so that potential outcomes of a project can be determined at every stage of the process. The step is repeated a number of times throughout this project life cycle and special emphasis is made during key milestones. “Risk Repository” serves as a database for all risks that were identified for accomplished projects. It can be consulted to gain an idea about potential risks that can occur while conducting a project. Similarly “Checklist analysis” is an analytical tool used to identify gaps and potential risks of a project. This process is based on the type of project that is being conducted and the experience of individuals involved in it. Lastly, “Expert judgement” also serves as a guideline during risk identification. “Experienced participants, stakeholders and subject matter experts” are interviewed or consulted to determine potential outcomes that could be detrimental for a project.
“Risk category” is a tool used by project managers to determine the extent to which a segment of a project is prone to risk. Based on opinions of Ghassemi and Darvishpour (2018), standard risk categories are provided by organisations and they are “Technical, External, Organisational and Project Management”. For instance, risk related to customers, market and suppliers of John Lewis are considered to be extended categories of external risk and a project manager needs to analyse these areas for efficient risk prevention. ‘Risk Analysis” is a crucial stage of the risk management process as it helps to examine how project outcomes could be negatively affected due to risk events. Upon identifying risks, they are analysed in detail so that”Qualitative and Quantitative” impact of risk can be identified and a suitable risk mitigation strategy could be designed for John Lewis. “Risk Exposure” is used by project managers to determine the extent to which a project is exposed to a risk and its value is determined by multiplying Impact rating with Risk Probability. These assessments help a project manager to develop a “Risk response planning”. Risk mitigation strategies may not be quick solutions aimed at resolving all risks of a project as some risks may require a strategy to be implemented over a prolonged time frame.
Limitation of risk reduction strategy
Project managers in John Lewis prevented the budget from exceeding the permissible limit by maintaining a cost breakdown structure. They continuously analysed capital that was being invested for installing software and technologies. Any areas to implement cost reduction were targeted. For instance, employees were offered digital training programmes and it ensured that training could be accessed remotely at any time of day (Hornby, 2019). Therefore productivity of employees was not jeopardised and production capabilities of John Lewis were sustained. However it gave rise to a challenge as employee’s required sufficient technology to support remote access of training programmes and also their learning outcomes could not be measured. Similarly ensuring privacy of consumer data had become challenging for the IT department of John Lewis. Due to a high probability of cyber-attacks, customers could refrain from sharing their personal information with the company. This would affect the quality of the digital interface and variable customer demands and preferences would not be achieved.
Risk Impact Matrix
| Risk | Impact | Detailed description of Impact |
| Risk of exceeding allocated budget. | High | Business capital of John Lewis would be impacted and return on investment would not be sufficient for the project. |
| Data privacy and probability of cyber-attack. | Moderate | Reluctance of consumers to share their data to organisation and reduction in quality of digital interface. |
| Reluctance of employees to accept change. | Low | High employee turnover and loss of workforce productivity. |
Table 1: Risk Impact Matrix
(Source: Created by Author)
Project management theory
The dispatching model
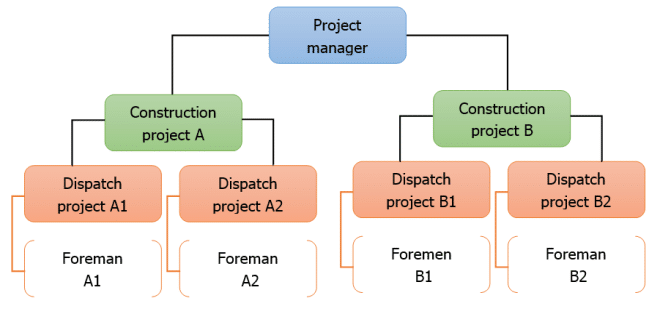
Figure 2: The dispatching model
(Source: Influenced by Moreno et al. 2019)
The dispatching model in project management helps managers in drawing flow charts between different flows of responsibilities and information in our chronological manner when information from project managers passes on to foreman and ground employees. Based on the opinion of Moreno et al. (2019), it can be stated that the dispatching model in project management helps in planning each and every project activities and tasks with a proper flow of command and schedule so that it can be executed easily with a single notification from the executor or project head. Focusing on this aspect, the dispatching model brings up a process through which information and delegation of responsibilities were transferred from head of project to staff and employees thereby maintaining transparency and a proper flow of hierarchy (Stoldt et al. 2018). Taking the case of John Lewis and the partnership initiative of coming up with JLPD, it can be stated that the dispatching model has effectively helped in maintaining coordination with project managers and employees who were responsible in bringing digital changes (Song et al. 2020). In fact, each and every work was delegated by project manager under supervision of engineers so as to make sure that overall digital process along with transferring of data and information is safe, secure and wholesome. Digital transformation through despatching model has effectively ensured that organisations like John Lewis taking up technological initiatives need to have proper collaboration with Google cloud platform so as to project more effectively with proper resources and delegations.
The thermostat model
The thermostat model of project management helps in controlling overall project elements along with maintaining standard of performance and quality. This model helps in understanding and measuring overall performance and output of project initiatives along with bringing variance between standard and measured value. Before conducting a project, in the planning stage, most project managers set certain key performance indicators through which they can monitor overall quality of project activities executed by employees (Inuwa et al. 2019). In addition to this, it has been further evident that these key performance indicators are considered to be basic quality standards that project managers through their executive strategies need to attain in order to maintain high-quality. Using the thermostat model, project managers can actually understand the difference between actual and standard quality checkpoints thereby allowing them to perform more efficiently. Taking the case of JLDP, it can be stated that project managers have effectively used the thermostat model in order to see efficiency of the project. When planning this digital platform and transformation in technologies in John Lewis and partners, organizational head is very much skeptical about quality of services and outcome of project tendering and therefore key performance indicators have been set. Key performance indicators in this digital setup have been mainly in terms of data security, privacy in sharing information, easy accessibility and customer benefits (Momanyi and Sang, 2019). This model has helped in analyzing differences between predetermined standards of quality and actual quality of services the project has served. Further, this model helps in managing projects under three main categories including planning process, executing process and controlling process which are interrelated to one another with changes, plans and performance data. The overall process of the thermostat model revolves around execution and processes managers have adopted in implementing projects and therefore constant monitoring and controlling is very much essential.
Conclusion
This study concludes with the importance of having project management in organisations in order to bring innovation and technological upgradation. Most of the organisation in recent times have been undertaking projects in order to implant technologies and digital platforms so as to give customers a better experience of both online and off-line platforms. On this perspective, it has been evident that organisations like John Lewis have recently come under a digital platform initiative that they have taken in improving their online retailing and have a better approach in saving information. On this note, they have come in collaboration with Google cloud platform where they can use big data and cloud computing in collecting and storing information safely and utilising it for improving digital buying experience of customers. This study takes into account risks and threat factors that organisation has been undergoing along with response of project managers to it. Further, to ensure a theoretical perspective, this study concludes with despatching and thermostat model as one of the most effective one for project management.
Recommendation
In summarising this study, it can be stated that the project managers in order to avoid the risk need to have a proper monitoring channel so that every activity and implementation process is well monitored. By doing this monitoring process, project managers in John Lewis can effectively identify the loopholes in technological implementation before it turns into cyber attacks and threats to cyber security. These monitoring processes and control systems can be further accompanied with constant technological upgradation so as to bring up the latest technologies in the business. John Lewis being a widespread company with more than millions of customers globally needs to have a strong network so as to give its customers a better online buying experience with JLPD. A constant investment in technological upgradation can improve the software and the overall outcome of the project can be better.
References
Davies, A., Manning, S. and Söderlund, J., (2018). When neighbouring disciplines fail to learn from each other: case of innovation and project management research. Research Policy, 47(5), pp.965-979.
Ghassemi, A. and Darvishpour, A., (2018). A novel approach for risk evaluation and risk response planning in a geothermal drilling project using DEMATEL and fuzzy ANP. Decision Science Letters, 7(3), pp.225-242.
Hornby, (2019). Our Award Winning John Lewis Digital Platform. Available at: https://medium.com/john-lewis-software-engineering/our-award-winning-john-lewis-digital-platform-2d093e03d542 [Accessed on 07 April 2022]
Inuwa, I.I., Joseph, S. and Musa, M.M., 2019, April. Effects of craftsmen supervisors project management skills on construction project success in Nigeria. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 513, No. 1, p. 012002). IOP Publishing.
Momanyi, M.S. and Sang, P., 2019. Project constraints influencing the construction of residential housing projects in urban centers in Kenya: A study of National Housing Corporation. International Academic Journal of Information Sciences and Project Management, 3(5), pp.165-183.
Moreno, R., Obando, J. and Gonzalez, G., 2019. An integrated OPF dispatching model with wind power and demand response for day-ahead markets. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 9(4), p.2794.
Song, X., Lin, H., De, G., Li, H., Fu, X. and Tan, Z., 2020. An energy optimal dispatching model of an integrated energy system based on uncertain bilevel programming. Energies, 13(2), p.477.
Stoldt, J., Trapp, T.U., Toussaint, S., Süße, M., Schlegel, A. and Putz, M., 2018. Planning for digitalisation in SMEs using tools of the digital factory. Procedia CIRP, 72, pp.179-184.
Ullah, F., Qayyum, S., Thaheem, M.J., Al-Turjman, F. and Sepasgozar, S.M., (2021). Risk management in sustainable smart cities governance: A TOE framework. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 167, p.120743.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

