Continuous improvement
This project discusses about the Latino Engineering company that has around 300 employees and is located in New South Wales, Australia. This company is engaged in designing, development and manufacturing of engineering equipments for many industries like gas, construction, and infrastructure.
This company was developed by Dominic Latino, a mechanical engineer having many patents for the engineering equipments designed by him. The company was operating from last 30 years and has a good clientele. The company has achieved many contracts, profitability due to its reputation. This was the main reason to attract many investors who wants to join the company or purchase it. But Dominic never wanted to sell its company.
Later he had sold his company to an investment group and after spending 30 years in the company has retired at the age of 65. The company had faced various issues after one year of take over. The company faced problems such as defective engineering equipments, poor design, the non-responsive customer service team, etc.
For solving these issues the company decides to develop a continuous improvement plan, and has engaged a project management consultant. The company will be discussing the root cause behind these issues, and will also propose a plan to eliminate the root cause. A continuous improvement plan will also be developed to make sure that these issues are not repeated in future.
Identify the root cause (s) by proposing the use of appropriate tools and techniques?
The company should adopt various different tools and technique to identify the root cause (s) which is: Root cause analysis, five whys analysis, failure mode and effects analysis, pareto analysis, fault tree analysis, fish bone diagram, etc.
Root Cause Analysis: It is one of the techniques which are used by individual or group to identify the real causes behind any problem. The main objective of this technique is finding out the ultimate reason behind the problem not just the symptoms of the problem. It further helps to identify the problem when you are unaware of the reasons or the problem is unexpected (Geerling, et al., 2014).
The process of this analysis is: firstly describe the problem in the company. Secondly, start gathering data which is related to the problem. Thirdly, start looking out for the potential cause of the problem. Fourthly, start looking what is the causes of the problem that the company wants to remove. After that, identify the possible solutions that will help to prevent the problem.
Then implement the changes required and monitor the changes made so that it can be ensured that the problems are eliminated effectively (Black and Vernetti, 2015). Root cause analysis will help the company to identify the problem of lack of communication at every level of management. This becomes a problem when people are not having concise knowledge about the goals to achieve.
Five why Analysis: This is a technique which a company adopts to move the past symptoms and start to identify the true cause behind the problem. The strategy of this technique is to look out for the problem and drill down by asking ‘Why’. This method is quite helpful for obtaining the results quickly.
Asking five times why it happened will help to identify strategically the root causes behind the problem (Lippi, et al., 2013). The process of using this technique is also simple: Just gather a team who are aware about the problem, after that start to define the problem and give a clear statement of the problem.
Then ask the first why in context of why the problem occurred. Then finally ask why four more times. And when you know that the root cause is identified then you can end this process (Liu, et al., 2013). Then just address the root cause and continuously monitor the measures you have adopted so that there are fewer chances of variations.
Here the problem identified is that the non responsive customer service team, the team was not effective enough to deal with the queries of the customers and in return it results into dissatisfaction among the customers.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: It is also called as the potential failure modes and effects analysis. It refers to a step-by-step approach that helps to recognize all likely failures in the design, development or manufacturing of a product or service (Liu, et al., 2011). It helps to identify the reason, cause of the problem, the underlying errors or the potential failures in a product or service before they are likely to occur.
The process of FMEA starts by recognizing the problem or root cause behind any failure and then adopting measures or taking actions that are needed to prevent the problem from occurring. It also helps one to monitor the changes taken over time (Ashley and Armitage, 2010).
Pareto Analysis: The Pareto analysis is a technique which is used to identify the problem that occurs. It works on an interesting principle that says 20% of the work creates 80% of results (Fotopoulos, et al., 2011).
This technique work best when there is multiple reasons for a problem. It can be applied in various areas such as: 20% of system defect cause of 80% problems, 80% of customer’s complaint occurs due to 20% of the company’s products or service. Here the problem identified was of poor quality control in the company (Upadhyay, et al., 2010).
Poor quality reflects that the company is not effective enough to cater to the needs of its consumers and they are not having effective control system to check the quality.
Fish Bone Diagram Analysis: This is also called as the ISHIKAWA diagram or the cause and effect diagram. This technique is used when there is a requirement to identify the root cause behind a problem, or any potential failure to occur in future. It is further used as a structure of brainstorming session.
The process of fish bone diagram is: start with identifying the problem that exists. After that identify the possible factors that are included in the problem such as equipment, system, material, etc (Wu, 2010).
Then start to identify the likely causes behind the problem and draw them on a diagram. Then start to analyze the diagram. Here the problem identified was that the poor design and development follow up with clients. The root cause behind this was that the management was not properly effective in delivering the desired results.
Plan to reduce the root cause (s).
The plan to reduce these root causes are as follows:
The company should firstly give a brief concise overview of the overall possible root causes to everyone so that they become aware regarding the various root causes.
When people will know about the root causes than it will become easy for them to make out strategies that will help to reduce the root causes (Ouslander, et al., 2011). The root cause like lack of communication at every level of management can be resolved by inviting everyone together to express their views, ideas, thoughts, etc.
It will help to improve the workflow as there will be more transparency among the entire workforce. At the same time, the root cause of non responsive customer service team can be managed by choosing the right channel to can speed things up in company’s favor.
The service team should always listen to the customers patiently regarding their interests, liking, etc. The team should accept their mistakes this will help to retain the customers for long time (Schoen, et al., 2011).
The problem of poor quality can also be reduced by adopting proper tools such as total quality management or six sigma techniques for enhancing the quality of the products or services. At the same time, the employees should provide regular feedback to the management in context of the quality of the products and services of the company (Kramer and Porter, 2011).
The another way to reduce the root cause of poor design and development follow up with clients is to enhance the performance of the employees so that they deliver effective results and they should be given training on how to improve the poor designs and how to deal with their clients so that they can be retained for long term (Prashar, 2014).
The company should reduce the response time and should give timely response to their customers/clients so that they feel that they are a part of the company. The company should not utilize much time for resolving an issue. As soon as an issue is depicted the company should try to find out the cause and start to develop strategies in order to reduce the root cause of the problem.
The management should come together as team in generating new and innovative solutions for the problem faced by the company. The company can give the opportunity of providing feedback by the customers so the company can also know the areas where they are lacking.
This will help to build a level trust among the customers towards the company. Further taking feedback from the customers will help to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the company (Faruqui, et al., 2010).
The company should involve everyone; it should not happen that the authority lies in the hand of a particular person and he is only taking the major decisions without involving the suggestions of anyone else.
The company should always have a proper and accurate schedule of the tasks, budget, cost, time and resources. This will help to reduce the possibility of errors and chance of risks that might affect the performance of the company.
Develop a continuous improvement plan
The development of the continuous improvement plan is very significant to remove the chances of problem and issues in the organization. Senior managers should implement the developed plan for continuous improvement in the quality of the product and remove the challenges which are faced by the organization (Hsu, et al., 2013).
A continues improvement plan includes the stages in the process for effective implementation such as define mission and role, select the goals, set objective, select strategy for action, consult major issues, strategy implementation and evaluate the result.
Define mission and role– In the starting of the process, the senior managers should define the mission and role of the planning for making the effects on the outcome of the planning.
The role of the particular employees should be decided to select the perfect person for receiving the effective outcome (Chassin and Loeb, 2011). In this case, the mission of planning is to continuous improvement in the quality of the production. Additionally, it will help to remove the repetition of the problem and issues in the production and manufactured products.
Select the goals– The goal should be selected for the purpose of achieving the higher level of satisfaction of the planning that is related to the continuous improvement. In this planning, the manager should keep in mind that the objectives of the planning should be accomplished.
The improvement goal will help the organization to overcome the issue and companions of the customer related to the quality of the manufactured product.
Set objective– Setting the objectives is very necessary for the planning of continuous improvement (Talib et al., 2011). The main objective of the planning includes the successfulness of the business with the reduction in the challenges and problems.
This case includes some important objectives that are the improvement in the production quality, remove the poor design, reduce the defectiveness, provide good customer service, and provide equipment to the client according to demining.
Select strategy for action– A continues improvement plan also use the important strategies and techniques to achieve the goal of the planning. These strategies and techniques are developed for the managing the quality of the products with the redaction in the variations (Bernhardt, 2013).
The success of the improvement plan is dependent on the proper implication of the strategy. There are several techniques that can be used by the management like root cause analysis, five whys analysis, failure mode and effects analysis, Pareto analysis, fault tree analysis, fish bone diagram, etc. In this case, the root cause analysis and Pareto analysis is the best technique for the continuous improvement in the organization.
Consult major issues– There several techniques that can be used for the purpose of developing the improvement plan for this case but each technique and strategy includes the issues in the implementation. In this stage of the planning, the management should analyze the major issues in provided strategies and negotiate the major issues to carry out the strategy in the proper way (Dale, 2015).
The selected strategy may have issues that can be consulted with the team members for implementing it with an effective manner.
Strategy implementation– The most appropriate strategy should be selected for the resolution of the problems and issues with the continual improvement in the production of the organization.
The implementation of the strategy is very useful to solve the routine problems which are occurring in the organization. The strategy should be implemented and adopted according to the situation that is provided in the planning. The strategy is implemented according to the program design and quality of the product so it can remove he issues and problems that are occurring in the organization.
Evaluate result– The organization should evaluate the results of the strategy that it is working properly or not. It should also ensure by the organization that if the provided strategy is not working properly, then there is a need of finding out the reasons. The evaluation of the result provides the information that supports the planning efforts (Phillips, 2012).
It confirms that the actions which are taken are providing the effective results and there is a need of adjustment. The evaluation controls the negative outcome of the planning of continues improvement and provides the solutions to the problems or issues.
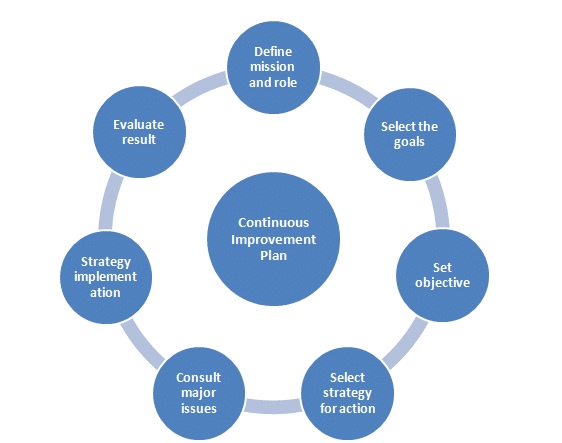
Figure- Continuous Improvement Process
From the above discussion, it can be concluded that the continuous improvement of the organization plays a vital role to make successful the business. The development of continuous improvement plan can be help to repeat the issues and problems that are faced by the Latino Engineering organization. It is because the organization used the good strategic plan for continued improvement in the development of the organization.
It is also concluded that the company is facing the problem due to several root causes such as unskilled staff members, lack of management, cost cutting, etc. The company should focus on the root causes to remove them as soon as possible to save the organization and for the successful future. Additionally, all the strategies that are provided have an effect to solve the problems of an organization but the ‘root causes analysis’ is the best technique for this case.
This technique will help the organization to hide the root causes that affect the organizational success. It can also be concluded that the provided propose plan will be effective for eliminating and reducing the root causes by the use of required resources. Finally, it can be said that the provided continues improvement plan can be helpful to remove the problems of the business.
Ashley, L., and Armitage, G. (2010) Failure mode and effects analysis: an empirical comparison of failure mode scoring procedures. Journal of patient safety, 6(4), pp. 210-215.
Bernhardt, V. (2013) Data analysis for continuous school improvement. USA: Routledge.
Black, N. H., & Vernetti, B. J. (2015) Root-Cause Analysis. Professional Safety, pp. 60-62.
Chassin, M.R. and Loeb, J.M., (2011) The ongoing quality improvement journey: next stop, high reliability. Health Affairs, 30(4), pp.559-568.
Dale, B. (2015) Total quality management. USA: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Faruqui, A., Sergici, S., and Sharif, A. (2010) The impact of informational feedback on energy consumption—A survey of the experimental evidence. Energy, 35(4), pp. 1598-1608.
Fotopoulos, C., Kafetzopoulos, D., and Gotzamani, K. (2011) Critical factors for effective implementation of the HACCP system: a Pareto analysis. British Food Journal, 113(5), pp. 578-597.
Geerling, J., Chernofsky, M., and Pratt, S. D. (2014) Root Cause Analysis. ASA Newsletter, 78(6), pp. 46-49.
Hsu, C.W., Kuo, T.C., Chen, S.H. and Hu, A.H., (2013) Using DEMATEL to develop a carbon management model of supplier selection in green supply chain management. Journal of cleaner production, 56, pp.164-172.
Kramer, M. R., and Porter, M. (2011) Creating shared value. Harvard business review, 89(1/2), pp. 62-77.
Lippi, M., Bertini, M., and Frasconi, P. (2013) Short-term traffic flow forecasting: An experimental comparison of time-series analysis and supervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 14(2), pp. 871-882.
Liu, H. C., Liu, L., and Liu, N. (2013) Risk evaluation approaches in failure mode and effects analysis: A literature review. Expert systems with applications, 40(2), pp. 828-838.
Liu, H. C., Liu, L., Bian, Q. H., Lin, Q. L., Dong, N., and Xu, P. C. (2011) Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy evidential reasoning approach and grey theory. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), pp. 4403-4415.
Ouslander, J. G., Lamb, G., Tappen, R., Herndon, L., Diaz, S., Roos, B. A., … and Bonner, A. (2011) Interventions to reduce hospitalizations from nursing homes: evaluation of the INTERACT II collaborative quality improvement project. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 59(4), pp. 745-753.
Phillips, J. J. (2012) Return on investment in training and performance improvement programs. USA: Routledge.
Prashar, A. (2014) Adoption of Six Sigma DMAIC to reduce cost of poor quality. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 63(1), pp. 103-126.
Schoen, C., Osborn, R., Squires, D., Doty, M., Pierson, R., and Applebaum, S. (2011) New 2011 survey of patients with complex care needs in eleven countries finds that care is often poorly coordinated. Health Affairs, 30(12), pp. 2437-2448.
Talib, F., Rahman, Z. and Qureshi, M.N., (2011) Analysis of interaction among the barriers to total quality management implementation using interpretive structural modeling approach. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 18(4), pp.563-587.
Upadhyay, P., Basu, R., Adhikary, R., and Dan, P. K. (2010) A comparative study of issues affecting ERP implementation in large scale and small medium scale enterprises in India: A Pareto approach. International Journal of Computer Applications, 8(3), pp. 23-28.
Wu, W. W. (2010) Linking Bayesian networks and PLS path modeling for causal analysis. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(1), pp. 134-139.


