IBM501 International Business Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of IBM501 International Business Assignment, written by the expert.
Introduction
All over the world, different nations are experiencing essential changes in the approaches they market and deliver various products, services and items. The national economies are towards accomplishing self-sustainability objective, which are currently evolving innovative routes towards International Business (Kollmann et al. 2016). The factor in relevance to this crucial change is development of innovation, infrastructure, communication, correspondence and so on. Business actions performed across national borders are associated with selling and purchasing of goods, services and commodities. The multinational enterprises through implementation of international business theories explore their trade opportunities outside domestic national borders for extending their own business activities (Meyer and Peng, 2016). Through international business, national economies are getting fused and borderless with world economy. Numerous multinational enterprises are making their way into worldwide business, which represents them with scope of tremendous benefits and development. International business and its strategies are important to both business organization as well as the nation.
It gives confidence to the nation in obtaining foreign exchange, which can be utilized for importing merchandise from global market. According to Cavusgil et al. (2014), International business helps the multinational enterprises to attain improvement in their profit making approaches through selling products in various nations where the cost is high. Moreover, it assists multinational enterprises to utilize the surplus resources and increase profit out of their activities. It also enhances in the development of organizational prospectus. It is due to international business, customers are feeling comfortable in using services and commodities manufactured in another country and thereby being helped in the improvement of their standard of living. International business is one of the methods adopted by multinational enterprises for achieving development in those multinational enterprises, which confront adverse marketing conditions in local market (Richter et al. 2016). With the focus to strive towards achieving more specific and higher goals, which are based on vision of harmonious growth, Toyota begun to revise their Earth charter towards the 21st century.
Explanation of Theories
Over the last two decades, the growing interest has been on the strategies of internationalization. Internationalization can be described as outward movement of multinational enterprises operations and thereby increasing its involvement in terms of international operations (Meyer and Peng, 2016). Through the internationalization strategies, multinational enterprises follow various patterns in their investment in various markets abroad through economic analysis of location advantage, internalization and ownership in a logical way. The multinational enterprises possess a worldwide approach towards markets and manufacture with functionalities in more than one country. The related areas of topic that need o be studied includes variations in legal systems, economic policy, labor standards, environmental standards, corporate culture, tariffs, trade agreements, education, political systems, local culture, living standards, accounting standards, climate, import and export regulations, language and others. All these factors need significant alterations in the strategies individual business operates from one country to another. International trade embraces various aspects of relation in various countries. Numerous theories regarding international business affairs exist. Those are worshipped by multinational enterprises in a strategic way with the prioritized aim being on revenue generation and business expansion (Kollmann et al. 2016). Some of those include absolute advantage, factor proportion theory, comparative theory, international product life cycle, mercantilism, national competitive advantage and new trade theory.
Theory of Mercantilism
Mercantilism can be defined as an economic theory highly practiced in Europe, which promoted Government regulation on the economy of nation with the purpose of augmentation of state power at the cost of rival nation’s power (Wynn-Williams, 2016). Particularly it helps in balancing the demands for conducting trade professionalism, which can be considered as financial complement of political absolutism. The main objective of following mercantilism theory in international business is to increase the national wealth through imposing governmental regulation, which is concerned about all the commercial interest of the nation (Cohn, 2016). The multinational enterprises believe that the nation’s strength can be maximized by drawing limitations on imports through maximizing exports and tariffs.
Origin of Mercantilism
Most of the economists in Europe during the era between 1400 and 1750 are considered as mercantilists today, who were accustomed to ‘mercantile system’. Thomas Mun was the creator of mercantile system specially designed for Treasure by Foreign Trade and the last most important mercantilist exertion was James Steuart’s principles of political economy.
Policies of Mercantilism
The mercantilism policies attracted many multinational enterprises to become its follower for their business development on a worldly basis (Dunn, 2015). High tariff rates on manufactured products are the universal feature of mercantilist policy. The other policies include:
- Developing a well structured network in overseas colonies;
- Mercantilism policy prohibits the colonies from trading with another nation;
- Moreover, it bans the exportation of silver and gold in spite of getting payments;
- This policy also restricted conduction of trade with the help of foreign ships;
- Exportation of subsidies;
- Mercantilism policy assists in promotion of manufacturing through direct subsidies and research;
- It maximizes the utilization of domestic resources in various aspects of business processes;
- Last but not the least, this policy confined consumption of domestic materials through implementation of non-tariff barriers in trade.
Mercantilists specifically put stress on circulation of rejected hoarding and money. They have always been focused on monetary metals wrapped with intellectual ideas in relevance to money supply such as the effects of simulation of growing money supply.
Criticism of Mercantilism
As opined by Ezell and Policy (2017), various flaws have been found in mercantilism policy, which paved the way to make some critics. The policy has various interlocking principles. Expensive metals such as silver and gold were deemed indispensably for wealth of the nation. Conditionally, the nation did not have mines and still having access to them, precious metals have to be obtained through trade. It was considered that balance in trade have to be favorable which means excessive exports compared to imports (Mueller, 2018). Mercantilism was criticized, when promoter of laissez-faire concluded that there is no significant comparison in between foreign and domestic trade. It is considered that all trade is beneficial to both the public and the trader. They also focused on maintaining the amount of treasure or money, which a state necessitated have to be adjusted automatically and the money or other commodity can exist in excess amount. The ideology that nation would be rich at the expense of other was denied and arguably considered that trading is a two-way path in reality.
Porter’s Diamond theory for National Advantage
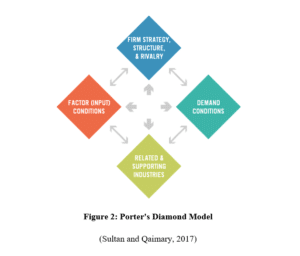
As stated by Antimiani et al. (2016), Michael Porter’s Diamond Model for gaining competitive advantage compared to other nations offers a well-developed model, which can be helpful in understanding proportional positioning of nations in a globally competitive market. The model has been specifically designed for key geographic regions. Porter’s diamond theory comes up for suggesting the existence of inherent reasons behind some nations, rather multinational enterprises within nations becomes more competitive compared to others in a global market (Samarasinghe et al. 2015). The argument lies on the fact national base of an organization provides them with special factors, which are responsible for potential creation of competitive advantage in global market.
Traditional national advantages
Traditionally, there are some factors mentioned by economic theories for bringing comparative advantage on regions and countries:
- Location
- Land
- Natural Resources
- Local population
- Labor
Determinants of National Advantage:
Factor Conditions: This includes those relevant factors, which can be better exploited by multinational enterprises in a nation. Factor conditions can be observed as advantages present in countries, which are consequently built upon by multinational enterprises for attainment of more advanced competitive factors (Sultan and Qaimary, 2017). Factors are not often advantageous, like workforce shortage can be considered as a potential factor, which strengthen competitiveness as this factor might enlighten the focus of the company towards zero defects and automation.
Demand Conditions: In certain conditions where the local demand for a product in the market is more or larger within the nation compared to foreign markets, local firms are observed to put on more emphasis in improving their work proceeding compared to foreign multinational enterprises (Urbanet al., 2015). This reflects in the potential increment of global competitiveness of locally based exporting multinational enterprises. As opined by Mboya and Kazungu, (2015), the rising demand in the nation market can be considered as the main driver of innovation, quality improvements and thereby growth. It can easily be understood that an excessive demand in local market tentatively brings national advantage. A trendy and strong local market assists local firms for anticipation of global trends.
Supporting and Related Industries: In scenarios where the local suppliers and industries are competitive, national multinational enterprises eventually gets more potential cost efficiency and get more innovative products and parts. This remarkably leads to development of great competitiveness in the strategies of national firms.
Firm strategy, Rivalry and Structure: The management system and structure of firms in various countries potentially affects in strategy building for gaining competitive advantage in a competitive market. Through utilization of Porter’s Diamond theory, leaders of numerous multinational enterprises analyze the competitive factors, which reside in the company’s home nation (Anton, 2015). Moreover, it is also estimated which of those factors can be easily exploited for gaining global competitive advantage. Business leaders often refer to use Porter’s Diamond model for strategizing internationalization by virtue of which the leaders fully utilize the model for analyzing the preferable chances of the national market factors invariable supports the internationalization process. Moreover, it is also apprehended the favorable conditions present in the nation are liable to provide competitive advantage in global market. Business leaders use this model for assessing the fact, in which countries investment can be made and which countries are more likely to provide sustainable development and growth (Rothaermel, 2015). The government plays a vital role for the followers of this model. The governments uninterruptedly encourage the organizations through passing various favorable policies and providing easiness in doing business. Moreover, it stimulates the organizations for expansion of their business. Finally, the government also helps in creation of growth in industries.
Criticism of Porter’s Diamond model
The variables mentioned in Porter’s Diamond model use useful in terms of analyzing competitiveness on a national basis, which in turn weakens to keep and exclusive focus on the concept of ‘home base’ (BORSOS et al. 2016). The model does not specify the nature and loopholes in regards to multinational activities. Moreover, it lacks in explaining the success factors of resources based industries and export dependency. Thus, this model needs appropriate modification and careful consideration.
Critical Analysis
As opined by Edirisooriya et al. (2016), with keen eyes to realize a prosperous life in synchronization with natural environment by creating a society with no CO2 emissions within 2050, Toyota industries have formulated their sixth environment action plan. It is a five-year action plan started in the year 2017 and is expected to end by 2021. Toyota Industries have placed immense emphasis on certain policies, which has been discussed in this report. As indicated by Toyota Industries, the focus will be mainly on Sixth Environment Action plan with the aim of promotion of four pillars, which has been stated as ‘Global Environmental Commitment’. The concerning factors adopted by Toyota Industries has been enlisted below:
- Establishment of low carbon emission society
- Establishment of a society based on recycling phenomena
- Reduction of environmental risks and thereby establishing a society in synchronization with nature
- Promotion of environmental management
Establishment of low carbon emission society
With the increasing pollution in the society, the Industries are now focusing on putting an end to this adverse practice of generating excess of CO2 for the lavishing life they are leading on this Earth (Wonglimpiyarat, 2016). The company is strategizing in the development of technologies and products, which can deliver highest intensity of environmental performances. The company is trying to develop their production engineering techniques, which is liable to lower CO2 emission and ensure full utilization of clean energy. The concentration has been put on developing technologies, which can effectively contribute more in energy efficiency. The focal point has been in the development of technologies that supports production of electrical products (Wolfram and Lutsey, 2016). Electrical mechanism implemented in the products of Toyota will run on battery and there will be least or rather no emission of CO2 in the environment and thereby restrict polluting the nature further (Martin et al., 2015). The company has expressed their earnest eager in developing technologies that are weight saving, which can reduce loss of energy largely. Toyota Industries are building technologies for the development of hydrogen society.
The purpose of Global Environmental Commitment is to reduce CO2 emission in activities related to production as well. The company’s center of attention is to introduce technologies, which reduce emission of CO2 gas in production cycle. As opined by Deresky, (2017), the reduction can easily be achieved by enforcing improvement activities on a daily basis. Innovativeness through developing CO2 reducing technologies has been ensured by utilization of sustainable energy. The aim can be attained through controlling other greenhouse gases apart from CO2 and thereby changes can be brought in terms of logistics. CO2 reduction can also be done in product distribution (Karavalakis et al. 2014). Toyota Industry is also expressing their interest in bringing improvements in the transportation efficiently by enhancement of load efficiency and modal shift. It has been observed that the company has been focused on working with 3R design that is reuse, reduce and recycle for using resources effectively. As stated by Okumura and Prokhorov (2016), the industry is urging the users worldwide for reducing the quantity of resource usage through prolongation in life spans. Reduction in the amount of using resources by modularization, standardization and reduction can be effective in meeting the organizational commitment. The industry is focusing on international business through reducing the quantity of using resources by weight reduction and downsizing. The company is promoting reuse of materials and parts worldwide.
Establishment of a society based on recycling phenomena
As opined by Bohnsack et al. (2015), Toyota industry is strategizing their international business through promotional measures to prevent depletion of resources by the process of recovering wastes and utilizing those as needful resources. Various measures have been strategized against sources of emission by improving the yield and by promoting internal reuse. Promotion by effectively utilizing resources in the company’s production activities can be considered as a brainstorming idea for maintenance of creativity in International Business through reduction in the amount of using packaging materials (Jindal et al. 2015). Toyota Industry is also preparing and promoting countermeasures in relevance to water depletion through determined grasping of wasted amount of water and water usage.
Reduction of environmental risks and thereby establishing a society in synchronization with nature
The industry is continuously focusing on minimization in using concerning substance. The company is strategizing to reduce emission of certain gas that improves atmospheric environment of cities and control chemical content in the products. For contributing in reducing environmental risks, Toyota Industry is designing an engine that satisfies the customer expectation depending on future regulations (Dunning, 2015). Sharing bio-diversified strategies every Toyota Group Industries are contributing towards expansion of habitat for living. The industry is also promoting preservation of biodiversity activities within the company.
Promotion of environmental management
The purpose is to promote and strengthen consolidation of environmental management. The company has achieved various things in establishment of organization wide environment management system and promotional activities:
- Abide by with environment related rules and regulations of each region in every country
- Development of a mid-term plan and prevention of risky activities, which are based on visualizing environmental risks
- Expansion of risk communication with community residents and stakeholders
- Achievement of top level performance in each region in every country
As opined by Suh, (2017), the Industry is realizing strategic environmental management through integration of business activities and environmental activities. The industry is focalizing on enhancement of awareness enlightening training and activities for expansion of International Business of Toyota Industries Group. The industry is promoting impressive compliance of rules and improving environmental performance with much stress on ‘Green procurement guidelines’. The company is cooperating along with business partners for promotion of environmental activities (Murray and Ma, 2015). The company is therefore improving brand image by active divulgence of information regarding Toyota Industries Corporation Group’s activities in relevance to environment.
Conclusion
International business theories are much needy and are helpful to know in-depth and perform accordingly for running international business perfectly and effectively. Throughout this report it has been reflected the importance of international business with respect to national economy, exportation and others. The report has focused on Toyota Industries’ proper utilization of natural resources with special adherence to elimination of harmful emissions. This in turn increases the rapid economic expansion and employment opportunities. This enables the multinational enterprise in expanding their international business by facing competition courageously by betterment of quality production having moderate prices.
References
Antimiani, A., Fusacchia, I. and Salvatici, L., 2016. Value Added Trade Restrictiveness Indexes. Measuring Protection with Global Value Chains. In 19th Annual Conference on Global Economic Analysis, Washington DC, USA: Global Trade Analysis Project (GTAP).
Anton, R., 2015. An Integrated Strategy Framework (ISF) for Combining Porter’s 5-Forces, Diamond, PESTEL, and SWOT Analysis.]
Bohnsack, R., Kolk, A. and Pinkse, J., 2015. Catching recurring waves: low-emission vehicles, international policy developments and firm innovation strategies. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 98, pp.71-87.
BORSOS, G., IACOB, C.C. and CALEFARIU, G., 2016. MODERN MANAGEMENT-A NEEDED SOLUTION FOR INCREASING THE COMPETITIVENESS OF INDUSTRIAL COMPANIES. Scientific Research and Education in the Air Force-AFASES, pp.705-714.
Cano-Kollmann, M., Cantwell, J., Hannigan, T.J., Mudambi, R. and Song, J., 2016. Knowledge connectivity: An agenda for innovation research in international business.
Cohn, T.H., 2016. Global political economy: Theory and practice. Routledge.
Deresky, H., 2017. International management: Managing across borders and cultures. Pearson Education India.
Dunn, B., 2015. Neither Free Trade nor Protection: A critical political economy of trade theory and practice. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Dunning, J.H., 2015. Reappraising the eclectic paradigm in an age of alliance capitalism. In The Eclectic Paradigm (pp. 111-142). Palgrave Macmillan, London.
Edirisooriya, A.C., Ekanayake, E.M.A.C. and Rengarasu, T.M., 2016, January. ESTIMATION OF VEHICLE EMISSIONS DUE TO VEHICLE AGE IN SRI LANKA-A CASE STUDY FOR TOYOTA AND NISSAN CARS. In Proceedings of the Undergraduate Research Symposium on Recent Advances in Civil Engineering.
Ezell, S. and Policy, G.I., 2017. ITIF Comments Regarding Cause of Significant Trade Deficits for 2016.
Jindal, S., Laveena, L. and Aggarwal, A., 2015. A comparitive study of crisis management-Toyota v/s General motors. Scholedge International Journal of Management & Development ISSN 2394-3378, 2(6), pp.1-12.
Karavalakis, G., Short, D., Vu, D., Villela, M., Asa-Awuku, A. and Durbin, T.D., 2014. Evaluating the regulated emissions, air toxics, ultrafine particles, and black carbon from SI-PFI and SI-DI vehicles operating on different ethanol and iso-butanol blends. Fuel, 128, pp.410-421.
Martin, R., Florida, R., Pogue, M. and Mellander, C., 2015. Creativity, clusters and the competitive advantage of cities. Competitiveness Review, 25(5), pp.482-496.
Mboya, J. and Kazungu, K., 2015. Determinants of competitive advantage in the textile and apparel industry in Tanzania: The application of Porter’s diamond model. British Journal of Economics, Management & Trade, 7(2), pp.128-147.
Meyer, K. and Peng, M.W., 2016. International business. Cengage Learning.
Mueller, J., 2018. Peace, Prosperity, and Politics. Routledge.
Murray, P. and Ma, S., 2015. The Promise of Lean Experimentation. Stanford Social Innovations Review.
Okumura, B. and Prokhorov, D.V., Toyota Motor Engineering and Manufacturing North America Inc, 2016. Remote operation of autonomous vehicle in unexpected environment. U.S. Patent 9,494,935.
Richter, N.F., Sinkovics, R.R., Ringle, C.M. and Schlaegel, C., 2016. A critical look at the use of SEM in international business research. International Marketing Review, 33(3), pp.376-404.
Rothaermel, F.T., 2015. Strategic management. McGraw-Hill Education.
Samarasinghe, N., Ariadurai, S.A. and Perera, M.E.R., 2015. Facing the Future Challenges of the Sri Lankan Apparel Industry: An Approach based on Porter’s Diamond Model for the Competitive Advantage of Nations.
Suh, Y., 2017. Knowledge Network of Toyota. Annals of Business Administrative Science, 16(2), pp.91-102.
Sultan, S. and Qaimary, D., 2017. Role of Universities in Enhancing the Competitiveness of Palestinian Agribusiness: Applying Porter’s Diamond Model.
Urban, K., Brockmeier, M. and JENSEN, H.G., 2015. Evaluating the effect of domestic support on international trade: a mercantilist trade restrictiveness approach. In 18th Annual Cofenerence on Global Economic Analysis.
Wolfram, P. and Lutsey, N., 2016. Electric vehicles: Literature review of technology costs and carbon emissions. The International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, pp.1-23.
Wonglimpiyarat, J., 2016. Towards the Detroit of Asia: Empirical research insights of Thailand’s OEM strategy. The Journal of High Technology Management Research, 27(1), pp.78-87.
Wynn-Williams, M., 2016. Managing Global Business. Macmillan International Higher Education.
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

