Impacts on Operations and Supplychain Assignment
Assignment Sample on Impacts on Operations and Supplychain Assignment.
Executive Summary
The current report has incorporated the major factors of Industry 4.0 and its impacts within the supply chain management. Furthermore, it has been found to impact sectors of inventory management, retailing, product development and procurement logistics. In addition to that, operations management has highlighted the new human resource competencies and skills required for establishment of Industry 4.0. Moreover, recommendations to improve digital transformation in organisations and proper employee training have been provided within the study.
Introduction
Industry 4.0 is currently referred to as the digital transformation of production and manufacturing procedures related to the value creation processes within the industries. Industry 4.0 has further emerged to retrieve its name from the fourth industrial revolution representing a brand new stage of gaining control over the industrial value chain. Moreover, the current report assesses the impacts of Industry 4.0 on the supply chain management across different organisations along with the operations management with respective industries. Additionally, the factors influencing the organisations along with the people in it through Industry 4.0 shall be focused on the concerned report.
Body
1.1 Industry 4.0’s Influence in supply chain
Industry 4.0 has created disruption within the companies that has further developed in the rethinking of designing the supply chain management. Moreover, incorporation of various technologies has helped in alterations in the traditional working of the supply chains. According to the words of Tjahjono et al. (2017), supply chain has undergone a significant change in operational logistics function highlighting the supply in production lines and delivery towards the customers. In addition to that, the visionary of industry 4.0 is associated with the global networking of machines within a smart factory. As per the opinion of Fatorachian and Kazemi (2021), Industry 4.0 has been significantly associated with the technological advancements on the improvement in the performances of supply change management across different industries. Moreover, the major 4.0 enabled technologies have emerged to be IoT, BDA, cloud technologies and CPSs for the improvement and drivers of Industry 4.0.
The impacts of Industry 4.0 on supply chain processes are further highlighted below,
1.1.1 Product development and production processes
The networked systems and machine-to-machine learning within the industry 4.0 enabled environments can further result in the fully automated production systems and smart factories. Focusing on the Industry 4.0 perspective, it can effectively allow for better analysis of patterns in demand and fluctuations that can effectively improve the planning and control of production processes (Li et al. 2016). Furthermore, the enabling of integration and transparency can further help in the improvement of higher flexibility and rapid implementation of requirements demanded by the customers. In addition to that, the incorporation of Internet of Things and CPSs can help in bringing higher visibility levels and connectivity between supply chain and manufacturing processes through accessing real time information handling and cooperation for allowing responsiveness (Park et al. 2016).
1.1.2 Fulfilment, procurement and logistics
The incorporation of Industry 4.0 enabled applications like IoT and CPSs has further improved the transparency and integration to effective order management. Moreover, the concerned technologies can improve the relationship between the supplier management through focusing on visibility and improved decision making for purchasing decisions and supplier selection (Chung, 2015). The real time information for visibility and accessing the auditing of suppliers can further ensure the compliance with the performance of financial and sustainability priorities.
Therefore, IoT and CPS technologies are significantly important for the embedded intelligence within the products, infrastructure and cities like vehicles or mobiles can prove to be essential in influencing the logistics management. Furthermore, the concerned management shall help in improvement of efficiency and productivity improvements within the supply chain management.
1.1.3 Inventory management
The incorporation of Industry 4.0 has helped in the improvement of inventory management through the association of sensors and RFID tags with the help of cloud based systems in indoor or outdoor GPS enabled systems (Redelberger, 2014). Moreover, it shall help in the development of distribution and inventory management through gaining control over the movements of products within the supply chain. Additionally, products with RFID tags attached can help in smarter and efficient inventory control and management for allowing the proper identification of the destination of the journey (Banker, 2015). The concerned capability can help in the improvement of product distribution and delivery through the advanced controlling mechanisms over the movements of products and further enhancing the sustainability dimensions.
1.1.4 Retailing
Industry 4.0 along with its technological advancements can be effective in the downstream of supply chain processes like retailing of products. Furthermore, the combination of sensors, analytics, and beacons along with the incorporation of technologies like the Internet of Things can help in the performance of smart retailing. For example, the beacons (indoor positioning systems) can remotely connect to the internet and with further integration from analytics and store applications are able to identify or recognise customers (Baxter, 2016). Furthermore, the customer recognition models supported by IoT technologies can further enable employees to send push notifications or text messages towards the customers.
1.2 Influence in operations management of a company by Industry 4.0
Operations management refers to the administration of business practices aimed at the achievement of highest possible efficiency levels being achieved within organisations. Moreover, the concerned management is associated with conversion of labor and materials into services and goods efficiently for the maximisation of organisational profits (Fettermann et al. 2018). Industry 4.0 with the help of their technologies are found to incorporate new capabilities towards their operation managers helping them in responding to critical factors and bringing further improvements in the key performance indicators. Therefore, the introduction of Industry 4.0 is further aimed at minimisation of production costs and maximisation of the production qualities that are depicted below,
1.2.1 Contributions of Industry 4.0 to operations management in cost minimisation
Incorporation of big data analytics technology and automated control through AI controlled robots are helpful in the minimisation of human labor and costs. Furthermore, the zero-people operations are further found to minimise the robots, human costs and production facilities associated with the operation management under threat of failures in certain circumstances. Moreover, words of Dolgui et al. (2018) stated due to the low availability rates of facilities, it shall further lead to the rise of human recovery costs and eventually lead to the increase in total costs of operations. Thus, the countermeasures supported by Industry 4.0 led technologies are depicted in the diagram below,
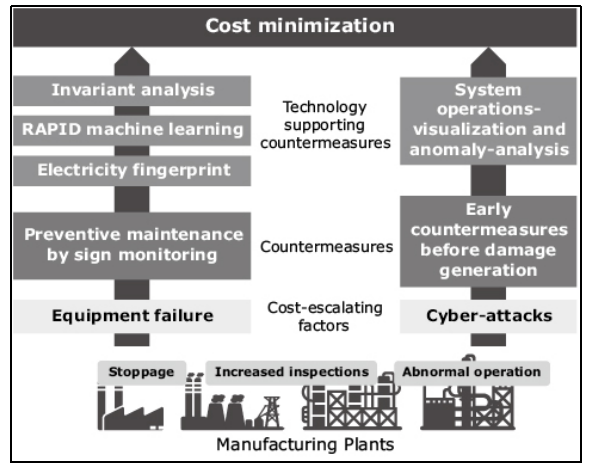
Figure 1: Technological support provided by Industry 4.0 in cost minimisation
(Source: Nec.com, 2021)
The figure depicted above highlights the two major cost escalating factors associated with the increase in costs of operations within a company that are the emergence of cyber attacks and equipment failures. Upon closer analysis, the countermeasures supported by technologies in the minimisation of costs are electrical fingerprints in reduction of additional electricity within the companies and helps in reducing electricity wastage through association of cloud based technology helping firms to analyse the energy usage in real time (Nec.com, 2021).
1.2.2 Operations management for quality maximisation through Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is found to incorporate artificial intelligence technologies in the development of and support of automation of production quality and materials being sourced for production quality management. As per the words of Ceccon et al. (2021), incorporation of smart machine systems shall further facilitate the arrangements of tasks and help in the adjustment of operational parameters highlighting increase in product quality and maximisation in productivity levels. Moreover, the examples of technological advancements supporting the maximisation of quality has emerged to be “RAPID machine learning”, predictive optimisation and production quality management that has been further highlighted in the figure below,
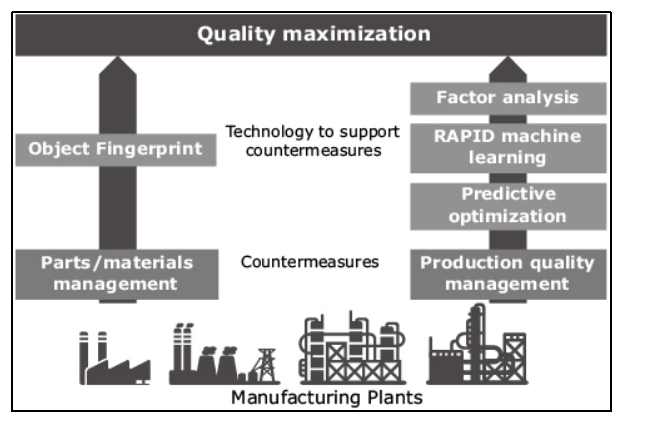
Figure 2: Technological support provided by Industry 4.0 in quality maximisation
(Source: Nec.com, 2021)
The image depicted above highlights the technological supports provided by Industry 4.0 in the maximisation of quality in the operations management of the companies. As per the words of Xia and Zhang (2015), predictive optimisation technology is associated with planning and decision making processes based on the predictions of artificial intelligence levels. Moreover, predictive modelling is conducted through the process of developing machine learning and data mining for prediction and forecasting of existing and historical data. Therefore, the concerned process helps in understanding of the past operations within the company and further aid in the improvement of efficiency levels.
1.2.3 Incorporation of technologies in operations management
For the successful implementation of Industry 4.0 perspective, the companies are further required to to adopt technological innovations (Brettel et al. 2014). The current section hereby focuses on the importance of Industry 4.0 enabling technologies and their functionality and potential impact on the operations management as highlighted below,
Cyber Physical Systems (CPSs)
Cyber Physical Systems are efficient in the enhancement of communication and sharing of information in flexible and seamless operations (Baheti and Gill, 2011). Furthermore, the higher levels of connectivity and application of different systems are helpful in efficient decision making through real-time collection of data from processes, businesses and machine environments. As per the words of Zhong et al. (2015), CPSs are found to be effective medium or drivers of Industry 4.0 allowing real-time acquisition and automatic data receival from different points of operations management leading to optimised decision making procedures. Therefore, the escalations of the aforementioned technology shall further help in improving the product delivery and customer satisfaction levels through increased responsiveness in operations management.
Internet of Things
IoT is found to incorporate specialised capabilities in expansion of the internet in smartphones and traditional computers through the inclusion of sensors and devices covering a vast space of processes and environments. Furthermore, the connected sensors or devices are further utilised to collect and resend the information to cloud based software processes that are useful in the Field Operations management (Koleva and Andreev, 2018). Field workers can essentially connect devices through Internet of Things sensors and gain field data and actionable insights that are guided towards improvement in productivity, profitability and compliances in health and safety measures of business organisations.
Figure 3: Impact of technologies in operations management
(Source: Influenced by Olsen and Tomlin, 2020)
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is also found to be an essential technology in modern operations management as it can be further extended through a range of operations like inventory management, forecasting of data, logistics and supply chain management, risk analysis and different big data approaches like strategies, techniques and architecture (Olsen and Tomlin, 2020). Moreover, big data analytics is also found to be useful in demand forecasting for the organisations through effective incorporation of technological foundation and investments. Therefore, the incorporation of big data has also proved to improve digitisation of the supply chain that has further helped in lean operational practices and overall supply chains of various companies.
1.3 Factors influencing organisations through Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 has emerged to significantly improve the working patterns of business organisations in the 21st century. Utilisation of various technologies ranging from cyber physical systems and big data analytics via the incorporation of Internet of Things, cloud computing and 3D printing has emerged to behave like an umbrella resulting in the unique transformation of the value chain.
Moreover, Industry 4.0 has focused on the integration of warehousing, manufacturing, usage of materials along with supply chain management for both organisations and businesses (Singhal, 2020). Organisational performance has been an important aspect for any organisation whether it is of profitable or non-profitable in nature. Thus, organisational performance is hereby defined as the extent to which organisations can satisfy or fulfill the shareholder’s needs and requirements (Rehman Khan et al. 2021). Therefore, incorporation of Industry 4.0 led technologies like cloud computing and big data analytics is essential in the management and optimisation of manufacturing processes and supply chain management within organisations. Incorporation of the real time data and insights helps the managers in organisations to further attain faster decisions and smarter problem solving techniques about their respective businesses ultimately helping in boost of productivity and efficiency levels of the firms.
Industry 4.0 is therefore found to incorporate various digital technologies that can react quickly to the market changes and help in offering of operational efficiency and personalised products. The major shift in Industry 4.0 are based on the following principles as discussed below,
- Decentralisation– Industry 4.0 helps in the redesigning of autonomous processes and CP elements in deciding autonomously.
- Interoperability– This refers to the process of ability to communicate and focus on the elements of cyber physical systems, robots, and smart products along with third party systems.
- Virtualisation– Improved ability to generate virtual copies of fabric through data collection and modelling of different industrial processes through virtual plant and simulation models.
- Real-time analytics– Industry 4.0 is also effective in collection and analysis of the big data that is essential in the controlling and management of processes facilitating derived processes.
- Service orientation – It provides the abilities to transfer new value generated towards the customers in new and improved services orientation.
1.4 Industry 4.0’s influence on people in companies
Industry 4.0 has also been found to significantly impact the workers in various organisations as they are found to majorly affect their employability levels in the manufacturing sector. Moreover, incorporation of Industry 4.0 has also impacted the challenges and has increased the overall shortage of skilled workers within the different industries. According to the words of Hecklau et al. (2017), has hereby highlighted on the different training programs associated with the management and development of education for the managers, engineers and researchers in the field of digitisation.
Thus, to reduce the negative impacts of Industry 4.0 for the reduction in the employability of the workers, it is essential to drive training programs for educating them with the technological advancements. As per the opinion of Sima et al. (2020), Industry 4.0 has emerged to affect the overall human capital across different industries which can be further developed through incorporation of new human resources skills and competencies. Thus, the current section is focused on highlighting the factors and influences Industry 4.0 has on the employees and workers of the companies.
1.4.1 Impact of Industry 4.0 in Human capital
The implementation of different technologies has further failed to develop the different operational activities for different employees across the organisations. Furthermore, the words of Hecklau et al. (2017) highlight the essential roles in organisations highlighting the HR policy making, training, knowledge management and reward system with proper job designing. In addition to that, the majority of the organisational performances are associated with equipping workforces with efficient up-to-date skills. Moreover, a dire need of substitutions of robot technologies along with automation strategies has further reduced in adaptation to human workers. As per the words of Vrchota et al. (2020), Industry 4.0 is associated with major technological changes in the production sector of business organisations that has impacted on the reduction in employability rates in the labor market. On the contrary, the words of Sivathanu and Pillai (2018) stated that smart human resources 4.0 is a conceptual framework that is tailored for delivering the employees and workers in production processes for further employment generation.
1.4.2 New human resource competencies and skills
The labour market has emerged to change significantly in recent years due to the incorporation of technological advancements within the industrial sectors. However, the emergence and successful rate of Industry 4.0 has been effective within the developed countries due to higher levels of automation (Vrchota et al. 2020). However, on the contrary the concerned effect has reduced the overall employment generation within the countries. Therefore, it has focused on the development of educational profiles maintained by the human resource capital with the assertions of new educational approaches. As per the words of Piwowar-Sulej (2018), Industry 4.0 is also aimed at the improvements or opportunities in connecting billions of people across the web in further development of organisational efficiencies. Therefore, the modification in educational profiles within the workers and employee force is essential in benefitting from technological benefits of Industry 4.0.
The effect of the fourth industrial revolution has highlighted the effect it has on human resources and their employability levels. Moreover, the concerned industrial revolution has unleashed a modern method of alterations and productivity in executions of works.
Recommendations
Therefore, the above analysis has highlighted the different factors impacted by the incorporation of Industry 4.0 and its technologies impacting on the organisations, people, employees and supply chain and operations management. However, the major negative impacts of Industry 4.0 were found to be occurring within the organisations and majorly affecting its employees.
Therefore, the recommendations for various business organisations associated with the incorporation of Industry 4.0 are as follows,
Proper training of employees
Companies should majorly focus on the development and providing proper support towards their employees through a well-grounded education and training sessions on topics highlighting Industry 4.0. Moreover, the demonstrating companies can further associate with the educational institutions for making their employees fit for industry 4.0.
Integration of digital transformation
Digital transformation strategy should be effectively integrated within the company’s strategy in the improvement of Industry 4.0 through the digital transformation of the services offered by the firm.
Stakeholders and value added network chain
Companies should also incorporate and coordinate with the value added chain of networks with their relevant stakeholders. The companies can further implement the external technical standards effectively without missing the development links in value added networks.
Conclusion
The current report has been hereby formulated on the impacts of Industry 4.0 and it has on the supply chain and operations management. Furthermore, the different technologies associated within the development of operations management have emerged to be CPSs, big data analytics, cloud computing technologies and the incorporation of Internet of Things. Furthermore, the report has also highlighted important aspects of Industry 4.0 in the organisational structure that was found to change real time analytics, service orientation and decentralisation of the organisations. Moreover, the recommendations to incorporate employee training in organisations is found to be essential to reduce the unemployment of employees due to Industry 4.0.
Reference List
Baheti, R. and Gill, H., 2011. Cyber-physical systems. The impact of control technology, 12(1), pp.161-166.
Banker, S. 2015. The Smart Factory, Industry 4.0, and Supply Chain Optimization. http://logisticsviewpoints.com/2015/05/14/the-smart-factory-Industry-4-0-andsupply-chain-optimization/
Baxter, A. 2016. Beacon technology targets consumers instore via smartphones. The Australian business review. http://www.theaustralian.com.au/business/the-dealmagazine/beacon-technology-targets-consumers-instore-via-smarthpones/newsstory/2969863cf77caad786c792765a150d2c
Ceccon, W.F., Freire, R.Z., Szejka, A.L. and Junior, O.C., 2021. Intelligent Electric Power Management System for Economic Maximization in a Residential Prosumer Unit. IEEE Access, 9, pp.48713-48731.
Chung, C. 2015. Industry 4.0: Smart Factories Need Smart Supply Chains Longitudes. https://longitudes.ups.com/smart-factories-need-smart-supply-chains/
Dolgui, A., Ivanov, D., Sethi, S. and Sokolov, B., 2018. Control theory applications to operations systems, supply chain management and Industry 4.0 networks. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 51(11), pp.1536-1541.
Fatorachian, H. and Kazemi, H., 2021. Impact of Industry 4.0 on supply chain performance. Production Planning & Control, 32(1), pp.63-81.
Fettermann, D.C., Cavalcante, C.G.S., Almeida, T.D.D. and Tortorella, G.L., 2018. How does Industry 4.0 contribute to operations management?. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 35(4), pp.255-268.
Hecklau, F., Orth, R., Kidschun, F. and Kohl, H., 2017, December. Human resources management: meta-study-analysis of future competences in industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intellectual Capital, Knowledge Management & Organizational Learning (pp. 163-174).
Koleva, N. and Andreev, O., 2018, June. Aspects of Training in the Field of Operations Management with Respect to Industry 4.0. In 2018 International Conference on High Technology for Sustainable Development (HiTech) (pp. 1-3). IEEE.
Li, F., A. Nucciarelli, S. Roden, and G. Graham. 2016. “How smart cities transform operations models: a new research agenda for operations management in the digital economy.” Production Planning & Control 27 (6): 514-528.
Nec.com, (2021). Industrial Operations Supporting Industry 4.0 Available at: https://www.nec.com/en/global/techrep/journal/g16/n01/160107.html [Accessed on: 17/11/2021]
Olsen, T.L. and Tomlin, B., 2020. Industry 4.0: Opportunities and challenges for operations management. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 22(1), pp.113-122.
Park, Sanguk., Sangmin. Park, J. Byun. Sehyun, Prak. 2016. “Design of a masscustomization-based cost-effective Internet of Things sensor system in smart building spaces.” International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 12 (8). doi: 10.1177/1550147716660895.
Piwowar-Sulej, K., 2018. Human resources management in the industrial revolution 4.0: General and polish perspective.
Redelberger, J. 2014. Industry 4.0 im Kontext Logistik – Connected Supply Chains Transformation. Campgemini consulting. https://www.de.capgeminiconsulting.com/blog/digital-transformation-blog/2014/08/Industry-40-im-kontextlogistik-connected-supply-chains.
Rehman Khan, S.A., Yu, Z., Sarwat, S., Godil, D.I., Amin, S. and Shujaat, S., 2021. The role of block chain technology in circular economy practices to improve organisational performance. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, pp.1-18.
Sima, V., Gheorghe, I.G., Subić, J. and Nancu, D., 2020. Influences of the industry 4.0 revolution on the human capital development and consumer behavior: A systematic review. Sustainability, 12(10), p.4035.
Singhal, N. (2020), “An empirical investigation of industry 4.0 preparedness in India”, Vision, Vol. 25, pp. 300-311, 0972262920950066.
Sivathanu, B. and Pillai, R., 2018. Smart HR 4.0–how industry 4.0 is disrupting HR. Human Resource Management International Digest.
Tjahjono, B., Esplugues, C., Ares, E. and Pelaez, G., 2017. What does industry 4.0 mean to supply chain?. Procedia manufacturing, 13, pp.1175-1182.
Vrchota, J., Mařiková, M., Řehoř, P., Rolínek, L. and Toušek, R., 2020. Human resources readiness for industry 4.0. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(1), p.3.
Xia, X. and Zhang, J., 2015. Operation efficiency optimisation modelling and application of model predictive control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2(2), pp.166-172.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

