Individual Portfolio Report Assignment Sample
Title: A Report on Offline-Online consumer Behavior’s in the Vegetarian Food Items Selection
Decision-Making Unit in purchasing and consumption of vegetarian foods
DMU or Decision-Making Unit refers to the group or those individuals who are taking an effective part in the purchase process of vegetarian items. According to Philip Kotler, there are six types of individuals who takes part in the purchase process such as users or the users- those who uses the purchased items, influencers- those who influences the buying process by setting pre-conditioners, buyers- who purchase the items, initiators- those who recognizes a problem and finds a solution, deciders- responsible individual for selecting supplier and gatekeepers- the information giver within decision-making process (Abbas 2020). In this decision-making process of purchasing vegetarian food items, almost all these roles take part, in this context the purchaser develops the role of users, buyers, initiators, and deciders while the marketing individuals develop the roles of influencers and gatekeepers.
In the purchase process of vegetarian food items, the purchase situation involves the following aspects-
Straight rebuy: It refers to the routine purchase of vegetarian food items from an established and trusted supplier without having second thoughts (Alexandrescu et al. 2021). In this regard, generally, the purchaser was happy with the purchased vegan items from the suppliers in terms of quality, quantity, freshness, and pricing strategy.
Modified rebuy: In this purchase process the buyer can involve one or two new components in the purchase process. For instance, milk products like ghee, butter, and curd can be included with the pre-purchased vegetables and fruit items from the same suppliers satisfying the quality.
New buy: In this regard, the new supplier is selected by the consumer as the buyer is not happy with the pre-purchased goods and services in terms of pricing, quality, and quantity (Arafah 2018). Moreover, new purchasers can also be included in this group who are going to make a purchase decision to buy vegan food items for the first time. In this discussion, the purchase behavior of a new purchaser of vegan foods has been taken into account.
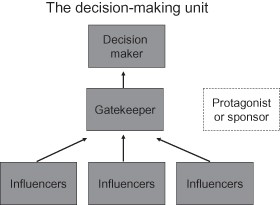
Image 01: DMU and its influential attributes ( Source: imgurl, 2021)
Buyer Persona in purchasing and consumption of vegetarian foods
A buyer persona can be developed for the new purchaser of vegan food items-
| Background
● Name: Ema Jane ● A college student ● From a non-vegetarian family. |
Goals
● Learning or developing the behavior of a vegan diet. ● Being aware regarding the vegetarian food item consumption. ● To eat healthy and fresh foods. |
| Demographics
● Female ● Age- 25 ● Financially dependent on her family income ● Lives in Newport |
Needs
● Information ● Guidance ● identification |
| Hobbies and interest
● Traveling ● Cooking ● Tasting different types of food items. |
Challenges
● Not a vegetarian from childhood or from the community perspectives ● Economical issues. ● Lack of knowledge regarding how to prepare vegan foods. |
| Use of Technology
● Utilize the internet for researching food items. ● She has a smartphone and for fitness activities she uses applications. ● Active social network user. ● Usually buys both from online and offline stores. |
Where the food supplier can win
● Eager to understand and learn the diet changes. ● Taking out vegan options. ● Affordable food items. ● Knowing the food behavior of the target customers. |
| Pain points
● Constantly missed the provided special offers. ● Do not have ideas about how to create a balanced diet with vegetarian foods. ● Do not have much knowledge about brands of vegan food brands. |
Motivations
● Concerned about the animal suffering ● Personal development. ● Motivated by health consciousness.
|
Table 01: Buyer persona for a new buyer of vegan food items (Source: Self-made)
The decision-making process
Identification of the problem: The purchaser has understood the benefits of consuming vegetarian food items (Barrios et al. 2020). But as she is from a non-vegetarian family background she does not have many ideas about vegetarian food brands, food options, and other associated attributes.
Information search: Through the collection of pertinent data and information available in the online sites, the purchaser has searched for the necessary information such as brands, quality, quantity, preparation process, and pricing strategy of different brands. In this regard, she can use the following sources for gathering information.
- Commercial sources: advertisements. sales people, promotional campaigns of the vegetarian food items.
- Personal sources: She can discuss with her friends who are vegetarian in order to achieve recommendations.
- Public sources: Newspapers, social media platforms and magazines
Alternative evaluation: In this stage, the purchaser will search for different alternative brands for evaluating the differences in quantity, brand value and pricing strategy (Beugelsdijk et al. 2018). For example, there are many renowned brands like Beyond Meat, VBites, The Vegetarian Butcher, Vivera and so on. The buyer is financially dependent on family income and from a non-vegetarian family will search for a cheaper option as well as search for a quality food brand by evaluating the reviews, quantity, preparing easiness and pricing structure.
Purchase decision: This is the most important stage, as in this stage, the purchaser will make the purchase decision (Castro et al. 2018). In this stage, after gathering all the information regarding the selected brands, the customer will make a logical decision to select the best option available.
Post-purchase evaluation: In this part, the consumer after consuming the purchased vegan food items will evaluate the purchased food products have met the identified requirements or not, is the customer happy with the vegan food items and if the brand has able to make the connection with the insight of the customer by offering best food options for vegan diet (Chan et al. 2018). In this regard, the customer may not be satisfied with the freshness, quality, quantity and taste of the products.
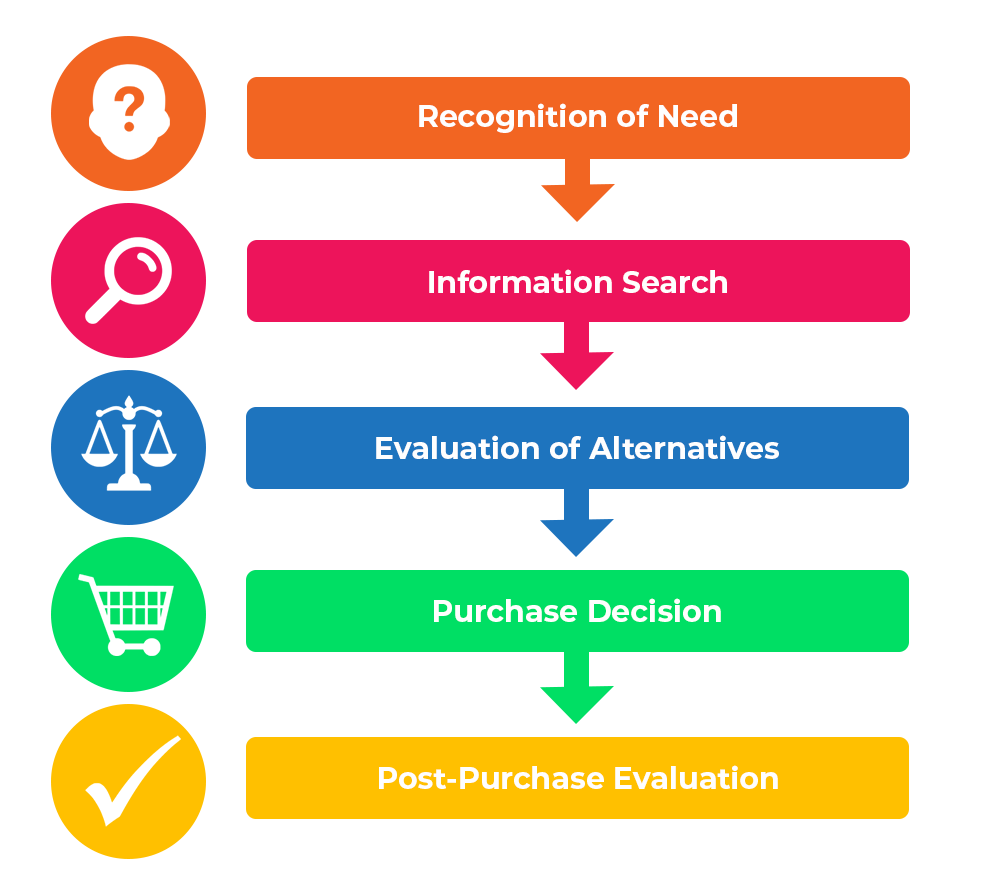
Image 02: Decision-making process of the purchaser. (Source: marketingtutor.net, 2021)
Decision-making models
In this discussion and according to the buyer persona, the following decision-making models can be taken into account.
Economical view model: According to this model, the buyer will take a rational decision by evaluating the benefits, drawbacks, pricing strategy and quantity in respect to the cost. Being a college student and dependent on the family for finance, the purchase will definitely use this model for selecting the best brand.
Passive view model: according to this model, the purchase decision of this customer will be highly influenced by the marketing influences and advertising appeals. However, this may lead this buyer to make an unrealistic decision.
Cognitive view model: As per this model, the purchase decision-making process of the vegan food buyers is highly dependent on the evaluation of if the products are meeting other needs. For example, here the customer will evaluate if the chosen vegan products will help her in self-development, being in shape and healthy lifestyle or not.
Emotional view model: In this regard, the purchaser will evaluate the purchase decision being emotional. As stated earlier, this college student has been influenced by animal suffering and thus has made a mind to purchase vegan food products.
Schiffman and Kanuk’s model: According to this model, the decision-making process of a consumer is highly dependent on the influence of external environmental factors (Dianto et al. 2020). These influences can involve the marketing mix elements of the supplier and information sources and the information sources from the friends, peers and neighbors. In this context, the decision-making process of the purchaser can be influenced by the reviews of the college peers, social class, cultural norms, religious beliefs, and social media posts by the marketers.
Influence of reference group
Types of reference groups
Reference group refers to those individuals that are associated with a particular customer. In this case, the reference group of the new purchaser can include college friends, clubs, religious groups and social media friends (Dimitrov 2018). As the negative influencer, the family member can prevent the purchaser from purchasing the vegan food items. However, the reference group in this aspect has endorsed the vegan food items either through active utilization or through developing statements about different vegan brands. Here the marketers will evaluate if the taste and preferences match with the available vegan food options or not.
In this regard, the reference groups can be formal or informal. Informal reference groups in this aspect can include school friends, college peers while associations, club friends, social media friends and religious organizations and website reviewers will act as formal reference groups. Celebrities may also act as reference groups as the vegan lifestyle of a particular celebrity can influence the purchase decision.
Influence from the following types of reference group
Informal groups: The informal groups will make the purchaser comfortable with the provision of the feeling that they are connected to the purchaser in the food preferences while the purchaser will feel confused with the vegan brands and food options available (Foschi et al. 2020). These informal groups usually provide clear and honest advice to a purchaser due to which the purchaser will feel confident in the purchase decision made.
Formal groups: Formal groups generally will speak less or might be professional associates. In this regard, the influence power of the formal groups is quite less as compared to the power of primary groups (Fu et al. 2020). The friends from the clubs, social media or religious associates may nor feel comfortable sharing their personal thoughts about the vegan food options as this may lead to a chance of dispute or favor situation.
Aspirational group: Aspirational group refers to those individuals that the purchaser wants to become a part of. In this regard, according to the buyer’s persona, the new purchaser wants to become a part of a healthy and developed personality group by making a healthy diet with vegan food products. Also, the purchaser has a concern regarding the animal suffering and by making a vegan lifestyle she wants to be a part of the vegetarian community.
Dissociative group: The individuals from this group generally are opposed to the aspirational group (Giyazova et al. 2021). Generally, the purchaser will feel to be disconnected from these groups in terms of food behavior. In this context, the relatives and family members can be considered as a dissociative group as the purchaser wants to disconnect herself from her family preferences in terms of food choices and has decided to consume vegan food options. In this regard, the family members can negatively influence the purchase decision of this purchaser to buy vegan food options.
Influence of lifestyle
Self-image and looking glass self: It is observed that the social identity of an individual often depends on his /her appearance. A person can not develop social identity unless others react to their appearance (Gnizy 2019). Here, the buyer wants to be socially and environmentally responsible. It is proven that the buying behavior of a person is directly influenced by the unique individual images that the person wants to conquer. As a result, the buyer is switching to vegan. Here, the self-congruity of the girl student plays a huge role in her decision of being vegan. The buyer generally chooses the products which are similar to their self-image. The buyer is influenced to purchase the products which are seen positively in society. For maintaining a positive self-identity this is essential.
Possible self: It is well established that vegetarian foods have more health benefits compared to non-vegetarian foods. The buyer is a college student and thus she intends to maintain her body for a long time. Vegetarian foods substantially reduce fats (Goncharova et al. 2019). She also intends to make a career that requires being fit and healthy. Being vegan, it became easier to stay lighter because fiber volume in the body is greatly pumped up by vegetarian foods. Moreover, as the buyer is now in college, for academic excellence she wants her brain to be very active and sharp. Researchers have found that vegetarian foods properly supply the energy needed for our brain and body. Because these foods are full of carbohydrates. Non-vegetarian foods emit enormous amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. By turning vegetarian, the buyer also satisfies the perspective of being environmentally responsible.
Psychological factors: Human psychology or self factors is a major attribute of customer behavior. These factors are generally not easily recognized but have enough potential to determine a purchase decision (Guo et al. 2019). As the new purchaser is a college student and has a concern about her health, well-being, outlooks, and concern about animal sufferings. These factors will influence the purchase decision of vegan food items. Moreover, the purchaser will search for an affordable brand so that she can purchase different vegetarian food products within a lower budget.
Self-motivators: The identified motivators, in this case, are health consciousness, personal growth by keeping the body shape and attractive and the consciousness regarding the animal sufferings (Halim et al. 2019). In the purchase decision, the purchaser may apply Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory to evaluate if the product has met the basic needs like hunger, food safety, self-development, and self-estimation needs or not.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs:
This psychological model consists of five tiers. This theory perfectly explains all the needs a human wants in their life. All the five levels are as follows-
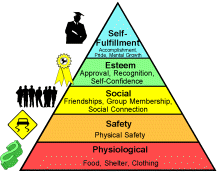
Image 03: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in customer purchase decision (shortpixel. Net, 2021)
- Basic needs: From the above context, it can be said that the basic need is food. If a human does not get the right amount of nutrition from the purchased vegan items, then he/she will not purchase similar food products again (Hunt 2018). A sufficient amount of as well as a large variety of vegetarian food is available in the market. Here, by switching to vegan, their basic needs of her will be satisfied well.
- Safety needs: Vegetarian foods are totally safe for consumption (Katsikeas et al. 2019). To make it more clear nowadays, organic farming is becoming more and more popular in the agricultural industry. The vegetables grown by organic technique have no pesticides, chemicals in them. So, the buyer can get sage vegetarian foods easily.
- Belongingness needs: This level depicts how one’s behavior is influenced by the surrounding people’s feelings and characteristics. As most of the friends of the buyer have already turned vegan or are intending to do so, this makes a great impact on the buyer’s decisions.
- Esteem needs: An adult human being can get full nutritional benefits from a vegetarian diet. The vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals. Rice, pasta, and bread are full of carbohydrate components and pulses. Pulses and beans are great sources of proteins.
- Self-actualization needs: This is the level where an individual finally experiences the positive sides of being vegetarian. The buyer experiences personal growth and self-fulfillment.
Lifestyle influence: Lifestyle is usually the attitude or the way of living that the purchaser develops from a community or society he/she belongs to. The purchase behavior of this new buyer is influenced by the college friends and club friends by observing their healthy lifestyle with the vegetable food options. In this aspect, as the buyer loves to taste different types of foods, she will definitely find vegan food options for replacing the huge range of non-vegetarian food options.
Consumer identity
To successfully expand the offline as well as online business ventures, it is crucial to target the viable group of customers and their individual consumption patterns. The necessity to understand the patterns of customer consumption helps to keep the organizations aligned with their choices and demands (Poirier et al. 2019). Consumer identity stands to be a bit differentiated from customer targeting since the patterns and trends are described by the consumers themselves. In the case of customer targeting, the organizations undertake an extensive survey to understand the choice patterns and demands offered by the audience or buyers which is often misrepresented at certain times. Consumers have the opportunity to explain their expectations and put forward their pattern of consumption which flows beyond mere satisfaction. Consumer identity has been undergoing a gradual changeover in the recent past since the buyers are no longer restricted to consuming goods and services for functional satisfaction. The concept of self-identity and consumer identity has taken a sharp turn to situational demand, brand awareness, product-centric and symbolic based to keep alignment with the continual maintenance of the identity.
The concept of consumer identity has also been influencing consumer behavior trends, which tend to offer an extensive range of opportunities to organizations, both offline as well as online. The purchase behavior within the global consumer forum is usually interlinked with personal identity and image as well (v 2018). The trend of vegetarianism has been gaining popularity across the globe, presenting the wide potential to involve offline as well online business patterns related to vegan or vegetarian food items. Often the idea of shifting towards vegetarianism due to various underlying factors of ailment, health, fitness, fashion, and the general social trend is observed across the world. The idea of vegetarianism encompasses a variety of alternative food items, choices, and food mannerisms which pose to be unique from the regular nonvegetarian or meat consumers. The typical dairy processing and meat products are excluded from the menu list of the vegetarians, providing basic alternatives for the same. Global surveys have looked into the presence of two main categories of vegetarians, one is by recent choice and the other category based on necessity.
The consumer identity and its influence on consumer behavior can be broadly identified into a few elements and their respective impacts on purchasing vegetarian food, either offline or online.
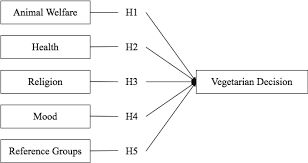
Image 04: Conceptual model of vegetarian decision making (researchgate.net, 2022)
The motivational inspirations which have been influencing the global population to shift to vegetarianism can be used as vital elements in identifying the customer trend and their identity. As observed from the conceptual model of consumer behavior and decision-making choices, five main motivational output or self-imagery ideas.
Age: In this regard, Age will have a greater influence on the purchase behavior of the new buyer. As the individual is from a youth population, she will have a greater purchasing influence from the inside (Soegoto et al. 2019). In this regard, the purchaser will search for different types of tasty and easy-to-cook vegetarian food options.
Income: Income has a greater influence in the purchase decision. As the new purchaser has no independent income, she will not have a higher purchasing power and will search for cheap and best vegetarian food options.
Family influence:
As family plays a big part in anyone’s life. The buying behavior is also significantly influenced by family. If other family members are accustomed to consuming a particular kind of product, then the buyer is also forced to consume that. As the family of the buyer is totally non-vegetarian, they at first deprived the buyer to be vegetarian. This acted as a negative influence on the buyer. But, after seeing the buyer’s clarity and in mind about vegetarians, they finally accepted her decision.
Animal welfare belief:
The buyer here is an animal lover. She feels a deep connection with all animals. But after seeing how the animals are being treated in firms across Britain, she changed her mind to be vegan. The animals are being brutally slaughtered in meat processing plants (Ștefan et al. 2020). The buyer was greatly disturbed after seeing these things. So, she deduced not to be part of this cruelty and inhumanity. The buyer believes that the animals also have the equitability to live without pain. The animals are kept in very unhygienic situations and they do not even get the primary medical treatment. She also wants to make sure that due to humans’ greed, the animals should no longer suffer. Thus, this factor will influence her to make vegetarian food products.
Influence of Paid influencers
Marketers
Now, the customers are very well aware of the effects of the foods they are consuming. They are becoming more health-conscious. As a result, they are constantly looking for better options. People are searching for more plant-based, natural alternatives for food values.
In this context, the vegetarian food market gets the advantage. This market is growing rapidly. In 2020, this market was estimated to be around one billion pounds. So, to acquire a lions’ percentage in this very lucrative market, all the vegetarian food retailers like Alpro, beyond meat are investing huge amounts of money in promoting vegetarian foods in the U.K. They are emphasizing the adverse effects of non-vegetarian food items on nature. They also give the maximum priority to the health benefits of vegetarian foods in their marketing strategy (Tucker et al. 2019). Here, marketers play a huge role. The marketers are advertising vegetarian foods in the mainstream grocers in different parts of the country. Now, several clubs, as well as discount chains, also sell vegetarian foods. Marketers are also approaching restaurants, food manufacturers to sell organic vegetarian food products. As a result, in the last few years, the U.K has seen a sharp jump in the number of vegetarian people.
Paid celebrities
Everyone has an idol in their lives. Most of the time the idols are celebrities, actors, sportsmen, etc. In this case, vegetarian companies are taking help from celebrities. In this digital age, most of the target customers are on any of social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, etc. They share about their vegan diet and also show the positive results of being vegetarian. People follow these celebrities in real life (Vieira et al. 2019). They speak about the pain animals faced during slaughtering. All these things change the mentality of customers. As a result, it also helps to convert non-vegetarian people into vegetarians. So, these paid celebrities promote the products of specific brands on these sites. This gives a real boost to the sale of those products.
Influence of culture on online customer behavior according to Hofstede’s cultural dimension theory
Hofstede’s theory is very effective in understanding the cultural differences across a country. It also helps any company how to do business considering different cultures. The power index in the U.K is quite low compared to the rest of Europe. This suggests that organizational structure is encouraged here. People also support power distribution.
According to the model human behavior is greatly regulated by the culture which acts as a powerful force. Marketing researchers consider culture as one of the most crucial underlying factors of customers’ behavior.
For making a business successful on the global stage, it is very important to connect with the consumers. Culture makes this bridge between the company and the customers. Nowadays, online shopping has become an international marketing trend. Online customers can check a variety of products in just a few seconds (Yunus et al. 2019). Vegetarian food retailers are giving more priority to their online segment of sales. People in the U.K are generally thought of long-term effects. They prioritize the future and ignore short-term gratification for achieving those future goals. As people are steadily realizing the adverse health effects of consuming red meat and other non-vegetarian items, there will be an impact on consumers’ behavior.
Besides social, psychological, and personal factors, cultural factors make the maximum impact in consumer behavior. A basic desire to buy something is often formed by culture. Due to the comprehensive character of culture, every part of it fits together logically. During the marketing of any product, a subculture has to be considered. Subculture is very essential for thorough market analysis. It gives an extra edge to focus on natural as well as sizable market segments. The beliefs, customs as well as values of the customers should be well determined for a total understanding of the customer behavior. Generally, British people are in large communities. The main characteristic of them is that they exhibit distinct ethnic proclivities. The impact of cultural values on consumer buying behaviors is greatly incited by the Hofstede model. Purchasing behaviors are significantly influenced by demographic variables like purchasing power, geographic regions, etc. As most of the Britishers are well educated and well established, the company can ask for high prices for better products. Various goods and services appeal to distinct income groups. In this case, cultural value also plays an important role as it comes out as a deciding factor while purchasing any products or availing of any services.
An individual who came from a particular community has a different set of ideologies. As a result, his/her online buying behavior is also greatly influenced by the cultural value which relates him/her to that specific community (Sharma et al. 2020). Every country has a unique social class. Not only income determines this social class. Family background, residence location, most importantly his/her educational background all make effects on social class. If a consumer’s social class restricts him/her from buying a particular product, then that product can get serious backlashes in sales. In the case of online marketing, the importance of cultural values gets more enhanced as it increases the capability of product positioning.
Influence of culture on offline customer behavior
Hofstede highlights individualism as well as collectivism in his model. Researchers often use this dimension to accurately measure how cultural values impact consumer buying behavior.
In the U.K, collectivism predominates over individualism. As a result, they always give more priority to the goals of the groups. Thus, one individual’s self-esteem is supported by others. As a result, the buyer’s buying behaviors also makes an influence on others’ purchasing behavior. The cultural values are transferred from one generation to the next generation. Thus, these values remain the same over a long period. Because of this, the choices the consumers make every day regarding their buying a product to major purchase are greatly determined by cultural values. One person’s cultural values are influenced by societal culture, subculture as well as familial culture. An individual has to face both the benefits and restrictions of these cultural values. As a result, from the beginning of life, his/her purchasing decisions get influenced by culture.
Hofstede also mentioned masculinity versus femininity. As people of the U.K are generally tougher, they often focus on material achievement as well as wealth-building. The negative impact of the products they are consuming often gets neglected. Consumer innovativeness, complaint behavior as well as impulse buying all are influenced by cultural values to a great extent. While purchasing any product, customers keep in mind brand, price, innovation, and quality. Before finalizing the purchase of any product, customers forecast the positive and negative outcomes of the purchase. Finally, the customers make decisions that are best suitable for the specific customers at that time (Salehi 2018). Consumers are not only an asset for a company, it is the main thing that brings success for the company in the market. In culture, the values and beliefs are the mental images of a customer. Customers’ attitude is directly affected by these values. Thus, these values make a deep impact on the choices of a customer in buying something. Cultural values are directly linked to the social norms and intentions of the customers.
Religious factors also have a huge role in consumer buying behavior. As most of the British people follow Christianity, they prefer non-vegetarian foods over vegetarian foods. They have grown up with the mentality that non-veg food can only give sufficient nutrients. Thus, it prevents the sale of vegetarian foods. Family is also a part of the cultural values of a customer. Companies also need to consider the family status of their target audience as it business strategy is significantly impacted by this.
Local areas are often represented by personal culture. If several customers have similar core values and personalities, then this makes a positive impact on offline customer behavior. Researchers have said that the brand preference of a customer is also influenced by cultural values. The interesting thing is that marketers do have not any power to control these factors. This shows the importance of cultural values in offline customer behavior. As a result, Firms and companies closely see customers buying behavior in offline stores and then make marketing plans for increasing sales. This also pushes the companies to develop new products. A company can get successful when it effectively overcomes these cultural boundaries. In this way, they have to make considerations about the various traditional beliefs, habits as well as preferences.
Practical recommendations for a company that wishes to enter the sector of producing and selling vegetarian products in the market
Experts in the food market field have predicted that the global vegan market will grow at a whopping 10.5 percent per year and become nearly 31.4 billion U.S dollars within 2026. As a result, there is massive space for new companies in this market.
Marketing strategy
The company needs to have a proper marketing plan before investing its capital in this market. With the help of a true marketing strategy, the company will have a clear idea about the particular group of segments that it wants to target.
The company has to spend a large amount of money on digital marketing. They can hire celebrities to market their products on digital platforms. In this case, the company needs to be very careful in choosing the right person for advertising their products. The celebrity should also follow vegetarianism in real life (Poirier et al. 2018). Moreover, the company needs to make its promotional activity in a way that will create awareness about the harmful effects of meat consumption on the environment as well as human beings. According to several scientific journals, vegetarian people live 5 years longer on average compared to non-vegetarian people. All these can attract more people to convert to vegetarianism. The requirements of the customers are changing regularly. So, the company must have an efficient marketing team that will make a close eye on the changing trend. Thus, the company can incorporate new products.
Conduction of surveys
The company also needs to conduct thorough market research to find out about the customer’s needs. In this way, the company can gain a competitive advantage over its competitors. It is the least expensive method to predict the market situation. These types of surveys include a large number of customers. The company will have to be precise about the requirements of the consumers in that particular geographic region. This can be done only for a short period. Then, the company can decide which marketing plan and product will be best suitable for that specific demography. With the advancement in technology, these surveys nowadays become easier through the internet. The company can distribute the questions about acceptance of veganism and the quality of the products they want to a very large customer base. In this way, surveys also significantly help a company to scale up its business both domestically and globally.
Strong supply chain
In the food sector, the supply chain has a huge contribution to any company’s success. Furthermore, the company should endorse its products by showing the health benefits of their products. The company should include all the safety protocols that the company maintains to start from procuring the raw materials to the manufacturing plant and in the final products in the promotional activities (Olson et al. 2018). Now the customers not only want their food to be safe but also want that the products are sourced responsibly. In this case, the company should make its supply chain transparent to the customers. The company should focus on making a diverse supply chain in which the company does not need to rely on a particular vendor for raw material.
References
Alexandrescu, M.B. and Milandru, M., 2018. Promotion as a form of Communication of the Marketing Strategy. Land Forces Academy Review, 23(4), pp.268-274.
Arafah, W., 2018. Marketing strategy for renewable energy development in Indonesia context today.
Barrios, E., Gemmill-Herren, B., Bicksler, A., Siliprandi, E., Brathwaite, R., Moller, S., Batello, C. and Tittonell, P., 2020. The 10 Elements of Agroecology: enabling transitions towards sustainable agriculture and food systems through visual narratives. Ecosystems and People, 16(1), pp.230-247.
Beugelsdijk, S. and Welzel, C., 2018. Dimensions and dynamics of national culture: Synthesizing Hofstede with Inglehart. Journal of cross-cultural psychology, 49(10), pp.1469-1505.
Bissessar, C., 2018. An application of Hofstede’s cultural dimension among female educational leaders. Education sciences, 8(2), p.77.
Bondarenko, V.A., Efremenko, I.N. and Larionov, V.A., 2019. Marketing strategy for hotel and tourist complex companies.
Castro, I.A., Majmundar, A., Williams, C.B. and Baquero, B., 2018. Customer purchase intentions and choice in food retail environments: a scoping review. International journal of environmental research and public health, 15(11), p.2493.
Chan, A. and Raharja, S.U.J., 2018. Marketing strategy of a creative industry company in Bandung City. Review of Integrative Business and Economics Research, 7, pp.232-240.
Cornish, A.R., Briley, D., Wilson, B.J., Raubenheimer, D., Schlosberg, D. and McGreevy, P.D., 2020. The price of good welfare: Does informing consumers about what on-package labels mean for animal welfare influence their purchase intentions?. Appetite, 148, p.104577.
Dianto, E., Anwar, S., Husnawati, H. and Zurnalis, Z., 2020. BNI Marketing Strategy for Credit Cards in Dealing Global Competition in State Bank Indonesia (Persero) Tbk Banda Aceh Branch Office. Budapest International Research and Critics Institute-Journal (BIRCI-Journal), pp.1134-1146.
Dimitrov, K., 2018. Geert Hofstede et al’s set of national cultural dimensions-popularity and criticisms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.02621.
Fleșeriu, C., Cosma, S.A. and Bocăneț, V., 2020. Values and planned behaviour of the romanian organic food consumer. Sustainability, 12(5), p.1722.
Foschi, E., Zanni, S. and Bonoli, A., 2020. Combining eco-design and lca as decision-making process to prevent plastics in packaging application. Sustainability, 12(22), p.9738.
Fu, H., Manogaran, G., Wu, K., Cao, M., Jiang, S. and Yang, A., 2020. Intelligent decision-making of online shopping behavior based on internet of things. International Journal of Information Management, 50, pp.515-525.
Gallego-Álvarez, I. and Pucheta-Martínez, M.C., 2021. Hofstede’s cultural dimensions and R&D intensity as an innovation strategy: a view from different institutional contexts. Eurasian Business Review, 11(2), pp.191-220.
Giyazova, N.B. and Davlatov, S.S., 2021, June. The relevance of a small business marketing strategy. In E-Conference Globe (pp. 4-6).
Gnizy, I., 2019. The role of inter-firm dispersion of international marketing capabilities in marketing strategy and business outcomes. Journal of Business Research, 105, pp.214-226.
Godfray, H.C.J., Aveyard, P., Garnett, T., Hall, J.W., Key, T.J., Lorimer, J., Pierrehumbert, R.T., Scarborough, P., Springmann, M. and Jebb, S.A., 2018. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science, 361(6399).
Gómez-Luciano, C.A., de Aguiar, L.K., Vriesekoop, F. and Urbano, B., 2019. Consumers’ willingness to purchase three alternatives to meat proteins in the United Kingdom, Spain, Brazil and the Dominican Republic. Food quality and preference, 78, p.103732.
Goncharova, N.A., Solosichenko, T.Z. and Merzlyakova, N.V., 2019. Brand platform as an element of a company marketing strategy. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(4), p.815.
Guo, J., Weng, D., Zhang, Z., Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Wang, Y. and Duh, H.B.L., 2019, October. Mixed reality office system based on maslow’s hierarchy of needs: Towards the long-term immersion in virtual environments. In 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR) (pp. 224-235). IEEE.
Halim, K.K. and Halim, S., 2019. Business Intelligence for Designing Restaurant Marketing Strategy: A Case Study. Procedia Computer Science, 161, pp.615-622.
Hopper, E., 2020. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Explained. ThoughtCo, ThoughtCo, 24.
Huang, S.S. and Crotts, J., 2019. Relationships between Hofstede’s cultural dimensions and tourist satisfaction: A cross-country cross-sample examination. Tourism management, 72, pp.232-241.
Hunt, S.D., 2018. Advancing marketing strategy in the marketing discipline and beyond: From promise, to neglect, to prominence, to fragment (to promise?). Journal of Marketing Management, 34(1-2), pp.16-51.
Iskandar, M.S. and Komara, D., 2018, August. Application marketing strategy search engine optimization (SEO). In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 407, No. 1, p. 012011). IOP Publishing.
Katsikeas, C., Leonidou, L. and Zeriti, A., 2019. Revisiting international marketing strategy in a digital era: Opportunities, challenges, and research directions. International Marketing Review.
Maldynova, A., Osmanov, Z. and Galiyev, D., 2018. Formation of marketing strategy for promoting an innovative product. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences, 13(7), pp.1951-1958.
Minkov, M., Dutt, P., Schachner, M., Jandosova, J., Khassenbekov, Y., Morales, O. and Blagoev, V., 2019. What would people do with their money if they were rich? A search for Hofstede dimensions across 52 countries. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management.
Morgan, N.A., Whitler, K.A., Feng, H. and Chari, S., 2019. Research in marketing strategy. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47(1), pp.4-29.
OBETA, U., OBI, M., GOYIN, L. and OJO, J., Abraham Maslow‟ s Hierarchy of Needs Dynamics in the Administration of Public Organizations under the President Buhari‟ s Democratic Dispensation in Nigerian Health Sector.
Olson, E.M., Slater, S.F., Hult, G.T.M. and Olson, K.M., 2018. The application of human resource management policies within the marketing organization: The impact on business and marketing strategy implementation. Industrial Marketing Management, 69, pp.62-73.
Pirlog, A., 2021. National Cultural Profile in the Republic of Moldova According Hofstede and Trompenaars-Hampden-Turner Models. Revista de Management Comparat International, 22(4), pp.450-457.
Poirier, T.I. and Devraj, R., 2019. Pharmacy in an improved health care delivery model using Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. American journal of pharmaceutical education, 83(8).
Rasheed, E., Yu, J., Hale, S., Booth, N. and Shahzad, W., 2019, August. Explaining the factors’ influencing young females’ interest in the construction industry using Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. In West Africa Built Environment Research (WABER) Conference (pp. 5-7).
Ryan, B.J., Coppola, D., Canyon, D.V., Brickhouse, M. and Swienton, R., 2020. COVID-19 community stabilization and sustainability framework: an integration of the Maslow hierarchy of needs and social determinants of health. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness, 14(5), pp.623-629.
Salehi, G., 2018. Exploring ethical purchase decision-making toward vegan food products (Doctoral dissertation, Master dissertation, Comillas Pontifical University).
Sent, E.M. and Kroese, A.L., 2020. Commemorating Geert Hofstede, a pioneer in the study of culture and institutions. Journal of Institutional Economics, pp.1-13.
Sharma, R., Kamble, S.S., Gunasekaran, A., Kumar, V. and Kumar, A., 2020. A systematic literature review on machine learning applications for sustainable agriculture supply chain performance. Computers & Operations Research, 119, p.104926.
Shi, F., Ning, H. and Dhelim, S., 2021. A Tutorial of Cyber-Syndrome viewed from Cyber-Physical-Social-Thinking Space and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.02775.
Śmiglak-Krajewska, M., Wojciechowska-Solis, J. and Viti, D., 2020. Consumers’ purchasing intentions on the legume market as evidence of sustainable behaviour. Agriculture, 10(10), p.424.
Soegoto, E.S. and Utomo, A.T., 2019, November. Marketing Strategy Through Social Media. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 662, No. 3, p. 032040). IOP Publishing.
Ștefan, S.C., Popa, Ș.C. and Albu, C.F., 2020. Implications of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory on healthcare employees’ performance. Transylvanian Review of Administrative Sciences, 16(59), pp.124-143.
Thomas, C., Grémy-Gros, C., Perrin, A., Symoneaux, R. and Maître, I., 2020. Implementing LCA early in food innovation processes: Study on spirulina-based food products. Journal of Cleaner Production, 268, p.121793.
Tucker, J. and Au, A., 2019. Reframing the marketing strategy for online education. International Journal of Information, Business and Management, 11(3), pp.176-186.
Vieira, V.A., de Almeida, M.I.S., Agnihotri, R., da Silva, N.S.D.A.C. and Arunachalam, S., 2019. In pursuit of an effective B2B digital marketing strategy in an emerging market. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47(6), pp.1085-1108.
Wang, C.N., Tsai, H.T., Nguyen, V.T., Nguyen, V.T. and Huang, Y.F., 2020. A hybrid fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and the technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution supplier evaluation and selection in the food processing industry. Symmetry, 12(2), p.211.
Yunus, E., Susilo, D., Riyadi, S., Indrasari, M. and Putranto, T.D., 2019. The effectiveness marketing strategy for ride-sharing transportation: Intersecting social media, technology, and innovation. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 7(2), p.1424.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

