KF7032 BigData and Cloud Computing Assignment Sample
Introduction
This project report contains two programming parts and two report parts. Training task 1 contains the programming part and outcomes of reducing traffic accidents and the Implementation section contains the program codes and outcomes of violent crime in Britain using big data. The other two report parts contain the literature review on violent crimes and big data and big data approach to analyze violent crime respectively.
Training Task 1
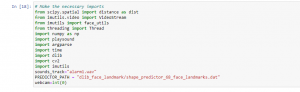
Figure 1: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
The above code describes the process of making a prediction model to reduce traffic accidents.
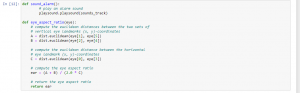
Figure 2: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
The figure contains the evidence of a program code. The above code has been used to make a model that reduces traffic accidents.
Figure 3: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
The above figure describes the program codes to reduce make traffic accidents.
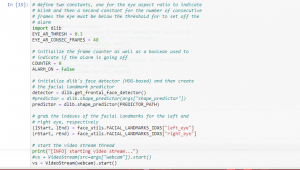
Figure 4: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
Task 2: Crime and Big Data
Literature Review
According to Ageed et al. 2021, databases, technology, and analyses are the top recommendations to assist government administration agencies in maintaining peace and security. The technique of anticipating murders before they occur is known as ‘police discretion.’ This is really not concerning comprehending the proper people as it is towards catching criminals (Aceto et al. 2020). To maintain law and order that in this time technology, they require armaments of a new type. Hundreds of European towns, including Southern California, Columbia, Augusta, Savannah, Olympia, and Santa Cruz, are adopting Redpoll statistics tools to combat criminality (Ageed et al. 2021). This technique is predicated on the assumption that people are difficult to suppress. Individuals tend to keep to habits and inclinations, no despite what situation to reject it.
According to him to put it simply, data have been acquired from documentary evidence, online networks, and other types of statistics, and technologies are utilized to evaluate the likelihood of the crime based on geography position, approximately time, demography and appropriate intervention is being followed. Obviously, it is impossible to specify the precise day, location, location, or perpetrator of the projected criminality, but it does provide security personnel with an understanding of violence clusters so that authorities should intervene as fast as necessary and avert tragedies (Ali et al. 2021). It all comes down to this at the correct place moment. Prior to actually evaluating the data, the depending on which part, environment, financial environment, time and a variety of other criteria are entered.
The massive quantity of information collected every day renders it greater challenging to go throughout, which is where Big Data gets in. Advanced Insights can assist anticipate the same kind of offences that may occur in a particular location at any given moment. Perhaps robberies will be more widespread in a specific neighborhood at a specific time frame? This activates the enforcement pressure to keep an eye down for other incidents. Despite the fact that individual criminal analyzers have an edge in terms of judgment, this method has shown to be more successful (Gill et al. 2018). Big Data has indeed been utilized to help in police prosecutions and to deliver punishment when necessary.
According to Li et al. 2017, weapons are a typical attachment in homicides, and the globe is seeing an upsurge in firearm ownership, particularly in the United States. It only creates more reason to trace these capable of mass devastation in order to apprehend the culprits. It is now feasible to track the weaponry or cartridge recovered at the homicide place in order to learn enough about its production, employment, and registration, which can help with the investigations (Li et al. 2017). Weapons have essentially become a type of money for cybercriminals, with supplies flowing between frontiers. Checking up on the behavior would result in the crooks in. Technologies must have made it feasible to track sexual offences such as trafficking, attacks, and pedophilia. Without a method, it’s difficult to keep sight of them. Lacking statistics, police find it difficult to make judgments from the enormous quantity of resources. Intelligence provides it easy to track perpetrators, discover links that might otherwise go unreported, and improve coordination throughout several organizations (Hosseinian et al. 2018). As an outcome, the majority of instances obtaining addressed and persons being saved has increased.
The author has also said that to capture a crime, behave like something of a crook. Perpetrators are inventing new people committing offences, but they have bright new weapons in the shape of technologies to battle them. It should be anticipated that everything just will receive brighter as technology advances. Combining Big Data Analysis with police discretion is the approach to go since it has produced tangible beneficial benefits (Han et al. 2019). It really is a good idea to go into combat with their best armor and armament in order to shift the situation in their favor.
According to Saiki et al. 2018, in certain areas, communication, specifically encryption texting, is regarded as a barrier to combating such instances. But, might technology genuinely help cops anticipate prospective offences and interfere already when they happen? Actionable insights, cognition, Big Data, Intelligent Systems, and selected online networks characterization all motivated us to participate in this approach, according to our findings. Technologies including PredPol, on the other hand, can assist refine the places where they are most probable to develop (Saiki et al. 2018). The program compiles information on the kind, position, dates, and duration of crime history action. This allows it to anticipate what and whether such offences may occur repeatedly. More similar technologies, which one may name ‘location characterization forecasting technology’ for expediency, are expected to appear in the future. Such technologies may well be utilized to determine protection procedures in urban centers conducting high profile gatherings, with military troops in exact measure to gate receipts.
According to him, Similarly, Big Data and analyses may aid in the fight against cybercrime by utilizing detected correlations to build classification algorithms. Security forces, for example, may indeed be prepared to avoid prospective crimes by evaluating ones who have already occurred in the region of authority (Khan et al. 2019). Data mining algorithms may also be used to uncover trends ranging from intimate partner violence to stealing to manslaughter, and sophisticated insights can be used to assist reduce crimes utilizing sentiment evaluation. Nonetheless, as comprehensive because these tactics look, it really is probable that while in the coming days, additional and therefore more complex electronic capabilities will just be created to assist the prosecution in identifying and following critical possibilities. In various respects, technologies can be making the environment a better condition by detecting possible charges with increased convenience and precision.
According to Singh et al. 2018, law enforcers have always relied on muscle and wits, but a new form of the equipment described as “inferential enforcement” promised to enhance organizational performance. A huge increase in the percentage of police departments entities in the United States and worldwide have begun to use advanced analytical equipment, which is predicated on equations that attempt to anticipate murders while things occur. The theory is straightforward: thieves observe tendencies and using algorithms similar to that used by merchants such as Wal-Mart and Google to detect customer purchase tendencies, investigators can predict whether the upcoming duration comes and, in some cases, preempt violence (Singh et al. 2018). Police organizations may detect offenders before they break a law by using cutting-edge analysis techniques. Big Data violence mapping, also known as violence statistics, is a valuable tool for community policing and preventative prosecution. This will not, nevertheless, be as successful if it were not for its customers. Police personnel are increasingly resorting to Big Data violence analytical techniques, and the first beneficial outcomes of computation collaboration already have been reported.
The Local Police Agency launched Big Data investigation and content in 2010. They determined that the occurrence of criminality follows a pattern analogous to that of seismic occurrences. However an earthquake is impossible to anticipate, it is much straightforward to assess where its successors will occur (Memon et al. 2019). Ingenious LAPD personnel loaded the identical statistical equation with crimes statistics, resulting in algorithms that include establishing trends in criminal recurrence. It appears that anytime a violation occurred someplace, additional crime was likely to occur elsewhere, and the arrangements of those illicit enterprises resembled earthquake structures.
According to Stergiou et al. 2018, in the current time, technically sophisticated environment, the prosecution apparatus, which is a crucial element of all three aspects of governments, namely the parliamentary, administrative, and judicial, utilizes extensive utilization of big data. It is a collaborative effort including the packet capture of enforcement personnel, attorneys, and guardians of converted into digital regarding economic documents. Big data is being used by law enforcement, murder prosecution authorities, and those in charge of the enforcement and application of legislation to discover offences seen over a long period of time. The prosecution administration is concerned with both the investigations and maintenance of public order (Stergiou et al. 2018). And big data is assisting in achieving these two goals in a wholly unconventional approach. Nevertheless, big data, like any other information, has restrictions and provides significant problems to the complete accuracy of prosecution.
Offender histories accumulated over time assist the enforcement in identifying violent areas. Big data has proven to be a huge help in this respect since archives of illegal behavior in the most remote places can now be kept in the tiniest of locations. This is extremely advantageous for enforcement headquarters with vast territories in terms of management duties specialization. Not just that, but being aware of felony offence areas ahead of time really assists in the prevention of illegal acts. Because big data is utilized to uncover and evaluate tendencies in people behavior, it is very beneficial in the judicial process, not especially for specialists working in cognitive research divisions concerned with cybercrime. The behavior of offenders doing various types of malicious deeds is analyzed in attempts to categories offenders based on their mode of operation, reasons for their offences, threat assessment, and so on.
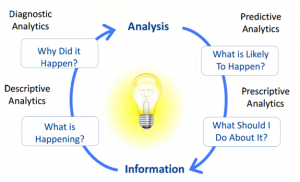
Figure 5: Types of Big Data (Source: researchgate.net)
According to Wang et al. 2020, When supervising is placed above a white the proceedings of criminals, digital marketing also assists prosecutors in determining the most just penalties. The tests demonstrated of all pertinent facts obtained on the offender in a specific instance is given due consideration. Considering that perhaps the offender is wrongly convicted, a fair penalty, such as probation, jail, or administrative custody, is imposed due to the substance and severity of the offence undertaken. As a result, big data can supply the greatest volume of content necessary in a prosecution, resulting in a fair hearing. Big data, maybe more than mere intelligence collecting, simplify operations in the lawbreaker prosecution process on a larger scale by allowing for quicker and larger preservation of the knowledge gained (Wang et al. 2020). In contrast to period the previous, outdated system utilized in criminal justice institutes for documents, such as surveillance videos and stretchy sound systems to acquire information of lawbreakers and other related operations, big data assists capture and gather all suitable data precise details of a specialized prime suspect or situation much more advantageously.
Big data employed in the judicial enforcement process is not immune to certain fundamental issues. The use and use of big data in law enforcement operations is a relatively new phenomenon. However, the court system has existed for centuries. Though that has improved through time, women’s expectations and biases in the manner of sexual inequality, ethnicity, caste, and theology have also infiltrated law enforcement agencies. Understandably, they have acclimated to the changing culture and strived to be as fair and unbiased as appropriate. However, big data has essentially not had the opportunity to expand. When finding trends, big data frequently highlights one group of individuals as more vulnerable to misbehavior than others.
QUESTION-ANSWER
Though there are many serious offences, they may be broadly divided into five categories: offences against with a person, property crime, incoherent crimes, statutory offences, and economic crime.
Criminal Acts Against with a Person: Crimes against one individual are defined as acts that cause bodily or mental harm to people. They are grouped into two categories: murder and other violent offenses. A perpetrator may be prosecuted with any of various forms of homicides, among first homicide, attempted manslaughter, or attempted murder, if the bodily injury to another person is so extreme that it results in death.
Property Infringement: In most cases, crimes against property include interfering with the part of the owner. Although they may cause bodily or emotional injury to another person, they typically result in the loss of the use or control of land.
Inchoate Crimes: Inchoate people are guilty that were started but never finished, as well as activities that aid in the execution of this other murder. Inchoate offenses need more than just a person wanting or expecting to commit a criminal act.
Statutory Crimes: Hard liquor offenses, drug offenses, traffic tickets, and banking collar crimes are the three most serious categories of statutory offences. These offences are particularly outlawed by statute in the expectation that they will dissuade people from committing these.
Financial and Other Offenses:
Financial fraud frequently entails deceit or fraud for earning money. And though the term “white-collar crime” refers to corporate executives who have historically committed them, everyone in every field can conduct interracial criminals.
2.
No, The ONS releases data on violence trends in England & Wales similar to the way on two different sets of crime stats: the Crimes Assessment for England & Scotland and authorities crime stats. Each source has various strengths and weaknesses, but when combined, they create a fuller understanding of violence than single series can provide on its own.
3.
The crime rate109.7 per 1,000 population crime rate In 2020/21, Middles brought, in England, had the highest incarceration rate of any patrol officers district in Wales. Other parts of central England have high murder rates, such as West Yorkshire, and it had a rate of violent crime of 107.2. The violent crime there in European metropolis, London, was 82.9 per 1000 inhabitants. North Riding, a very rural district, has the highest murder rate in Britain, with a criminal activity of 47.5.
4.
The Office of National Statistics (ONS) provided the unemployment stats and yearly numbers of participants for 34,753 Lower layer highly advanced areas (LSOA) in England & Wales during January 2017 to September 2020. The number of unemployed people comprises the monthly total of Universal Credit and Income Support participants. From January 2011 to September 2020, we matched this to annual crime reports from all UK departments from Police UK for 34,750 LSOAs with accessible crime numbers.
5.
Criminal defendants are mostly derived from two sources: victim questionnaires and authorities offences. For a more in-depth examination of these two components, At particular in Wales and England, researchers have suggested that the CSEW is preferable to police-recorded information; as mentioned further below, the UK Characteristics Pertaining argued that arrest records do not offer realistic predictions of crime reported to police. However, it is not intuitively clear whether people accept this reasoning unreservedly. Using surveys raises at least as many questions about the authenticity and dependability of the data as using witness statements.
Crimes brought to the notice of the government by potential witnesses take a different path: events being reported to authorities without the need for a specific police action. When victims “create” crimes, it is commonly assumed that the phenomenon is not influenced by contemporaneous police procedures, but rather by the surviving victims or witness’ desire to engage with the cops.
6.
The Government declared in June 2020 that part of the world limitations to curb the development of Covid-19 will be removed in much of England. At the very same moment, it indicated that additional municipal limits will be required in Leicester. This was in response to a significant number of persons in this region failing a drug test for both the illness. Non-essential commercial firms would be forced to close under the new guidelines. Schools would likewise be shuttered, with the exception of vulnerable young people and important personnel. Personal and government meetings were likewise restricted.
The administration has now been chastised for the manner in which it proposed and then changed the regional lockdown law. On July 29, 2020, during Upper chamber discussion is on the initial closure guidelines. Leicester Municipal Government received roughly £2.5 eligible for financial assistance, while Leicestershire Town Council obtained roughly £2.3 million.
Implementation
Big Data Product: Violent Crime in Lockdown Britain

Figure 5: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
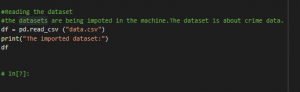
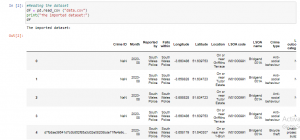
Figure 6: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
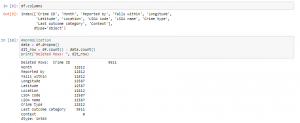
Figure 7: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
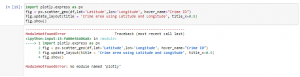
Figure 8: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
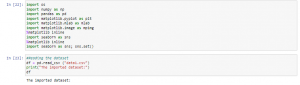
Figure 9: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
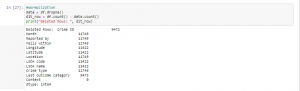
Figure 10: Program Code (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
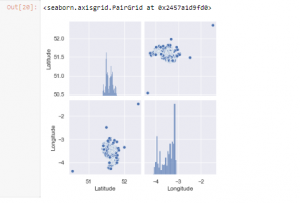
Figure 11: Program Output (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
Figure 12: Program Output (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter)
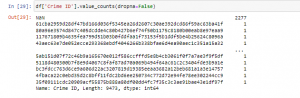
Figure 13: Program Output (Source: Self-Created in Jupyter
A Critical Assessment of the Big Data Approach to Violent Crime Analysis during Lockdown
Introduction
This article explains the fundamental ideas of big data. This tries to bring together the subject to varying debate on what defines big data, whether measures describe the scale and other aspects of big data, and whatever methods and resources existing to leverage big data’s capabilities. Big data has piqued the interest and, to a somewhat measure, the anxiety of everyone from business executives to municipality administrators and intellectuals. Many people have been caught off guard by the fast growth of big data. Previously, the latest technology advancements were initially reported in professional and academic journals. Big Data is used to describe big and complicated datasets ranging in size from megabytes to pet bytes of data of the database (Stergiou et al. 2017). These massive and complicated statistical models are inaccessible to typical data analytics tools such as RDBMS. Big data has made utilized to control these massive data collections in this case. In this section, the actual focus has been made on the categories of Big Data analytics approach to violent crimes reduction during the lockdown period.
Categories of Big Data Analysis
Big Data Analysis may be classified into several types:
- Analytical Prediction
This intelligence is mostly predictive in nature. Predictive Modeling analyses a data collection to anticipate what could transpire. It simply evaluates previous statistical models or documents to forecast.
- Predictive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics analyses a collected material to identify what measures should be made. It’s an important assessment, although it is not generally utilized. Many medical insurance industries employed these analytics on the bottom of different roles to control their company operations.
- Described Analytics
Advanced statistics examine the environment to identify whatever happened and reasons. It is therefore beneficial to visualize this information in the dashboards, whether in the manner of a graphical depiction or another manner.
- Analytical analysis
Diagnostic Analytics works with contemporary sets of knowledge. It is also utilized to identify the parameters on multiple databases that are sent in. This assessment is used by many organizations, such as advanced analytics, to produce positive analytics and visualizations.
Approach to Violent Crime Reduction
There are basically three types of approaches to violent crime reduction. All these approaches are described as follows:
Techniques to Crime Prevention that Concentrate on the Respondent: Complainant methods to criminality prevention emphasize taxpayer dollars on a limited population of key, recurrent perpetrators in order to combat murder rates. This assessment examines six recidivism monitoring techniques, covering classic criminal operations, weapon clampdowns, concentrated prevention, projected secure environments, bespoke communications, and stop, questioning, and strip. To minimize criminal culture, standard criminal prosecution techniques focus on repression, authoritarian engineering, and legislative punishments. Such tactics are founded on a hypothesis, which holds that increasing drug cartels’ judgments of the promptness, predictability, and threat of consequences for illegal action reduce illegal activity (Yassine et al. 2019). The minimal practical data available would not corroborate standard marginalization compliance as a successful temporary or lengthy method to reduce street crime; on the contrary, this could actively promote gang cohesiveness and intensify drug cartel law-breaking. Nonetheless, other researchers believe that specialist divisions might increase enforcement efficacy in reducing mobster homicide by shifting police reaction from a broad deterrent focus to a systematic problem-solving strategy. Nevertheless, others suggest that suppressing may be a component of a holistic gang eradication approach. Therefore, components of preventive and rehabilitation addressed conditions that lead to crime syndicate involvement and unlawful conduct should indeed also be included in the plan.
Police departments frequently begin tough punishment in order to clamp tough on serious crime. Operation Escape was a joint mass shootings management program that emphasized raising the hazards connected with unlawful pot smoking by expanding successful indictment of defendants, and therefore increased potential punishments, for unauthorized gun ownership. In conjunction with government persecution, Operation Exile focused a national educational effort – marketed in newspaper and broadcast channels to strengthen deterrent messaging relating to unlawful weapon ownership and usage. Despite based on personal experience evidence hailed a breakthrough, the little analytical investigation presents complicated results of the method’s performance. It indicates that mass arrests on weapons might result in significant reductions in aggressive offences; nonetheless, further studies use to be done before judgments can be drawn. Developed to address proposals are constantly reported to be beneficial in lowering aggravated assault offences perpetrated by cartels powerful factions, victimization engendered by synthetic drug marketplace, and aggressive misdemeanors being decided to commit by extremely engaged offending behavior (Yang et al. 2017). They are required to improve assaulter behavior thru all the number of co strategy that combines police departments, welfare services, and neighborhood action. Despite not devoid limits, available scientific data clearly supports that concentrated discouragement methods have a beneficial relatively brief influence on criminal activity, prompting academics to advocate for the addition of directed discouragement in the repertoire of violent prevention techniques.
Strategies to Crime Prevention in Specific Locations: Location violence prevention initiatives are predicated on the notion that homicide frequency is geographically repetitive and clustered in certain locations. Landscape psychology, reasoned action concepts, criminal patterns philosophy, and punishment theory are among the different theories that promote position surveillance tactics. This analysis examines two techniques to location-based enforcement: pinch points enforcement of the law and position examinations, often known as Placement Networking Interrogations (PNI). Problem areas patrolling is concentrating public funds on some of the greatest crime-infested segments and sub inside a jurisdiction (Win et al. 2017). The substantial research collection on the effects of pinch point’s police initiatives shows that these tactics yield moderate violence preventive advantages and are able to spread those improvements into communities around the mountain areas designated by the operation. Despite not being beyond limits, the existing studies clearly advocate including hot areas monitoring initiatives, specifically those that use a real concern technique, in the repertoire of scientific proof violence mitigation techniques.
Techniques to Violence Prevention in the Environment: Techniques that attempt to organize localities to cooperate in the violent management system are included in swat team’s neighborhood methods to aggression prevention. This analysis examines three community-policing approaches: neighborhood enforcement, cracked windshields enforcement of the law, and organizational fairness enforcement of the law. Community-focused policing techniques emphasize engagement in the formulation of neighborhood issues and remedies, decentralization of police organizations, and a concentration on cognitive behavioral techniques. The deployments of neighborhood enforcement have been reported to change but generally adhere to this fundamental structure. Experimental research suggests that neighborhood monitoring has a negligible influence on conflict prevention (Stergiou et al. 2018). Cracked windshields enforcement, also known as disruption surveillance, is an authority, neighborhood method to aggression prevention that focuses on concerns of architectural and socio-economic disturbance in hopes of avoiding more heinous offences.
Benefits of the approach for technological, societal, and ethical views on violent crime assessment
- The earliest explicit promise of statistical forecasting advantage is that assets may be targeted more precisely in duration and location. In order to determine high-risk regions, prospective enforcement approaches are utilized, which depend on both historical crime reports and a broader variety of data (Namasudra et al. 2020). Sophisticated areas of high detection methods and hazardous geography evaluation, for example, are utilized to predict where illegal behavior is the most probable to appear. Criminality information is collected via big data are important in this study and based on the acquired: evidence that has no apparent significance but might possibly assist to minimize and forecasting people from committing crimes.
- A second particular argument is that predicted enforcement approaches assist in identifying persons who may be entangled in criminal behavior – perhaps as a casualty or as a perpetrator (Stergiou et al. 2017). It can be said that the predicted techniques may be utilized to determine the membership of criminal groups which further have a high probability of violence break out amongst them. Persons who may become criminals in the present can also be recognized via induction fingerprinting. People having characteristics that correspond with an increased probability of engaging in violent activity can potentially be tracked or addressed in advance using these strategies.
Drawbacks of the approach for technological, societal, and ethical views on violent crime assessment
- The warning note expressed in the current research is whether the techniques can always be completely appreciated by security forces due to the software estimation techniques’ absence of openness. If law enforcement personnel do not grasp the elements that raise the likelihood of crimes, the efficacy of their efforts may suffer (Stergiou et al. 2017). Furthermore, it is critical for police authorities to generate appropriate conclusions from the intelligence and ensure that it is correctly comprehended in order to establish appropriate tactics.
- Liability issues may arise due to a shortage of openness and knowledge of prediction technologies. It can highlight the possibility that legislation enforcement officers may not be able to properly grasp and evaluate the technology’s output and will see the output as insufficient information for judgment calls. This might result in an accounting breach when law enforcement staff are incapable to grasp the algorithms and hence cannot identify prejudices in the programs.
Conclusion
Ultimately, it can be said that utilization of Big Data Analytics Instances, people can incorporate a lot of benefits to multiple industries and businesses because then they can comfortably evaluate the outcomes of any difficult and complicated request, especially when looking at a big information set, and so people can also anticipate evaluation, which will support us gain a competitive edge. All the possible advantages and disadvantages have been summarized in this project report.
Reference List
Journal
Aceto, G., Persico, V. and Pescapé, A., 2020. Industry 4.0 and health: Internet of things, big data, and cloud computing for healthcare 4.0. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 18, p.100129.
Ageed, Z.S., Zeebaree, S.R., Sadeeq, M.M., Kak, S.F., Yahia, H.S., Mahmood, M.R. and Ibrahim, I.M., 2021. Comprehensive survey of big data mining approaches in cloud systems. Qubahan Academic Journal, 1(2), pp.29-38.
Ali, M.H., Hosain, M.S. and Hossain, M.A., 2021. Big Data Analysis using BigQuery on Cloud Computing Platform. Australian JofEng Inno Tech, 3(1), pp.1-9.
Gill, S.S., Arya, R.C., Wander, G.S. and Buyya, R., 2018, August. Fog-based smart healthcare as a big data and cloud service for heart patients using IoT. In International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (pp. 1376-1383). Springer, Cham.
Han, S., Min, S. and Lee, H., 2019. Energy efficient VM scheduling for big data processing in cloud computing environments. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, pp.1-10.
Hosseinian-Far, A., Ramachandran, M. and Slack, C.L., 2018. Emerging trends in cloud computing, big data, fog computing, IoT and smart living. In Technology for smart futures (pp. 29-40). Springer, Cham.
Khan, M. and Ansari, M.D., 2019. Security and privacy issue of big data over the cloud computing: a comprehensive analysis. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (TM), 7(6s), pp.413-417.
Li, Y., Gai, K., Qiu, L., Qiu, M. and Zhao, H., 2017. Intelligent cryptography approach for secure distributed big data storage in cloud computing. Information Sciences, 387, pp.103-115.
Memon, I., Fazal, H., Shaikh, R.A., Muhammad, G., Arain, Q.A. and Khatri, T.K., 2019. Big data, Cloud and 5G networks create smart and intelligent world: A survey. University of Sindh Journal of Information and Communication Technology, 3(4), pp.185-192.
Namasudra, S., Devi, D., Kadry, S., Sundarasekar, R. and Shanthini, A., 2020. Towards DNA based data security in the cloud computing environment. Computer Communications, 151, pp.539-547.
Saiki, S., Fukuyasu, N., Ichikawa, K., Kanda, T., Nakamura, M., Matsumoto, S., Yoshida, S. and Kusumoto, S., 2018, July. A Study of Practical Education Program on AI, Big Data, and Cloud Computing through Development of Automatic Ordering System. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (BCD) (pp. 31-36). IEEE.
Singh, A., Kumari, S., Malekpoor, H. and Mishra, N., 2018. Big data cloud computing framework for low carbon supplier selection in the beef supply chain. Journal of cleaner production, 202, pp.139-149.
Stergiou, C. and Psannis, K.E., 2017, July. Algorithms for big data in advanced communication systems and cloud computing. In 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI) (Vol. 1, pp. 196-201). IEEE.
Stergiou, C. and Psannis, K.E., 2017. Efficient and secure big data delivery in cloud computing. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(21), pp.22803-22822.
Stergiou, C. and Psannis, K.E., 2017. Recent advances delivered by Mobile Cloud Computing and Internet of Things for Big Data applications: a survey. International Journal of Network Management, 27(3), p.e1930.
Stergiou, C., Psannis, K.E., Gupta, B.B. and Ishibashi, Y., 2018. Security, privacy & efficiency of sustainable cloud computing for big data & IoT. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 19, pp.174-184.
Stergiou, C., Psannis, K.E., Gupta, B.B. and Ishibashi, Y., 2018. Security, privacy & efficiency of sustainable cloud computing for big data & IoT. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 19, pp.174-184.
Wang, J., Yang, Y., Wang, T., Sherratt, R.S. and Zhang, J., 2020. Big data service architecture: a survey. Journal of Internet Technology, 21(2), pp.393-405.
Win, T.Y., Tianfield, H. and Mair, Q., 2017. Big data based security analytics for protecting virtualized infrastructures in cloud computing. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 4(1), pp.11-25.
Yang, C., Huang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, K. and Hu, F., 2017. Big Data and cloud computing: innovation opportunities and challenges. International Journal of Digital Earth, 10(1), pp.13-53.
Yassine, A., Singh, S., Hossain, M.S. and Muhammad, G., 2019. IoT big data analytics for smart homes with fog and cloud computing. Future Generation Computer Systems, 91, pp.563-573.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

