Assignment sample on LD7088 Innovations in Business & Technology
Introduction
Part A: Discussion of Innovation Strategies
Critical analysis of innovative theories
Innovation Diffusion theory
Diffusion innovation theory is known to be one of the oldest theories that have originated for prioritising communication. Al-Rahmi et al. (2019) identified that diffusion innovation theory; it is possible to make explanations of product ideas that are able to get momentum along with diffusing through a particular population which includes University students. Through the development of web service it is possible for students to adapt new behaviour ideas as well as products which are counted to welfare aspect for their educational career nu NU Ltd. Adaptation declares about performing activities differently by individuals that have already been done by them. In respective scenarios through Web services students of University are able to perform their studies in better manner along with performing new behaviour in getting adapted to Web services through knowledge about respective software products. According to the view of Al-Rahmi et al. (2021), one of the principal aspects in adaptation of Web services as per diffusion innovation theory is parsing capability of students regarding new or innovative product behaviour and ideas. Diffusion innovation theory helps in performing diffusion at a high rate which would be making students more technical in the educational field as well and is thus to be used by NU Ltd.
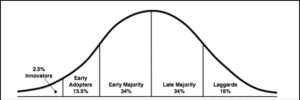
Figure 1: Innovation Diffusion theory
(Source: Inspired by Al-Rahmi et al. 2021)
Personally, such students who are able to adopt themselves quickly in latest creation of Web services are expected to be having better characteristics and quality as a student than personalities who would adopt innovation at a slow rate. Through promoting innovation by application of diffusion innovation in development of Web services by NU Ltd one of the most important aspects understands characteristics of target population. Main cause behind it is it helps as well as hinders in adaptation of innovation in a better manner. Widianto (2020) observed that there are available of five types of adaptors available yet most of the target audience are found to be falling under the middle categories which have understanding characteristics of target population. During promoting innovation with help of the fusion innovation theory there is presence of multiple strategies which are used for appealing towards various adaptor categories.
Technology acceptance model
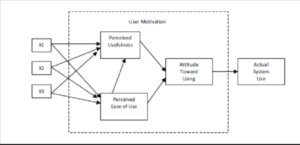
Figure 2: Previous Version of Technology Acceptance Model
(Source: Inspired by (Kemp et al. 2019)
Technology acceptance model is known as a strategic model for digital marketing in technology that is used for digital transformation. As stated by Alsharidaet al.(2021), main aim of technology acceptance model is measuring new technology adaptation which is dependent on customer attitude. In case of respective scenarios students of University are in need of web services made by NU Ltd from University such that they can improve their educational activities appropriately. Main cause for the invention of technology acceptance model is not only explaining a rather predicting system such that it can be used not only by its managers rather than vendors as well (Kemp et al. 2019). According to technology acceptance model adaptation of latest technology is based on attitudes that are positive in nature regarding its usability.
Latest Version of Technology Acceptance Model
Through use of technology acceptance models it is possible to measure important aspects which are found to be easy and perceived usefulness. According to technology acceptance model there are two factors which are accountable for determination of acceptance made by potential users such as perceived ease and perceived usefulness. As per the viewpoint of Salloum et al. (2019), one of key characteristics of following model is emphasis on perceptions of potential users. Main purpose of technology acceptance model is prediction of acceptability of tools along with identification of modernisations which is necessary for web services of NU Ltd’s for University. Postulation made by technology acceptance model is usability of information system for determination made by behavioural intention. It is also accountable for hypothesis direct link between “perceived ease of use” and perceived usefulness.
Innovative solution for creating web service for student of university for digital student identity card
Virtual cards or digital cards for students are found to be becoming a crucial section in the growing ecosystem. According to Hsu et al.(2019), digital cards are known to be the virtual form of regular credit cards which are used for carrying transactions online. Similar to digital payment cards, the ID card for students is also to be used for containing information of students digitally within the card. Through use of digital ID cards of NU Ltd students are able to get access to their University and perform their educational activities. Revathi et al. (2020) asserted that primarily digital ID cards of students can be issued not only in universities rather in colleges and schools as well. Although the respective card is digital, it does not need any kind of internet connectivity and provides an advantageous opportunity to students to use it offline as well.
Digital ID cards after being generated are to be sent to students on their respective mobile phones which are to be played before entering into university rather than carrying physical identity cards first. As per the views of Barhoush et al. (2019), in order to make digital identity cards, students do not need to provide additional information or physical documents to universities as it can be done by themselves through taking their own photos from photo libraries by using the respective apps. Important messages to card holders such as students are to be sent in order to communicate and alert on progress of digital identity cards.
After gaining a digital ID card it is not necessary for students to carry plastic identity cards in all places which provide accessibility in digital cards only. Cendana (2020) suggested that it is forecasted that through digital identity cards of students visual verification of students is done which provides proof of affiliation with a particular University. As soon as digital identity card is punched into latest system developed by NU Ltd which consists of databases of all student information that are also present in digital identity card it allows students to enter into University. In addition to this during integration with systems that are also present it is being used for checking into classes as well as events. As inferred from the study by Santoso et al. (2019), digitalised identity cards of University students also provide facilities to have accessibility towards other occurrences in university which includes accessibility in campus building and paying for lunch as well. As identity cards are provided by the University which make the card to be authentic they also help in receiving not only important messages rather alleys as well from universities through push notifications.
Evaluation of innovative strategy for creating proposed web application
There is a necessity for a digital identity strategy that is innovative in nature for generating revenue, increasing engagement of customers and maintaining high standard privacy. As stated by Bouncken and Barwinski (2021), increase in level of engagement among customers and make it successful, it consists of a series of interactions as well as communications. Successful customer engagement in innovative strategy for digital identification also consists of other aspects which includes data cauterisation which is dependent on enterprise wide identity experience as per NU Ltd. It is found that one of best innovative strategies that are related to identification of personalities digitally satisfies customer digital experiences’ highest strategies (Schoemaker et al. 2021). Innovative strategies include proper management of data privacy during driving personalisation. Future success is noticed to be not promoted by recent time’s best practices and thus there is a high need for innovation in practices.

Figure 2: Fresh Product of Nature’s Neighbour
(Source: Wixsite)
From this image, it has been identified that information about this business and product based information can help customers to analyse all types of services that can help in improving production rates and control functional choices. As mentioned by Horst and Hitters (2020), speech enabled television, think voice assistance as well as wearable technologies are latest innovation in digital identification. Present approaches that are to be used by NU Ltd related to targeting and digital identity are found to be crumbling. It is also expected to be a limited time approach as ways of engaging brands are seen to be changing at an exponential rate. Development of right identity is not considered to be point-in-time effort or spot solution; rather, it is counted to be a highly orchestrated method (Mohammed, 2019). One of most difficult tasks in this basis is known to be following customers present in all digital platforms yet it is a necessary fact as well.
Fresh Cheese of Nature’s Neighbour
Digital identity cards of customers are known to be a robust identity profile of customer as before beginning the process; incoming data is needed to be complete by maintaining consistency and cleanness. Cakranegara et al. (2022) identified that building a data based identity is a critical aspect irrespective of not knowing source of data which are multiple and includes in-person marketing program, website or mobile. Primarily data hygiene is needed to be maintained by NU Ltd for building a robust identity profile of customers which is first step of an innovative strategy. Second stage that is compilation of identity profiles through appending non-digital data such as phone number and address of university student to digital data stream (MARTECH, 2020). Next step includes identification of resolution which is needed to be developed on data that are present for adding both preferences as well as personal information (Fedrecheski et al. 2020). Moreover it is known to be directly leading towards revenue generation which is one main priority of NU Ltd. During identity resolution stage information that is being collected from stage one is needed to be combined. Apart from efficiency, valuation is also increasing at a high rate as well from capturing data in appropriate digital identity processes over time.
Part B: Discussion of Technologies and Web Development
Principles of user experience design and web-based technologies
User experience (UX) is a solution for overcoming challenges that were faced in designing complicated design of objects and was overlooked. According to the view of Hinderks et al. (2019), changes in UX design are found as recently it is known to be a pre-eminent approach of thinking regarding user-led design. Although concept of UX design is misunderstood to be only focusing on user, yet application of principles of UX design in practice is complicated in nature. One of main principles of UX is focusing on user as it is responsible for underpinning all other principles of UX. It is known to be core of UX design as it assists in combating common issues in website design as designers are more expert in working on complicated design frameworks (Liao et al. 2020). Personalised user identification cards are to be developed for university by UX expert designers of NU Ltd only through user-centric design which would declare about user-friendly interface. In the case of digital identity cards for university students such kinds of technologies can be used as well which is counted to be bringing innovation.
This design and service based information can allow customers to analyse their requirements and present that information towards this business to fulfil their needs. Consistency is a specified UX design principle as its importance is high in case of developing successful digital identity cards. Gregor et al. (2020) observed that implementation of consent principle of UX is needed to be approached between three techniques. Among all techniques, the most appropriate one for university students’ digital identity card according to NU Ltd is consideration of all ways through which users are able to make interaction with sites as any kind of issues are faced in logging in using a digital identity card. Hierarchy is another principle of UX design as hierarchical approach depicts thinking through all information and functionality that are present in a digital system.
Similar to principles of UX there is also availability of principles of web-based technologies as well. Green et al. (2019) argued that usability of digital technologies is noticed to be aiding identification of individuals, and authorising their identity. Key characteristics of digital technologies based on perspective of NU Ltd are summarised and emerged in usability of digital technologies in common technical architectures and ID systems which are basic principles of web-based technologies. Suitable use of technology is one of principle of web-based technology which declares clearly about achieving inclusivity, privacy as well as security (Turmudi, 2020). Digital technologies have capabilities of supplementing existing manual processes which cannot be replaced entirely. In central repositories, biometric data are stored which is not sustainable and ill-informed.
Foundational ID systems are responsible for making sure about separation of responsibilities which is different from functional ID and is used for various purposes. According to Astuti et al. (2020), over time evolution of identity system occurred into three identical information models which includes federated, decentralised, and centralised systems. Most applicable one is federated system according to NU Ltd as it allows individuals in choosing identity providers from set of choices. Another principle is identification, authentication and credentials factors and there are three identification factors which are privacy, cost and accuracy. It is also considered to be psychological features as well as verifications are either performed through computer-assisted princess or manually (Ibáñez et al. 2020). There are presences of other important aspects which include identity artefacts which is quick response (QR) code which provides permission for scanning conveniently of identity information encoded in it.
Usability of innovative web prototype
Web prototype
Role played by digital identity cards for undergraduates in universities is not only evident as it makes consideration of role in security of equipment, facilities and students. University is known to be such an environment which has a high requirement of starting security protocols (Byler et al. 2022). In addition to this, it also needs to handle in a significant manner on traffic flows without presence of any kind of hindrance which is one main concern of NU Ltd in developing innovative web prototypes. Approximate balance within security as well as portability can be easily found from digital card cards which are well chip-equipped and smart within and outside university premises (Cendana, 2020). Through establishing connectivity with data system of university and experiences of digital identity along with digital identity platforms have efficiency of enabling learning experience of users which are university Students. Learnings from Universities have increased responsibility as well as large-scale personalised, analysing student performance insights which makes hosting and storage of student data faster and more secure.
Tracking and management digital ID Cards
ID cards of students in digital platforms are considered to be graphic design documents which serve as identification papers for students for use on-campus for proving identity. Bhattarai et al. (2019) declared that multiple applications and software are used by schools, academies, colleges and universities for developing student ID cards for using word-processing programs such as Apple pages, Google Docs, and Microsoft Word. Apart from that, in respective web prototype use if photo-editing software is done this includes Adobe Photoshop or illustrator for working on student ID for gaining high quality images. After selecting a format for developing student ID, editing is to be done through using photo-editing applications and word processing together with file formats (Ahmed et al. 2019). After selection from file format, on the menu, graphic design is needed to be edited which would be the same for all students or else an online editor can be used for better graphic design.
Information that is to be present in digital ID card is name of educational institution, along with university logo as well as the format section of graphic document. Through incorporation of both logo and university name it makes sure about fact that students are accessing equipment and facilities of university. As per the views of Xu et al. (2019), digital identity system would allow authorities to be well aware about leaving and entering of students from university premises. Moreover, it would also be known to be providing allowance to students in efficiently managing the entire method of creation of their own digital ID cards till end from beginning (Castrillon et al. 2021). In respective application students are able to crop, upload and edit ID cards from photo laboratories in application. Attendance of students can be tracked automatically through application of digital student card.
Justification of design and application of innovative web prototype
Irrespective of presence of rapid advancement in digital technologies which are used for composing digital ID cards, reliability issues are still found. Eltemerov and Fedorova (2020) suggested that exclusion of individuals is found to be led from services and benefits due to faults in hardware and software systems, and availability of gaps in network connection among them. Due to faults students in previous time were found to be facing issues in getting accessibility for attending important classes in universities which are to be mitigated through respective ID card applications designed by NU Ltd. It would contain a high amount of highly accurate recognising factors which are applicable for all students of all departments in university (Novelan, 2020). Biometrics is counted to be one of strongest authentication factors from a cyber security perspective as it is based on a database which consists of students’ accurate information.
Foundational ID cards are more important and prioritised by NU Ltd as they are accountable for conducting methods of authorising, identification as well as authentication. As foundational ID systems have expansive scope therefore it is important to design it carefully along with regulating strictly through legal as well as technical means for prevention of such abuse. In all identity systems that are to be developed for university primary identity providers is administrative body of nation which is UK. As inferred from the study by Barhoush et al. (2019), one of most crucial aspects of information regarding digital ID systems is residence of huge amounts of metadata as well as sensitive personal data. NU Ltd being identity providers needs to store information of undergraduates in a protective place as they are accountable for using credentials. Privacy policies are to be followed as well by relying parties as they perform activity related to discarding and verifying information related to creation of identity cards.
Switching to digital ID cards from traditional ones is not only an important rather necessary aspect as it would help in different ways. Among all most prominent ones there is no necessity of printing. Digital ID cards for students is noticed to be a smart move as caring hard copy was a difficult one. Revathi et al. (2020) opined that irrespective of registering in case of digital ID card there would be no hassle related to distributing or printing. On an immediate day rather than the time of registration in web service of NU Ltd students would be able to get their smart ID card rather than waiting for a certain period of time.
Part C: Evaluation of Innovations
Effect of future disruptive innovation impacting organisation
Interruption of disruptive technology is considered to be a crucial aspect in making transformation of higher education through assumptions, policies and practices. Ellis et al. (2019) established that tools that are truly disruptive in nature are found to be not only forcing new approaches rather than thinking as well for ensuring learning of students in higher education in University. Based on NU Ltd’s perspective, online learning could be enabled as well which has high potentiality in making qualification as disruptive innovation. Pressure for changes were found to be generated as an urgent need for making changes in way of educating undergraduates in university. One of main pressures that are found is declination of revenue. Necessity for change is being accepted by not only students but rather faculties of universities yet they are found to be not well aware about ways of making changes. Potentially disrupted power is derived by technology from interpretation of policies as well as practices. As insertion of computerised factors is found among students and faculties, it provides advantage to both parties in performing their tasks appropriately (Al-Imarah and Shields, 2019). Through implementation of the latest disruptive future in future, students and faculties would not need to waste time in taking attendance of students in university which would be done automatically.
Consequences of technological innovation
Block chain-based digital ID of students is considered to be next big innovation in history of ID card creation. As influenced by Schlatt et al. (2022), block chain-based digital ID is noticed to be emerging as an extremely practical factor as a solution to challenges in student’s ID card. In universities from different nations such as UK, rolling out of digital student ID is being heard. There are various reasons which make digital ID cards an attractive thing for universities for immediate pursuit. Coalescence of foundational technology such as block chain, target audiences who are university and end user profile who are students are found (Gilani et al. 2020). All above three helps in creating perfect target for purpose of innovation in ID cards. According to perspective of students they are primary subject of pain points as they face problems in archaic physical ID cards.
Block chain-based ID cards of undergraduates are being addressed as solutions to it. Thus secondary costs are paid by universities for failure in innovation in form of material cost and worker hours for maintaining back office of physical system of ID cards. As observed by Bandara et al. (2022), main issue is faced by losing a physical ID card which is possible in case of smart ID card and thus is highly prioritised and is a positive consequence faced due to technological innovation. Key aspect in scalable technology success is end user adoption and is thus compared with digital identity as a fundamental one. University students are counted to be mostly technologically adaptive individuals in a greater population which states that they have high adaptive capabilities of latest technologies in digital student ID. It is being provided to students on their personal number in smart phones. Perspective of a university is also positive as a university imposing innovation upon students.
In recent digital era, mobile applications are used for enabling cardholders in storing their identity digitally on mobile devices which they carry with them at all places. Kshetri (2020) identified that, it is considered to be providing a digital solution regarding using ID cards that are not only easy to use rather highly convenient as well due to its facility of being stored on mobile devices. One noteworthy facility for university students is there is no need of internet in using digital ID and can be displayed in proper format only (Gadekallu et al. 2021). There is a need for a signature for cardholders as an identity proof which is being added to mobile ID cards. Digital student ID is a common aspect which is highly in need for university as per NU Ltd. universities odd nature cannot be reconciled easily along with simultaneously most cutting-edge one as well. On other side of coin, without it is important to make changes for making identity cards more digitised.
Impacts of usability of innovative web technologies on environment, political and social agenda
Impact of digital technology on the environment is a positive aspect although it depicts about usability of energy. On other hand, there are negative impacts of it on the environment as well as factories that are known to be making technologies that are in need of resources and power for causing pollution. As asserted by Rosman et al. (2022), positive effect of digital technology is storing, sharing as well as connecting information. Social media, internet and email that are used by students as well for educational purposes gives accessibility towards gathering information along with ability of sharing it as well.
Impact on society of digital technology is also a noteworthy fact as it provides assistance to the world in making it more peaceful and fairer. As inferred from the study by Małkowska et al. (2021), digital technologies carry efficiencies in accelerating as well as supporting achievement of all sustainable development goals. It includes edging extreme poverty till reduction in infant and maternal mortality. Moreover, it also promotes decent work, and sustainability along with achievement of universal literacy. In contrast to this, privacy is threatened by technologies as well together with fuelling inequality as well as eroding security.
Influential roles are played by technologies in shaping political landscape in different ways. Politics are highly influenced by technology which is considered to be tools through consideration of it as a political topic (Rotz et al. 2019). Effectiveness of politics is known to be a tool for political actors who are politicians, governments, as well as other firms in better recognition and engaging people to cause. Two of most powerful approaches for usability of technology as tools are data collection as well as digital media.
References
Al-Imarah, A.A. and Shields, R., (2019). MOOCs, disruptive innovation and the future of higher education: A conceptual analysis. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 56(3), pp.258-269.
Al-Rahmi, W.M., Yahaya, N., Alamri, M.M., Alyoussef, I.Y., Al-Rahmi, A.M. and Kamin, Y.B., (2021). Integrating innovation diffusion theory with technology acceptance model: Supporting students’ attitude towards using a massive open online courses (MOOCs) systems. Interactive Learning Environments, 29(8), pp.1380-1392.
Al-Rahmi, W.M., Yahaya, N., Aldraiweesh, A.A., Alamri, M.M., Aljarboa, N.A., Alturki, U. and Aljeraiwi, A.A., (2019).Integrating technology acceptance model with innovation diffusion theory: An empirical investigation on students’ intention to use E-learning systems.Ieee Access, 7, pp.26797-26809.
Alsharida, R., Hammood, M. and Al-Emran, M., (2021). Mobile Learning Adoption: A Systematic Review of the Technology Acceptance Model from 2017 to (2020). International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (IJET), 16(5), pp.147-162.
Astuti, L., Wihardi, Y. and Rochintaniawati, D., (2020). The Development of Web-Based Learning Using Interactive Media for Science Learning on Levers in Human Body Topic. Journal of Science Learning, 3(2), pp.89-98.
Bandara, E., Shetty, S., Mukkamala, R., Liang, X., Foytik, P., Ranasinghe, N. and De Zoysa, K., (2022). Casper: a block chain-based system for efficient and secure customer credential verification. Journal of Banking and Financial Technology, 6(1), pp.43-62.
Barhoush, Y.A., Erichsen, J.F., Sjöman, H., Georgiev, G.V. and Steinert, M., (2019), July. Capturing prototype progress in digital fabrication education. In Proceedings of the Design Society: International Conference on Engineering Design (Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 469-478). Cambridge University Press.
Bhattarai, R., Pappel, I., Vainsalu, H., Yahia, S.B. and Draheim, D., (2019). The impact of the single digital gateway regulation from the citizens’ perspective. Procedia Computer Science, 164, pp.159-167.
Bouncken, R. and Barwinski, R., (2021). Shared digital identity and rich knowledge ties in global 3D printing—A drizzle in the clouds?. Global Strategy Journal, 11(1), pp.81-108.
Byler, D., Franceschini, I. and Loubere, N., (2022). Surveillance, Data Police, and Digital Enclosure in Xinjiang’s ‘Safe Cities. Xinjiang Year Zero, pp.184-203.
Cakranegara, P.A., Butarbutar, D.J.A., Poetri, A.L. and Pakawaru, I., (2022). ANALYSIS OF MSME SALES STRATEGY IN THE DIGITAL ERA. Jurnal Ekonomi, 11(03), pp.1720-1726.
Castrillon, A.M.S., Serrano, E.G.F. and Castrillon, A.S., (2021). Model for the Generation of Digital Academic Certificates. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol, 14, pp.298-331.
Cendana, D.I., (2020). Designing a digital payment framework for HEI’s using smart ID. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng, 12(1), pp.1-7.
Ellis, V., Steadman, S. and Trippestad, T.A., (2019). Teacher education and the GERM: Policy entrepreneurship, disruptive innovation and the rhetorics of reform. Educational Review, 71(1), pp.101-121.
Eltemerov, A.A. and Fedorova, S.N., (2020), November. The use of digital technologies in the professional training of cadets. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1691, No. 1, p. 012214). IOP Publishing.
Fedrecheski, G., Rabaey, J.M., Costa, L.C., Ccori, P.C.C., Pereira, W.T. and Zuffo, M.K., (2020), June. Self-sovereign identity for IoT environments: a perspective. In (2020) Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Gadekallu, T.R., Manoj, M.K., Kumar, N., Hakak, S. and Bhattacharya, S., (2021). Block chain-based attack detection on machine learning algorithms for IoT-based e-health applications. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 4(3), pp.30-33.
Gilani, K., Bertin, E., Hatin, J. and Crespi, N., (2020), September. A survey on block chain-based identity management and decentralized privacy for personal data. In (2020) 2nd Conference on Block chain Research & Applications for Innovative Networks and Services (BRAINS) (pp. 97-101). IEEE.
Green, L., Sung, M.C., Ma, T. and Johnson, J.E., (2019). To what extent can new web-based technology improve forecasts? Assessing the economic value of information derived from Virtual Globes and its rate of diffusion in a financial market. European Journal of Operational Research, 278(1), pp.226-239.
Gregor, S., Chandra Kruse, L. and Seidel, S., (2020). Research perspectives: the anatomy of a design principle. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 21(6), p.2.
Hinderks, A., Schrepp, M., Mayo, F.J.D., Escalona, M.J. and Thomaschewski, J., (2019). Developing a UX KPI based on the user experience questionnaire. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 65, pp.38-44.
Horst, S.O. and Hitters, E., (2020). Digital media entrepreneurship: Implications for strategic identity work and knowledge sharing of beginning entrepreneurs. Nordic Journal of Media Management, 1(1), pp.23-44.
Hsu, H.P., Wenting, Z. and Hughes, J.E., (2019). Developing elementary students’ digital literacy through augmented reality creation: Insights from a longitudinal analysis of questionnaires, interviews, and projects.Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(6), pp.1400-1435.
Ibáñez, M.B., Portillo, A.U., Cabada, R.Z. and Barrón, M.L., (2020). Impact of augmented reality technology on academic achievement and motivation of students from public and private Mexican schools. A case study in a middle-school geometry course. Computers & Education, 145, p.103734.
Kemp, A., Palmer, E. and Strelan, P., (2019). A taxonomy of factors affecting attitudes towards educational technologies for use with technology acceptance models. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(5), pp.2394-2413.
Kshetri, N., (2020). Block chain-based financial technologies and cryptocurrencies for low-income people: Technical potential versus practical reality. Computer, 53(1), pp.18-29.
Liao, Q.V., Gruen, D. and Miller, S., (2020), April. Questioning the AI: informing design practices for explainable AI user experiences. In Proceedings of the (2020) CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1-15).
Małkowska, A., Urbaniec, M. and Kosała, M., (2021). The impact of digital transformation on European countries: insights from a comparative analysis. Equilibrium. Quarterly Journal of Economics and Economic Policy, 16(2), pp.325-355.
MARTECH, (2020), New digital identity strategies needed … now Available at: https://martech.org/new-digital-identity-strategies-needed-now/ [Accessed on: 2 January, 2022]
Mohammed, I.A., (2019). CLOUD IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT–A MODEL PROPOSAL. International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and Technology, 6(10), pp.1-8.
Novelan, M.S., (2020). Application of Attendance Monitoring System Using RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and Interface. Jurnal Mantik, 4(3), pp.1837-1842.
Revathi, R., Suganya, M. and NR, G.M., (2020). IoT based Cloud Integrated Smart Classroom for smart and a sustainable Campus. Procedia Computer Science, 172, pp.77-81.
Rosman, M.R.M., Rosli, N.N.I.N., Shukry, A.I.M., Razlan, N.M. and Alimin, N.A., (2022). Entangling the Interrelationship Between Demographics Profiles, Referencing Competencies and Individual Performance in the Digital Environments. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (Online), 17(9), p.125.
Rotz, S., Duncan, E., Small, M., Botschner, J., Dara, R., Mosby, I., Reed, M. and Fraser, E.D., (2019). The politics of digital agricultural technologies: a preliminary review. Sociologia Ruralis, 59(2), pp.203-229.
Salloum, S.A., Alhamad, A.Q.M., Al-Emran, M., Monem, A.A. and Shaalan, K., (2019).Exploring students’ acceptance of e-learning through the development of a comprehensive technology acceptance model.IEEE access, 7, pp.128445-128462.
Santoso, S., Kauf, J. and Aristo, N.C., (2019).The Information System of Name Card Sales Based on Digital Marketing to Improve Creativepreneur on College E-Commerce Website.Aptisi Transactions OnTechnopreneurship (ATT), 1(1), pp.64-72.
Schlatt, V., Sedlmeir, J., Feulner, S. and Urbach, N., (2022). Designing a framework for digital KYC processes built on block chain-based self-sovereign identity. Information & Management, 59(7), p.103553.
Schoemaker, E., Baslan, D., Pon, B. and Dell, N., (2021). Identity at the margins: data justice and refugee experiences with digital identity systems in Lebanon, Jordan, and Uganda. Information Technology for Development, 27(1), pp.13-36.
Turmudi, D., (2020), April. Utilizing a web-based technology in blended EFL academic writing classes for university students. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1517, No. 1, p. 012063). IOP Publishing.
Widianto, M.H., (2020). Analysis of application of online work exchange using technology acceptance model and innovation diffusion theory.Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 98(10), pp.1697-1711.
Xu, J.Y., Liu, T., Yang, L.T., Davison, M.L. and Liu, S.Y., (2019). Finding college student social networks by mining the records of student id transactions. Symmetry, 11(3), p.307.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

