Leading Through Digital Disruption Assignment Sample
Introduction
Digital disruption is associated with the changes made in accordance with the new digital technologies or innovative business models that would alter the industry experience (Skog et. al. 2018). The term is referred to as disruption in that it disrupts the status quo of the existing process that could forcibly revaluate the current markets served by the organization. The report presents the Case of an organization that has undergone digital disruption and its tools for digital business agility. There is a need for the management to maintain the infrastructure or the culture that effectively supports the digital business. Thus, some instances make it possible to collaborate the functions and handle the digital operations through effective leadership. There is an involvement of a CCO (Chief Collaboration Officer), who has been undertaking the role and responsibilities of the digital disruption.
Task 1
Sainsbury is a supermarket chain that has been ranked second largest in the UK markets. The firm has been effectively dealing in many more sectors other than the supermarket chains like the businesses in Café, fuels and banks. The firm has numerous subsidiaries working well in the UK markets. Sainsbury has over 600 supermarkets and over 800 convenience stores across the UK.
The need for change in Sainsbury and shifting to Sainsbury Online has been a case for heading into the E-Commerce business and taking advantage of the market. Sainsbury’s online is the channelizing of the revenue from the online platforms. The digital approach of the firm is quite clear to be the market leader. Argos, a subsidiary of Sainsbury, has been considered the third most visited retail website in the UK. There is a large workforce of 189,000 colleagues that has been working for success.

Figure 1: Logo of Sainsbury
(Source: Walton, 2020)
The purpose of digital disruption in any firm can be associated with the benefits that can be reaped from digital disruption in any firm:
- Digital disruption helps improve the working capacity and productivity of the workforce employed in the business. It saves time and effort by eradicating the duplication of the work andultimately diverting their time and effort to practicalactions (Baiyere and Hukal, 2020).
- It is also responsible for the increase in customer satisfaction and ease for the customers to purchase without the traditional brick and mortar model. Sainsbury online has made growth during the pandemic as the mobility restrictions did not hinder the purchasing ability of the consumers.
- The firm’s growth is directly linked to the pace kept with the dynamic and complex working environment that has been globally working. The development and expansion are possible if it enters an E-commerce business and breaks the barriers of time and place. Digital company in Sainsbury has made it possible to deal with customers in far off classes.
Hence, the ultimate purpose of Sainsbury is to conduct the digital disruption that has been leading the business sector and take the seamless experience of no bars for places and time in the growth and expansion of the business.
Task 2
Gaining Digital Business Agility
Digital Agility is the transformation in the current process for providing ease in the business operations and adapting to the new challenges in the business (Chan et. al. 2019. There needs to be an embedded culture of digital agility to drive future success. Digital agility is a great tool that can help cope with the crisis times like the Covid pandemic, which imposed mobility restrictions all across the globe.
Different frameworks support the firm’s structure, which can easily undertake digital operations. Digital agility in business has the following significance expressed in the points enlisted below:
- Digital agility is the aspect that brings innovation to the firm. Digitalisation is the age of experiencing new and advanced in all the elements that will help the firm get a competitive advantage (Mangalaraj al. 2021).
- Time and effort are saved for the firms regarding digital agility implied in a business—the employees’ productivity increases when their actions are shifted to crucial functions.
The business agility model is based on three pillars that guide the firm to attain long term success. These pillars are not the novel market technologies that would promote growth but are different capabilities to be developed by the firm to remain agile and competitive. These three pillars are described as:
- Informed Decision making
- Hyperawareness
- Faster implementation and execution
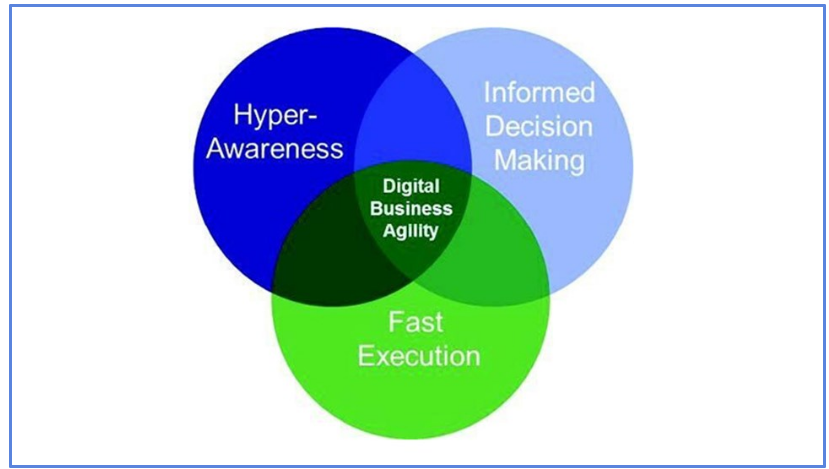
Figure 2: Pillars of Digital Business Agility
(Source: Wade, 2016)
Informed decision-making is the first pillar that concerns the firm’s long-term decisions. The authorities can make the best possible decisions in a given situation. Informed decisions can only be made when the management properly gathers the market trends and facts. The data collected from the market is effectively done when the concerned department is hyperaware of the ongoing conditions of the market. The data collection should be qualitative in nature and error-free to gain practical interpretation of the data and allow sound decision-making (Earley, 2016). Managers who rely highly on intuitions and past experiences have chances of falling due to the dynamic nature of the market. The senior authorities are more concerned with informed decisions making.
Hyperawareness is the sceptical behaviour of the management to note the changes in the internal or external business environment, which can affect the business operations directly or indirectly. The organisation must maintain hyperawareness with the organisation for the reason that the market presents opportunities and warns about the upcoming threats that would affect the business. Therefore, hyperawareness as a pillar of business agility would build a high sensibility and allow the firm to adapt to changes in the environment and absorb any shock.
Planning and forming strategies to run a business is quite common, but the most critical part is the execution or the implementation of the process in the firm. Faster performance is one of the aspects which requires the management to take quick action the carry out the relevant activities. Speedier execution is associated with the capabilities to design the appropriate solutions for the given problem in the specified time frame (Kotarba, 2018). Many hurdles can bar the implementation of the faster execution of the policies, like the complex or haphazard organizational structure or improper channels of communication. Sainsbury’s market agility is considered adequate as the firm has been continuously investing in research and development of the digitalisation channels and giving a seamless experience to the customers.
The AI and machine learning technology introduced in Sainsbury has been helpful to build digital business agility. Sainsbury has deployed the technologies to understand the changing customer tastes. Sainsbury collaborated with Accenture and GCP to develop a platform that would tap the latest eating trends among the customers from online platforms rather than focus on traditional advertising methods. The media developed can also use machine learning tools that clean and classify the collected data for drawing relevant inferences. The data interpretation is carried out through predictive analytics to find new trends in grocery shopping, which the management can further adapt in Sainsbury.
Sainsbury has been indulged in the practice of using AI in the supply chain functions. It is one of the crucial steps that would challenge its competitors in the market in terms of digital agility level. Artificial intelligence is referred to as the ability of robots or computers to perform human tasks which require intelligence and discernment (Dick, 2019). Sainsbury’s is set to engage the operations with Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Software) on building an artificial intelligence. The platform will be based on the forecasting of the demand from the customers and also works to replenish the software platform covering the overall supply chain of Sainsbury.
The collaboration between two firms is not merely the robotic working under the artificial intelligence but there are additional elements which are provided in the form of macro space planning, warehouse management, space management and labour management capabilities (Walton, 2020). The functions undertaken in Sainsbury are for the designing a platform which is autonomous self-learning supply chain platform equipped with the advanced machine learning capabilities.
There are two other ways in which Sainsbury indulges itself in the digital operations with its customers. There is an app designed by the firm for Shoppers’s queuing to get into a supermarket with which they will be able to reserve their spot in the shop or supermarket.
Another is their payment app which is SmartShop Mobile Pay app. This payment application and the queuing application have been interactive in the digital reference in Sainsbury (Sainsbury, 2022).

Figure 3: Use of Artificial Intelligence
(Source: Goddard, 2020)
Task 3
Create a Digital Ready Culture
The digital-ready culture for a firm requires trained IT staff that is efficient enough to manage the technical glitches in the firm and can carry out the online transaction management successfully. Digital ready culture in Sainsbury has been a combination of the values and attitude of the staff to conduct the operations digitally (Westerman et. al. 2019).
There are four aspects of digital disruption which are to be undertaken within the organisational culture and affect the potential of the business are described as:
- Business
- Technology
- Industry
- Society
The firms which have planned to or grown in the face of digital disruption need to undertake the following elements as essentials or prerequisites:
The company-wide digital culture needs to be developed to embrace the novel technology or methodology effectively (SMITH, 2021). The employees need to be trained with the novel technology, setting up the digital-based skills. The digital-ready culture also makes it necessary for the customers to gain insights into better experiences.
The digital-ready culture supports the critical parameters that are explained in the following way:
- Putting customers first
- Creating a collaborative culture
- Instilling a culture of innovation
- Becoming a digital-champion
The four aspects fulfilled in any organisation would create an aura for successfully operating in digital mode. Any organisation needs to be open, autonomous, and impactful to accept the digital disruption to its core. Firms can undertake the use of novel technology and identify whether it is yielding fruitful results against the one existing in the current period (Miller, 2020). The Reorientation of organizational processes according to new technology should be done in parallel, which would not damage the ongoing projects in Case of failure in the use of new technology. All the perspectives and the results should be monitored and reviewed to gain clear insights on using the same in the future.
Task 4
Steer Collaboration
The steer collaboration among different departments is necessary to balance the change that has been implemented in the organisation. Sainsbury needs to designate a post for the Chief Collaboration Officer, who would perform the functions to coordinate the different business departments and remove the gaps in terms of communication or relevant information sharing. The roles and responsibilities of such an officer in any organization can be understood with the following points:
- Strategy formulation and implementation: CCO is responsible authorities for forming relevant strategies that would maintain harmony and coordination between the departments. CCO is also associated with the management of human assets that are available within the organization and can divert their skill and competence to digital learning. The digital agility or the changes would be easier to adopt for such a workforce.
- Formulation of the teams: CCO is also concerned with the functions of formulations of groups which would be helpful to manage the IT functions and focus on the revenue generation capability of the organization.
- Growth and development perspective: CCO is associated with the Attending key partners and client meetings and reporting to the senior officials, which would enhance the growth and development of the organisation. There is also the capacity of the CCO to raise funds and manage the wealth to utilise the investments made in the business optimally.
Sainsbury should engage a CCO who is efficient enough to conduct the following functions and effectively manage the business agility. The role of the CCO has been considerably accounted for when the digital disruption changes the business functions, and there are massive changes from physical aspects to the digital aspects of the business (Schwertner, 2017).
Task 5
Develop your Leaders
Leadership is the ability to influence the decisions of individuals and groups to achieve group goals. It is necessary to develop leadership to reduce the resistance to change that may occur when digital disruption is caused (Silva, 2016). There are different leadership styles that make it possible to handle the changes or the digital disruption in the firm. Leadership is not merely associated with the work’s direction but also includes motivation and enthusiastic working.
The digital transformation in the firm is to be carried out with the help of one of the leadership styles, as stated by Goleman. Various styles have been presented in the following manner:
- Coercive Leadership Style:
- Affiliative Leadership Style: Affiliative leadership is all about the people. Leaders need to create a positive and healthy work environment that is efficient enough to raise their productivity. Such administration has a backlog in that the team rarely receives actionable correction from the leaders, which may create hazy ideas for the team members (Campion, 2018).
- Authoritative Leadership Style: This is a style where the leader is associated with the giving team direction and motivation to achieve a goal. This is “visionary” leadership that develop a roadmap for the team members to attain their objective in any possible manner.
- Democratic Leadership Style: This style involves all the team members being a part of the leader’s decision making. Each member has a valued voice which the leader’s respect. This style is also referred to as “participative” leadership. It is applicable in places where the organisational culture is more collaborative and flexible in nature (Reunanen and Kaitonen, 2017). One of the drawbacks of such a leadership style is the time and effort involved in hearing the opinion of all the members and coming to a conclusion without conflicting viewpoints.
- Coaching Leadership Style: This is the style that suits the name, and the leader is focused on the personal development of the individuals in their teams. Such kinds involve working one-on-one with their employees to improve efficiency. Such a technique is apt in organisations where the employees are open to improvement.
- Pacesetting Leadership Style: Such leaders are example setting people against the teams. They follow the policies and high standards that are placed in front of their followers.
Sainsbury should use a coaching leadership style to guide the employees well with the digital culture that is to be employed. Hence, all the other techniques would preferably suit well with other organisations.
Conclusion
Digital disruption may be good or bad, but the challenging process brings numerous benefits to the firm. Various technologies and models have been critically used to attain the digitalisation in the business. Machine learning or AI are the novel technologies which have made the business functions easier but the implementation of the same require high degree of coordination and effective leadership which would settle the alignment of new with the old. The report has represented all the facets of business agility in Sainsbury, where the online functions are conducted.
References
Baiyere, A. and Hukal, P., (2020). Digital disruption: A conceptual clarification. Sage.
Campion, L., (2018). Leadership styles: considering context and climate. TechTrends, 62(4), pp.412-413.
Chan, C.M., Teoh, S.Y., Yeow, A. and Pan, G., (2019). Agility in responding to disruptive digital innovation: Case study of an SME. Information Systems Journal, 29(2), pp.436-455.
Dick, S., (2019). Artificial intelligence. Sage.
Goddard, W., (2020). Where is Artificial Intelligence Used Today?. [Online]. Accessed through: <https://itchronicles.com/artificial-intelligence/where-is-ai-used-today>. Accessed on March 29, 2022.
Kotarba, M., (2018). Digital transformation of business models. Foundations of Management, 10(1), pp.123-142.
Mangalaraj, G., Nerur, S. and Dwivedi, R., (2021). Digital Transformation for Agility and Resilience: An Exploratory Study. Journal of Computer Information Systems, pp.1-13.
Miller, V., (2020). Understanding digital culture. Sage.
Reunanen, T. and Kaitonen, J., (2017). Different roles in leadership styles in modern organization. In Advances in human factors, business management, training and education (pp. 251-262). Springer, Cham.
Sainsbury official Website, (2022). [Online]. Accessed through:< https://www.sainsburys.co.uk>. Accessed on March 29, 2022.
Schwertner, K., (2017). Digital transformation of business. Trakia Journal of Sciences, 15(1), pp.388-393.
Silva, A., (2016). What is leadership?. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, 8(1), p.1.
Skog, D.A., Wimelius, H. and Sandberg, J., 2018. Digital disruption. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 60(5), pp.431-437.
SMITH, R.R., (2021). Building digital-ready culture. Sage.
Wade, M., (2016). Digital business. Online. Accessed through: <https://www.imd.org/research-knowledge/articles/digital-business-agility-and-workforce-transformation>. Accessed on March 29, 2022.
Walton, C., (2020). Sainsbury’s adds artificial intelligence to supply chain functions. [Online]. Accessed through:< https://www.logisticsmanager.com/sainsburys-adds-artificial-intelligence-to-supply-chain-functions>. Accessed on March 29, 2022.
Earley, S., (2016). Data virtualization and digital Agility. IT Professional, 18(5), pp.70-72.
Westerman, G., Soule, D.L. and Eswaran, A., (2019). Building digital-ready culture in traditional organizations. MIT Sloan Management Review, 60(4), pp.59-68.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


Somebody essentially help to make significantly articles I’d state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and up to now? I surprised with the research you made to make this actual post incredible. Fantastic job!