MAN501 Cross Cultural Difference Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of MAN501 Cross Cultural Difference Assignment, written by the expert.
INTRODUCTION
Culture is considered as learned behaviour and traditions that are shared and transmitted among different individuals of the society. Along with this, it is also considered as the practices that are conceded from one generation to another. In the present era, cross culture is considered as a crucial issue in international environment as it results in arising social differences, mental differences among the individuals etc. that directly impact their activities. The present assignment focuses on reviewing different national cultures that is India and Australia to measure existing differences among both the cultures. The key purpose of this assignment is to gain insight knowledge regarding cultural differences among both the countries for this Greet Hofstede cultural dimension model has been applied that distinct the culture of both countries on different dimensions.
Culture of India
India is among one of the oldest and diverse culture in the world that is about 4500 years ago, when the civilization has begun in India. There are distinct and unique cultures of different religions and communities that are present in India. Indian culture mainly possesses amalgamation of different cultures and communities over many years that is often influenced by the history. There are different elements of India’s assorted cultures that have direct impact on activities of other country across the world that mainly include Indian philosophy, India cuisine as well as religions (Moran, Abramson and Moran, 2014). While, reviewing the past history of India it has been assessed that culture is mainly influenced by the Dharmic religion existing in the economy that plays huge role in shaping literature, philosophy, art and architecture.
According of census 2011, it has been assessed that there are 6 common religions that are followed by the people within the country. The majority of population follows Hinduism religion that is around 79%. After that 14% of India’s population follows Islamic practices. Other than this, people also follow Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism as well as Jainism. Despite of religion, there are other aspects of Indian culture that is language, food as well as art that depicts the diverse and rich culture of Indian society. According to The Constitution of India, India has 28 different states with seven territories in which people speak different language. Officially there are 23 languages that are spoken by people in India and Hindi is viewed as the major language spoken by majority of people. Food is also considered as an important element that describes the culture of India from the 16th century when Mughal invaded India that marked significant impact on the Indian cuisine as they were mainly known for using the herbs and spices for cooking dishes (Zimmermann, 2017). Along with this, Indian Culture also focuses on traditional culture that is respecting the family as it mainly focuses on collectivism approach people prefer their family on priority as compared to taking decisions individually.
Culture of Australia
The Culture of Australia is consequent from Britain; they implement western culture but it is affected by the inputs of Aboriginal as well as oceanic people those who reside at the outskirts in past years. In the present era, Australia is considered as an ethnically diverse society across the world as different nationals individual reside in the region (Deresky, 2017). Reviewing the past it has been revealed that before entrance of British Colony in Australia it was occupied by First Australians i.e. Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islander. The region was colonized by them but after the arrival of British it changed the culture of 50000 years and emerge the entrance of other people from different part of world. Presently, indigenous people that are First Australians are less in number up to only 2.5 percent of total population is Australian population.
The culture mainly depicts the language that is often spoken by the residents of Australia. Australian English is the language that is spoken by majority of people for communicating with each other. Auslan is the national sign language of Australia that is derived by them for the deaf people. It has been also understood that in past there were around 200 to 300 Australian Aboriginal language from which only 70 of the languages has been preserved or survived. It is in the culture of Australian people to respect the individual, their dignity as well as their values and beliefs (Australian value statement, 2017). Through reviewing culture of Australia, it has been assessed that around 16 percent of Australian property is owned or restricted by Indigenous people those are residing there. The land is usually set up in remote or local areas that are often linked to their culture and beliefs. Some holy sites have detailed traditions or rules that need to follow by the other people while living there.
Comparison of India and Australia culture
Greet Hofstede model focuses on six dimension of national culture that support in gaining insight knowledge regarding country’s culture. The different dimensions of Hofstede model represent sovereign preferences for one state of affairs over another that differentiate countries (rather than individuals) from each other.
With the help of using this model it has accumulated information regarding different dimensions or drivers of culture that distinct the Indian culture with Australian culture. The different dimensions of culture are as follows-
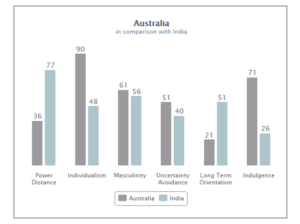
The foremost cultural dimension is power distance index that mainly deals with the reality that individual within the society are not been treated equally that is power is been distributed unequally within the economy. Under this dimension India scores 77 that signify hierarchy as well as top down approach in society and organization. All the individuals within society are treated equally but the centralized authority or power is with the managers and they distribute power equally among each and every one. Along with this, communication is formal and democratic. On the other hand, Australian culture scores low that is 36 in power distance index that indicates for convenience hierarchy has been establish in which both manager and employees consult with each other and engage in participative decision.
Another cultural dimension includes individualism vs collectivism through reviewing this Indian culture scores 48 that is society focuses on both collectivism and individualism traits. Under collectivism individual within society prefer social framework in which they act or perform according to the group situation (Smith, 2011). In addition to this, action of individual is also influenced or affected by the opinion of their family, social groups as well as networks. Other than this, individualism cultural aspect is also present within India it can be seen in form of dominant religion that is Hinduism as they believe in the god and have belief that god has created cycle of death and rebirth. On the contrary to this, Australian culture gains higher score under individualism vs collectivism that is 90 it indicates high individualism that is people are more self-conscious and supposed to look after themselves only. Under this individualism culture people have high self-serving aim and have their full control over the choices that ultimately lead to their self-satisfaction.
Third cultural dimension of model is masculinity vs femininity; by reviewing Indian culture it has been assessed that India scores high in masculinity that indicates heroism within the society that results in making society more competitive. It also showcases that society will be motivated through establishing value system that would lead to high level of competition (Bouton, 2008). On the other hand, Aussies culture also scores high in masculinity aspect that specify individual behaviour in school, play and work is grounded on the share values that is imparted by the society in which they live.
Another cultural dimension is uncertainty avoidance index it mainly depicts the manner in which society deals with the different uncertain situation. With measuring the Indian culture, it has been assessed that it scores 40 that showcase medium preferences for avoiding or overcoming the uncertainty. In India, there is recognition of imperfection there is nothing to be perfect nor planned that avoid the uncertainty or risk within the society. Thus, people within society are not self-driven to take initiative and action for the unknown situation they never try to control the future situation. Along with this, it has been stated that nothing is impossible in India but the people of India are unaware regarding the work adjustment that increases the emergence of uncertain situation. On the contrary to this, in Australia the uncertainty avoidance index scores 51 that showcase Australia plays very intermediate role in avoiding the uncertainty. It also believes that an individual within society has created beliefs and institutions that would support in avoiding the uncertainty so that they can easily control the future.
Another dimension of culture model is long term orientation vs short term normative orientation. This dimension indicates that every society need to maintain some relationship with their past activities so that they can easily deals with the present and future challenges. The society who scores low would have to uphold different norms as well as time bound activities so that it effectively views societal change (Wood, 2000). On the other hand, culture those who attain high score need to be indulge in pragmatic approach that is they may engage in encouraging educational activities among individuals through which they can prepare them for the future. With reviewing the culture of India, it has been stated that India scores high of 51 under this dimension. The word Karma plays significant or dominant role in philosophical and religious aspect (Spring, 2016). The society have high long term orientation that encourage thrift as well as impart modern education among the individual that would influences their views, practices, beliefs etc. Through distinction with the Indian Culture Australian culture mainly focuses on creating norms as well as rules with the key aim to change the society and its individuals. Australia scores low (21) thus have normative culture that assist them in having strong concern regarding establishing truth. The individual within this cultural society respect the traditions and focuses on accomplishing fast results.
The last dimension within the cultural model is indulgence vs restraint that differentiates Indian and Australian culture. Indulgence ensures that individual within society is self-satisfied and indulges in self driven activities that accomplishes their requirement and results in enjoying their life. While, restraint focuses on meeting individual needs that is restricted by strict norms and regulation. Therefore, it is stated that weak control is term as indulgence and strong control results in restraint. With reviewing the Indian culture, it scores low that is 26 that signifies restraint aspect within the society. The restraint society within India does not focus on imparting leisure time it mainly controls the individual desires. Therefore, with this people perception and actions are controlled created social norms that individual feel disconnected from the society. On the contrary to this, in Australian culture there is weak control or authority power. Individual within society are indulging in activities that would results in meeting their needs and desire. It scores high that is 71 which indicate people have positive attitude and have propensity towards optimism (Greet Hofseted, 2017). In addition to this, individual act according to their wish and spend the required money to meet their desire.
Thus, from assessing the above different dimensions of culture it is concluded that there is huge difference among both the countries culture that is India has diverse background and religious people that more believes in collectivism culture as compare to individualism. For instance, individual in society prefer to prioritize their family prior to themselves (Difference between social culture in India and Australia, 2017). On the other hand, Australian people mainly have individualism culture that is individual place more emphasis on meeting their need prior and perception of others cannot change their behaviour or activities. Moreover, when it comes to privacy it marks huge difference among both the countries. People residing in India do not safeguard their own privacy or other’s privacy as it is in their culture to have informal communication. On the other hand, Australian people are far better in maintaining their privacy level as well as making other’s information more private. Besides this, another difference among culture of both the countries includes caste system. India has history of caste system and few of the people in contemporary scenario are caste oriented. This strong caste system within India results in not adopting the western culture. On the other hand, Australia in the present scenario is one of the leading egalitarian societies that benefit the individual in having broad aspect regarding caste system. In Australia people strongly oppose the caste system and sit down together clear their misunderstanding and move ahead in life.
Food form is also considered as significant aspect within culture. In Australia mainly phrases have been used by the individual for having picnic or dinner that is ‘Bring a plate’. In Australia this phrase indicates that individual those who are invited at party need to bring some food along with them that would be eaten straight away. On the other hand, if this idiom would mark on Indian then it would be drastically changed its meaning. It is not in culture of Indian to use idioms and phrases for inviting to a picnic. Indian mainly uses this motto ‘Athithi Devo Bhava’ that means guests is god and they have to be treated like that (Cultural Differences Between India and other Countries: A Dinner Invitation. 2010). Therefore, the way of speaking is also different in both the countries that distinct India from Australia.
Core values in Indian culture compared to Australian society
| Indian Society | Australian Society |
|
· Individualist
· Egalitarian · Trust in business deals. · Fluid social hierarchy. · Multicultural. · Looser family bonds. · Earn trust. · Large personal space. |
CONCLUSION
From the above assignment it has been concluded that cross culture is considered as significant aspect that refers to different beliefs and behaviour of individuals in different countries. With the help of Greet Hofstede model easy comparison has been made on present Indian and Australian culture. Along with from the above different dimensions of culture it is concluded that there is huge difference among both the countries culture that is India has diverse background and religious people that more believes in collectivism culture as compare to individualism.
REFERENCES
Books and Journals
Bouton, L. F., 2008. A cross‐cultural study of ability to interpret implicatures in English. World Englishes. 7(2). pp.183-196.
Deresky, H., 2017. International management: Managing across borders and cultures. Pearson Education India.
Moran, R. T., Abramson, N. R. and Moran, S. V., 2014. Managing cultural differences. Routledge.
Smith, P.K., 2011. The nature of school bullying: A cross-national perspective. Psychology Press.
Spring, J., 2016. Deculturalization and the struggle for equality: A brief history of the education of dominated cultures in the United States. Routledge.
Wood, G., 2000. A cross cultural comparison of the contents of codes of ethics: USA, Canada and Australia. Journal of Business Ethics. 25(4). pp.287-298.
Online
Australian value statement, 2017. [Online]. Available through: <https://www.border.gov.au/Trav/Life/Aust/living-in-australia-values-statement-long>. [Accessed on 14th August 2017].
Cultural Differences Between India and other Countries: A Dinner Invitation. 2010. [Online]. Available through: <https://agypsy.wordpress.com/2010/09/14/cultural-differences-between-india-and-other-countries-a-dinner-invitation/ >. [Accessed on 14th August 2017].
Difference between social culture in India and Australia. 2017. [Online]. Available through: <http://www.indianconnection.com.au/the-difference-between-social-culture-in-india-and-australia-australian-culture-awareness/>. [Accessed on 14th August 2017].
Greet Hofseted, 2017. [Online]. Available through: <https://geert-hofstede.com/australia.html >. [Accessed on 14th August 2017].
Zimmermann, 2017. Indian Culture: Traditions and Customs of India. [Online]. Available through: <https://www.livescience.com/28634-indian-culture.html>. [Accessed on 14th August 2017].
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


Dear immortals, I need some wow gold inspiration to create.