MOD3327 Economics for Business
Introduction
Circular flow diagram model represents flows of money along with goods and services in the market to analyse relevant economic aspects. This diagram mainly contains economic production of several areas like households, firms, markets for products and markets of goods and services. With help of this diagram, flow of cash inputs and outputs in UK economic sectors are being highlighted that help to understand the whole process of circular flow of money. Apart from these, its implications on the UK economy are also being discussed with relevant economic sources. Furthermore, a brief discussion has been drawn particularly highlighting labour issues and increasing household financial difficulties because of rising inflation rates in UK economic markets.
Task 1:
Circular Flow Diagram
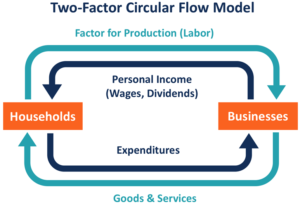
Figure 1: Circular Flow Model
(Source: Influenced by Barros, 2023)
The basic and foremost purpose of circular flow model is to evaluate the flow of money moves within the market economy. According to Barros et al., (2023), circular flow model is a process to measure a nation’s income, and revenue growth, as this model keeps a track of both outflow and inflows. This model breaks the market economy into two main players, those are households and corporate markets, among which the circular flow is carried on repeatedly. Apart from these, this model helps to build an interconnectivity between these two sectors by claiming that money usually operates within these two sectors. To understand the mechanism behind circular flow model, it is necessary to understand that a nation’s income is mostly collected by two major segments (Economicsonline.co.uk, 2023). These two parts mainly comprises household segments and corporate markets are engaged in collecting and measuring nation’s revenue and profitability.
Scope of UK specific event during 2021 and 2023
In UK countries, these two segments are highly involved in collecting capitals and hence, it impacts GDP and PCI of UK countries. With a detailed observation, it can be concluded that the money is flowing from one direction to another direction. In simple words, money is flowing from businesses to individuals in order to maintain household activities and again, money is coming back to businesses in order to provide goods and services in market. As mentioned by Kuzior et al., (2023), circular flow model is one of the most common economic factors that might get affected due to relevant macroeconomics factors. This is considered as most basic circular flow in an economy where money flows from individuals to businesses as household and consumers’ expenditure and flows back to corporate economy market as dividends, wages, or as business profits. However, this circular flow of money might get affected by several macroeconomics factors. Such as, an increasing inflation rate in UK economic markets might impact household financial decisions and hence, consumers might be facing difficulties while making household consumption decisions.
As mentioned by Coscieme et al., (2020), it helps the UK countries to calculate gross national income and per capita income. Apart from these, macroeconomic factors like high interest rates are also highly affecting families from taking loans for their domestic purposes. Moreover, rising inflation rate and rising interest rates are increasing labour issues in UK countries that leads to an imbalance in the circular flow of economy. This has become one of major challenges for UK corporate world as rising input price inflation continues to remain their top concern. “Input price inflation” is basically an imbalance in supply and demand, as it may cover labour, raw materials or even transportation costs. According to data of October 2022, input price inflation and energy prices are on the top concerned list for UK businesses, which at present increased by a rate of 24% and 23% respectively (Ons.gov.uk, 2023). Due to rising inflation rates, a massive hike in costs of consumer goods and services is noticeable in UK countries, and therefore, household consumption is gradually decreasing.
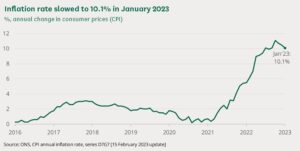
Figure 2: Inflation rate of UK in recent years
(Source: Commonslibrary.parliament.uk, 2023)
As the graph shows, the inflation rate of UK has increased at a rate of 10.1% in January 2023, which shows a massive increase in consumers’ goods and services (Commonslibrary.parliament.uk, 2023). Apart from these, strong demands and supply chain bottlenecks are some major reasons for rising inflation. Moreover, rising food prices are also a concerning matter for households, as it is affecting their consumption ability.
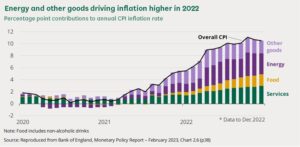
Figure 3: Energy and other goods inflation rate in UK in recent years
(Source: Commonslibrary.parliament.uk, 2023)
According to above-mentioned graph, it can be assumed that UK countries are experiencing a massive hike in energy prices and food prices along with other goods and services. Rising energy prices are one more reason for rising inflation rates including household energy traffics and road fuel (Commonslibrary.parliament.uk, 2023). From January 2022 to January 2023, domestic gas prices have increased at a rate of 129% whereas domestic gas prices have increased by 67% in last two years. Thus, it can be assumed that this inflation rate of energy and household goods and services somewhere impacted consumer’s purchasing power.
Impact on UK economy for specified events
Rising inflation rates of consumers goods and services and other raw materials are highly affecting circular flow model of economy in UK countries. Due to rising input prices, manufacturing companies are unable to produce goods and services in a limited amount and thus, it is circularly becoming one major reason for raising inflation rates. According to Greenwood and Hanke (2021), input prices inflation is one of major concerns by manufacturing industries, as somewhere it directly affects labour costs. These macroeconomic factors are connecting corporate and household issues in a circular motion, where individuals from both ends are being affected by rising prices. For instance, above-mentioned inflation rates are somewhere affecting consumers’ purchasing of goods and services in order to reduce unnecessary expenditures. Thus, due to less household consumption, businesses and manufacturing industries in UK might be unable to increase their profitability and hence, it would hamper their revenue collection mechanism. This affects industries to delay in their labour payments and wages on time and hence, it consequently raises labour issues in UK countries.
As per view of Moradi et al., (2021), macroeconomic factors like unemployment issues are often interrelated with rising inflation rates. Inflation rates are affecting households for more and sufficient consumption, which has its negative impact on manufacturing businesses. It can be assumed as one major concern of employees and labourers, as industries might be unable to pay them properly. Thus, it would lead to reduction of labour costs and hence, employees might experience insecurity in their corporate life. Moreover, UK countries might experience high unemployment rates or in contradiction, lack of good opportunities might encourage people to settle in other developed countries for better positions.
On other hand, it can be assumed that UK industries, when manufacturing their goods and services, usually calculate costs of raw materials, labours and other plants and equipment. As suggested by Godfrey et al., (2022), goods and services offered by companies that are completely usable for household consumption, comprise all labour and raw material costs as their selling prices. Therefore, businesses are bound to sell their goods and services at high prices, in order to maintain their cost of goods sold. Henceforth, it might be another major cause of rising inflation rates. Thus, it can be concluded that in both cases, the circular flow of economy is being affected by several macro and micro economic factors that lead to rise in labour issues and household consumption.
Task 2:
Impact of circular flow mechanism in real-world economic events.
A two-way circular flow model helps to understand its implications over real-world economic events that describes the whole mechanism of monetary transactions from both ends. It is a common factor of economy that describes proper functionality of give and take mechanisms, including several sectors. According to Turner et al., (2019), circular flow model is a way to show how money travels within different segments to fulfil market and individual requirements. Thus, to understand real-world economics, a circular flow model is an appropriate way to define the routes of money from one entity to another entity. For instance, individuals receive money in form of salary or wages to purchase household consumption of goods and services. This is termed as “consumption” in circular flow model that represents most significant part of the entire process. Alongside, industries and firms collect those money received from household consumption and utilise them for their labour cost, raw materials and capital goods. Apart from these, government collects taxes from corporations and households, which represents another leakage of circular flow model. It helps government to utilise these finances in different sectors like infrastructure of administrative buildings in order to enhance public facilities. When real economy is much more complicated to understand, circular flow model is much more useful to understand concepts of real world economy (Stlouisfed.org, 2023).
On other hand, circular flow model helps nation’s government to keep a track on all monetary transactions that happen between households and industries in order to collect taxes on time. Developed countries like US and UK, where exports of goods and services take place very frequently, circular flow of four-sector models must be helpful to understand imports and exports mechanisms. The four-sector circular model describes that money flows and comes in terms of capital and income from foreign traders of international markets. In addition, government of US and UK countries might use a circular flow model to measure their gross domestic production (GDP) and Per Capita income (PCI). It helps them to acknowledge whether their economy is being affected by macro and micro economic factors and how it might be recovered in an estimated timeframe. Thus, in real-world economic sectors, contribution of circular flow model is quite crucial in gauging overall capital flow from countries households and the corporate world.
Scope of US specific events during 2021 to 2023
After pandemic impact over the entire world, it has become very difficult for several countries to overcome major macroeconomic factors to recover their economic status. Developed US countries are also facing macro and micro economic challenges from surging and rising inflation rates and slowing economic activities (Oecd.org, 2023). Thus, it can be assumed that due to rising economic challenges, their circular flow of economy might have been affected. Strong consumer demands, supply constraints and raising commodity prices lead to the rise of inflation rate in US economy which, simultaneously tightening household financial expenditures. A survey has claimed that total income and wealth distribution in recent years among US middle class families are much lower than their higher- and upper-class families (Oecd.org, 2023). Thus, several US middle class families are facing economic challenges because of rising inflation rates and hence, an imbalance of economy is taking place. Moreover, it is hampering one major segment of circular flow model as several families are unable to purchase goods and services for household demands. Apart from these, another major challenge that US government is facing is the rising unemployment issues affecting circular flow of economy. Often market fluctuation leads to a rise in market demands and hence, results in a high inflation rate (Studysmarter.us, 2023). Middle class families that are being considered as key drivers of US economic growth are experiencing the rising effects of housing, education, childcare, health care and other relevant economic activities. These rising costs with weak growth of household incomes are reducing purchasing power of households and thus, somewhere affecting capital growth of industries.
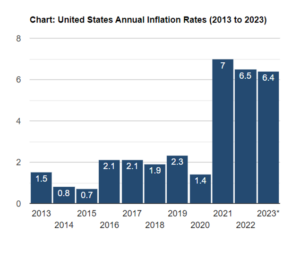
Figure 4: US inflation rate from 2013 to 2023
(Source: Studysmarter.us, 2023)
As per above-mentioned graph, it can be claimed that US countries are experiencing a massive hike in their inflation rates from the year 2021 as compared to pre-pandemic situations (Studysmarter.us, 2023). It has been assumed that US economic factors might face fluctuation in recent years due to rising demands of goods and services and other necessary aspects. It results in reduction of corporate economic growth and thus, tends to rescue labour costs. Henceforth, a cycling mechanism is involved between these two major sectors of economic growth that are household and industries. These macroeconomic factors are interrelated with each other like a circular model of economy, which gradually impacts US economic factors. With help of proper understanding of circular flow diagram, it might be easy to analyse major economic challenges of US countries.
Impact of US events on their circular flow of economy.
It is quite necessary to keep a track on every monetary activity that affects the circular flow model of US economy in order to understand its implications. The pandemic has drawn its impact over main key drivers of US economic growth such as middle-class families and manufacturing industries. According to Coban (2022), high interest rates often come out to be a burden over middle class families and rising corporations. In other words, US countries are facing economic challenges due to high interest rates and tax rates. This leads to rise of high household debts, where middle class families are unable to pay high interest rates. Thus, US banking sectors might be experiencing a lack of revenue collection due to depreciation in loan approvals for household purposes. Apart from these, it can be assumed that US countries might experience high inflation rates in upcoming years, which might affect families and manufacturing industries.
Similarly, it has been assumed that US countries might suffer from a rise in unemployment rate due to a reduction of labour and manpower among US industries. As per view of Awan and Sroufe (2022), firing labour and workers from corporations might impact a balanced circular flow of economy. That means, middle class and poor families would suffer due to lack of annual income and thus, US countries might experience a massive decline in their PCI. Therefore, it is quite necessary to control these negative impacts of macroeconomics on US economic factors in order to maintain a balanced circular flow. With the proper mechanism of circular flow diagram model, US government might be able to acknowledge several major issues affecting their household consumption and manufacturing industries.
As mentioned by O’Ryanet al., (2020), circular flow model comprises segments like households, corporations, importing and exporting factors and other relevant drivers who drive the economic growth and productivity of a particular country. Thus, reduction of high interest rate might help families to take loans from banking sectors and financial institutes in order to purchase goods and services. This would allow US financial sectors to collect sufficient revenue for paying government taxes and hence, encourage government to utilise those finances to supply public goods and services. Therefore, proper utilisation of money might enhance the mechanism of circular flow model in US economy.
Conclusion
Circular flow model represents the cycling flow of money from one major segment to another major segment in order to fulfil every individual’s requirement. In this assessment, the mechanism of circular flow model has been described with proper economic examples of two developed regions that are the UK and US. Apart from these, major macroeconomic factors are being highlighted that mostly affect economic growth of these two countries, while drawing attention towards circular flow model. Alongside, real-world examples are being discussed in order to understand proper implications of circular flow diagram over real economic factors. Furthermore, relevant challenges are being highlighted that might influence a nation’s growth and income.
References
Awan, U. and Sroufe, R., (2022). Sustainability in the circular economy: insights and dynamics of designing circular business models. Applied Sciences, 12(3), p.1521.
Barros, M.V., Salvador, R., Gallego-Schmid, A. and Piekarski, C.M., (2023). Circularity measurement of external resource flows in companies: The circular flow tool. Waste Management, 158, pp.136-145.
Çoban, S., (2022). Gender and telework: Work and family experiences of teleworking professional, middle‐class, married women with children during the Covid‐19 pandemic in Turkey. Gender, Work & Organization, 29(1), pp.241-255.
Commonslibrary.parliament.uk, (2023), About Inflation rate of UK Available at: https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-9428/#:~:text=Documents%20to%20download&text=The%20cost%20of%20living%20increased,goods%20and%20services%20for%20households. [Accessed on 14/02/2023]
Coscieme, L., Mortensen, L.F., Anderson, S., Ward, J., Donohue, I. and Sutton, P.C., (2020). Going beyond Gross Domestic Product as an indicator to bring coherence to the Sustainable Development Goals. Journal of Cleaner Production, 248, p.119232.
Economicsonline.co.uk, (2023), About Circular Flow Model Available at: https://www.economicsonline.co.uk/managing_the_economy/the_circular_flow_of_income.html/ [Accessed on: 12/02/2023]
Godfrey, D.M., Price, L.L. and Lusch, R.F., (2022). Repair, consumption, and sustainability: Fixing fragile objects and maintaining consumer practices. Journal of Consumer Research, 49(2), pp.229-251.
Greenwood, J. and Hanke, S.H., (2021). On Monetary Growth and Inflation in Leading Economies, 2021‐2022: Relative Prices and the Overall Price Level. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 33(4), pp.39-51.
Kuzior, A., Arefiev, S. and Poberezhna, Z., (2023). Informatization of innovative technologies for ensuring macroeconomic trends in the conditions of a circular economy. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 9(1), pp.10-20.
Moradi, M., Appolloni, A., Zimon, G., Tarighi, H. and Kamali, M., (2021). Macroeconomic factors and stock price crash risk: Do managers withhold bad news in the crisis-ridden Iran market?. Sustainability, 13(7), p.3688.
O’Ryan, R., Nasirov, S. and Álvarez-Espinosa, A., (2020). Renewable energy expansion in the Chilean power market: A dynamic general equilibrium modeling approach to determine CO2 emission baselines. Journal of Cleaner Production, 247, p.119645.
Oecd.org, (2023), About US Economic Challenges Available at: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/united-states-continue-to-tackle-macroeconomic-challenges-while-supporting-the-middle-class-and-preparing-for-population-ageing.htm [Accessed on: 12/02/2023]
Ons.gov.uk, (2023), About Inflation Rate in UK Available at: https://www.ons.gov.uk/businessindustryandtrade/business/businessservices/bulletins/businessinsightsandimpactontheukeconomy/6october2022#:~:text=For%20October%202022%2C%20input%20price,%25%20and%2023%25%2C%20respectively. [Accessed on 13/02/2023]
Stlouisfed.org, (2023), About Circular Flow Model Available at: https://www.stlouisfed.org/education/economic-lowdown-video-series/episode-6-circular-flow#:~:text=Money%20flows%20clockwise%2C%20while%20goods,in%20the%20economy%20fit%20together. [Accessed on 31/01/2023]
Studysmarter.us, (2023), About Economic Challenges of US Available at: https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/macroeconomics/macroeconomic-issues/#:~:text=The%20macroeconomic%20issues%20in%20the,GDP%2C%20unemployment%2C%20and%20inflation. [Accessed on 31/01/2023]
Turner, C., Moreno, M., Mondini, L., Salonitis, K., Charnley, F., Tiwari, A. and Hutabarat, W., (2019). Sustainable production in a circular economy: A business model for re-distributed manufacturing. Sustainability, 11(16), p.4291.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


Hi Neat post Theres an issue together with your web site in internet explorer may test this IE still is the marketplace chief and a good component of people will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem
very informative articles or reviews at this time.