Importance and objectives of the operation management
Articulation of the importance and objectives of the operation management will be done. It shall also showcase the application of the operation management in the particular business environment. The various issues experienced by the company shall also be analyzed through provision of OM solution. This would optimize the internal system along with enhancing the schedule of production and supply chain management.
The objectives of the operation management shall be discussed thorough in this part along with depicting the current status of the company. The scope and task required to be done shall also be focused in this section.
The implementation of various OM practices and strategies shall be discussed. Our company based on which the entire study shall be performed is an Australian manufacturing-based company. Implementation of the lean operation shall also be discussed. The SCM strategy and its usefulness in business field. The quality management and the method of implementation of quality management strategy will be discussed in this section.
Product design
“Product design is the very core of innovation” (Patil, et al., 2017). For a company to be successful and sustainable in the market place new products and services need to be developed on a regular basis (ibid.). The process of product design is often interrelated with the concept of product development and as such need to be factored in together. There are eight major phases in the process of product design and development – “Analysing market and customers’ needs,” “Product concept generation,” “Product design specifications,” “Design for manufacturing,” “Development of concept and prototype,” “Detailed design,” “Design evaluation and review” and “Product launch.” These phases have been detailed below for the project. Appendix 4 gives a description of the product design and development process.
Analysing market and the consumer’s needs
Jiao and Chen (2006) state that, “the journey of achieving customer satisfaction starts with effective capturing, analyzing and understanding customer’s genuine requirements.” Customers’ need are generally ambiguous and more qualitative however in certain cases they can also be complex, multiple or very specific depending on their expectations from the product (Patil, et al., 2017).
The concept for the product was developed on the basis of market research conducted throughout the region. Most of the dairy productions in the country are going towards production of related products like yoghurt, cheese, butter and the likes and not enough circulation of milk is in place. The varieties of milk that are available on the market are more often than not skimmed of their fat and sold as skim milk. This has created a gap in the market for high quality rich milk and as such efforts need to be made to fulfil that need. Flavoured milk, in a pre – packaged ready – to – use form has been in demand for quite some time now. This is why the product was envisioned.
Patil, et al. (2017) state that, “to start with Product design and development it is necessary to generate product idea or concept to evaluate whether it is going to be commercially saleable or not.” As such a need or a gap in availability for the consumers need to be determined, and then the concept for a product is to be agreed upon. “A concept is an early representation of a product, incorporating only minimum details; just enough to show the main characteristics of the product” (Patil, et al., 2017).
Based on the research conducted, it was found that there was a demand for creamy flavoured ready to drink milk products. Additionally market research also showed there is a greater favourability towards natural flavouring substances. There also is a scope for introducing this product as there are no existing products that fulfil this demand. This product was designed as a result of the assessment of these demands from the consumers.
According to Unger and Eppinger (2011) “companies face several risks during new design. The company should be able to categorise most risks as technical, market, schedule, or budget.” Based on the requirements, the product will have to have above 25 % fat content with natural flavouring like chocolate and the likes. The product will have to be supplied in both ready to drink tetra packs and PET bottles. “Market risk stems from whether product design specifications meet customer needs; if not, a technically successful product could fail in the market” (Unger and Eppinger, 2011). As such, the design of the product has been made according to the requirements and needs assessed of the potential consumers.
Product design needs to take into account not just the design of the product but also the design of the manufacturing process. Clear documentation needs to be maintained for the entire process so that the various departments involved in the design process for both the products and the manufacturing process are on the same page. Appendix 5 gives a clearer picture of the process.
Development of Concept and Prototype
According to Wankhede, et al. (2014), “the prototype development stage of product design is when design concepts and solutions are developed through drawings and mock-ups or on Computer Aided Design tool. The solutions should meet the requirements of the product design specification.” Krishnan and Ulrich (2001) suggest that “along with product specifications and the product’s basic physical configuration, the extended product offerings such as life-cycle services and after-sale supplies can also be defined by prototypes.” As such special effort has been done through research and development to find the right product not just for the actual consumable but also for the packaging that would be best suitable for the current and future scenario of the market.
This is the stage where the geometric models of the assembly line and the product specifications are designed. According to Jauregui-Becker and Wits (2013), “during the process assumptions need to be made, introducing possible errors. Large errors may even lead to not reaching the target requirements and forces the design team to return to the conceptual stage.” As such all such implications have been taken into account. The subsequent planning has been detailed further in the report in the following sections of the main report.
Patil, ET al. (2017) suggest that “design evaluation is a function which is carried out at various stages of the design process. Its purpose is to check that the design solution is in accordance with the original design objectives.” Further, Jauregui-Becker and Wits (2013) suggest that “the product must be verified against customer acceptance criteria and validated that it provides the customer with the operational capabilities actually needed; any divergences from expectations must be diagnosed and characterized as defects for disposition in a subsequent iteration of product development and product design should undergo necessary changes through detail design phase.”
Lee, et al. (2012) note that, “developing a strategy for a product launch is the last stage in product design and development process. For successfully launching and sustaining the product in the market, the voice of customer on their requirements must be responded.” The decisions involved in the process include “what to launch, where to launch, when to launch, and why to launch” (Chiu, et al., 2006). Patil, et al. (2017) further elaborate that, “even a superior product may fail due to poor product launch strategy. If products launch strategy matches with actual market conditions then product launch becomes successful.” As such the product launch of the product will be carefully designed and implemented so as to maximise the potential reach of the product.
PART A – Management Progress Report
The part of the organization in which management is responsible to carry out the entire production of commodities and services to their customer or clients is commonly considered as operation management. One need to have a clear idea regarding operation system to gain the proper concept of operation management.
While talking about the objective of the operation management we generally point out the customer services and resources utilization.
The Warrnambool Cheese & Butter Company launched the brand Great Ocean Road in the year 2013. This company engages in production of high quality of milk and cheese.
The principles and strategies
- Instinctive sound judgement.
- Consistent efficiency.
- Eliminate the situation of over analysis, thereby obtaining concrete solutions to every problems.
- Accumulation of important information and potentiality of making appropriate decisions.
- Team work so as to attain the various developing objectives.
- Proactive functioning.
- Paying more attention to details.
- Demonstration of enthusiasm and commitment.
- Proper attention to practical aspects along with the strategic ones.
Sungold Milk is the product which we have considered as the product of the project. Sungoldmilk is a product sourced from prominent dairying Australian district which contain high quality of fresh milk. This product launches wide ranges of milk having less fat and high rate calcium and protein. This product is enriched with cream and is available I various flavors like chocolate and Iced Coffee flavors. This is a very fresh product and has a probability to revolutionize the milk product industry. The theories of operation management can be utilized to keep the concept of product in practice.
It is a strategy designed especially to define the process of raw material conversion into final output. There are primarily four types of process strategies viz., repetitive focus, process focus, mass customization and product focus.
The business efficiency relies completely on the selection of the best layout design for the long run. The layout which is product-oriented is moderated by machine utilization and job instruction so as to carry out the production process. Computed volume will be sufficient for the equipment utilization, the requirements of the customers are already justified and successfully completed to ensure the raw materials’ quality and equipment. This product oriented layout will be helpful in reducing the variable costs per unit of the product and also the cost of handling in the pre production process. This will also decrease the amount of work needed to be done in the process inventories.
The manufacturing operations have been designed as follows.
Expected sales – 14000 units per week
Available time – 2 shifts, 8 hours per day, 7 days per week
Number of production lines – 2
Volume of milk per batch – 300 litres (~ 300 units)
| Activity Code | Activity | Predecessor | Time (minutes) |
| A | Preliminary storage of raw milk | – | 120-180 |
| B | Hot water preparation | – | 7-10 |
| C | Ice water storage | – | continuous |
| D | Heat treatment of milk | A, B, C | 40-65 |
| E | Intermediate storage | D | 40 |
| F | Filling line | E | 2 |
| G | Randomized checks | F | 15 |
| H | Final packaging and storage | G | 6 |
Total time per package = 223 mins
Available time = 2 shifts * 8 hours per day * 7 days per week * 60 = 6720 mins per week
Cycle time = 6720 minutes per week / 14000 units per week = 0.48 mins per unit
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Practically speaking, capacity depict the number of products which can be produced within a specific amount of time. Rise in capacity can be too costly whereas low capacity can reduce the rate of interest of the customers. Thus identification of the level of capacity is very vital. (Schmitt and Vollmann, 1982)
The following chart gives a more accurate description of the time consumed per batch of ram milk (300 litres).
Optimal throughput time = 120 min + 40 mins + 40 minutes + 2 mins + 15 minutes + 6 minutes = 223 minutes
Bottleneck of the process = The heat treatment of the milk and the intermediate storage with the milk for cooling are the actual bottlenecks of the process at 40 minutes each.
It is the capacity which represent the optimum level of output which can be generated under a given perfect condition. But in most cases, the actual capacity is considerably lesser than the assumed capacity because of the circumstances which couldn’t restrict the organization.
It is the rate of expectation which organizations are targeting to attain a set goal. Efficient rate of capacity is repeatedly less than the designed capacity because of several reasons which can incident upon unexpected times like breakdown of machinery, unavailability of employees and external factors.
It is the capacity that can be generated under every possible circumstances. This value can be maintained as it is equivalent to effective capacity along with huge amount of invention.
It is the case in which prediction or measurement of the future event is done. The forecasting are usually carried out through studying the past records of the industry or company, such as sales records or any other records of the past. Basically there are 3 categories of forecasting:
- Long Range Forecasting
- Medium Range Forecasting
- Short Range Forecasting
It is regarded as the one of the most costly assets of any organization. Near about 50 percent of the invested capital on the inventory of product manufacturing process depends on the stocked inventories. Let us consider the project is based on ABC analysis. ABC analysis consist of monitor inventories, which is expensive and inexpensive inventories. The main objective of this analysis is to determine the annual outcome. Here, the inventory items are classified as A, B, and C. A depicts the highest percentage and their inventory representation is very low, B defines the medium percentage and their representation is also medium and lastly, C depicts the lowest percentage with low rate of inventory representation.
A separate advantage is also attached with this ABC analysis while the inventories management. The classification of the entire inventories also makes the entire procedure very organized and simple. The table below shows the forecasted commodities for Sungold Milk.
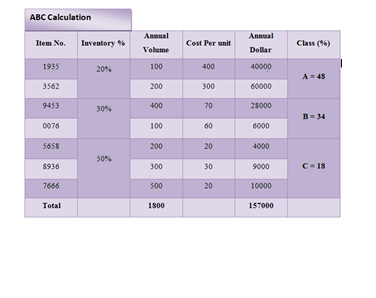
| Item No. | Inventory % | Annual Volume | Cost Per unit | Annual Dollar | Class (%) |
| 1935 | 20%
|
100 | 400 | 40000 | A = 48 |
| 3562 | 200 | 300 | 60000 | ||
| 9453 | 30%
|
400 | 70 | 28000 | B = 34 |
| 0076 | 100 | 60 | 6000 | ||
| 5658 | 50%
|
200 | 20 | 4000 | C = 18 |
| 8936 | 300 | 30 | 9000 | ||
| 7666 | 500 | 20 | 10000 | ||
| Total | 1800 | 157000 |
This is a process which help us to mitigate the wastes that enhance development so as to fulfil the requirements and expectations of the customers. Thus, it is necessary to implement the lean operation which can effectively influence the entire framework of the business in a positive way (Kennedy and Widener, 2014).
Effective Supplier Partnership
The producer has to collaboratively function together with the suppliers having common goal of mitigating the wastes. This might benefit the purchases along with the supplier, thereby reducing unnecessary activities. This may also enhance the quality of the product and reliability and consignment.
This form of layout helps in reducing the amount of waste while locating the raw materials via production line. Curtailing the distance between the locations of workstations.
Quality is the aspect which attracts the customers. With the raising quality the customers expectation also raises and this give rise to enhancement of demand of the product. “Successful quality management leads to the succession within differentiation, response and low cost. Talking further, differentiation creates competitive advantages in order to lead the world market” (Anon, 1993).
When it comes to TQM i.e. Total Quality Management, it generally defines the total quality of the production of an organization. TQM can be successfully achieved through various additional concept. Around 7 types of concepts exists through which TQM can be effectively attained.
Here, the entire requirements of the fresh innovative invention of the product has been identified. The steps of the product design are required to be followed so as to make the entire process of production a successful one. Sharp focus on product oriented strategies are given so as to organize the entire process of production. It is expected to maintain effective capacity so as to fulfill the demand and requirement of the customers. Market surveys are also required to be done. ABC analysis has be conducted for the future forecasting. Therefore the steps and the discussed strategies along with the approaches can efficiently make the fresh new product of the brand popular and demanding.
Reference(s)
Chiu Y. C., Chen B., Shyu J. Z., Tzeng G. H., (2006). An evaluation model of new product launch strategy, www.elsevier.com/locate/ technovation, Vol. 26, pp. 1244-1252. In Patil, HM, Sirsikar, SS and Gholap, NN (2017). Product Design and Development: Phases and Approach, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), 6(7), pp. 180-187
Dhoul, T., (2019). What is Operation Management? Viewed on: 23rd October. Retrieved from: https://www.topmba.com
Jauregui-Becker J. M. , Wits W. W. (2013), An information model for product development: a case study at PHILIPS Shavers, 2nd CIRP Global Web Conference, www.sciencedirect.com Procedia CIRP, vol. 9, pp. 97 – 102
Jiao J(R)., Chen C. H. (2006), Customer requirement management in product development: A review of research issues, Concurrent Engineering: research and applications, Vol. 14, No. 3
Lee H. C., Herawan T., Noraziah A. (2012). Evolutionary grammars based design framework for product Innovation, INSODE 2011, www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Technology, vol. 1, pp. 132 – 136
Patil, HM, Sirsikar, SS and Gholap, NN (2017). Product Design and Development: Phases and Approach, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), 6(7), pp. 180-187
Unger D., Eppinger S. (2011). Improving product development process design: a method for managing information flows, risks, and iterations, Journal of Engineering Design Vol. 22, No. 10, pp. 689–699
Wankhade N. P., Sridhar V. G., Annamalai K. (2014), New product development by DFMA and rapid prototyping, ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 9(3).
Wcbf.com. Great Ocean Road – Milk. Viewed on: 23rd October. Retrieved from: https://www.wcbf.com.au/en/our-products/gor-milk
Increase in profitability through Quality
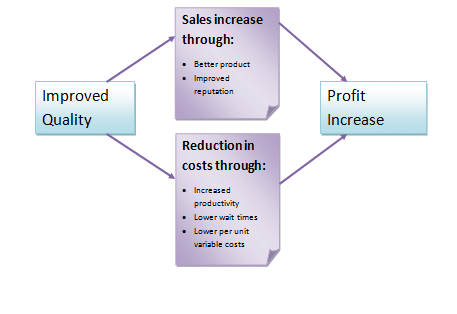
Appendix 2
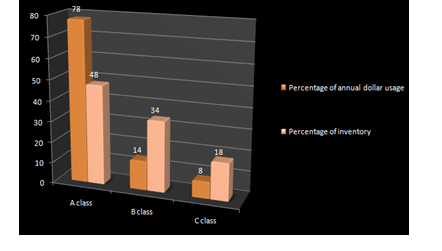
Appendix 4 (Product design and development process)
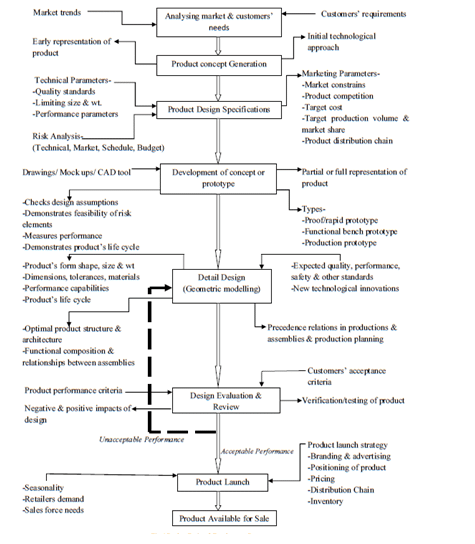
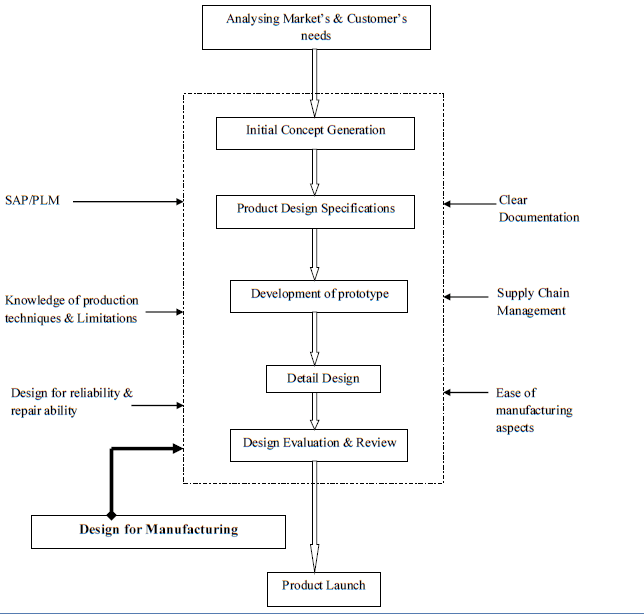
Design Manufacturing Process


