OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT AND SERVICE EXCELLENCE
Executive Summary
The present report has shed light on the discussion of operation management and service excellence of Starbucks. In the first part comparison between Starbucks and Greggs has been done using 4Vs model, performance analysis and design analysis. In the second part globalization strategies of Starbucks and role of quality management have been discussed. Besides, major requirements and challenges faced by Starbucks in quality management have been analysed. Furthermore, analysis of quality management and its important resources have been done in this report. Some recommendations have been done to improve the performance of Starbucks.
The 4V analysis of an organization gives an idea about their business existence. This 4V indicates volume, variety, variation and visibility. As mentioned in the study by Block et al. (2019), these parameters are measured by high to low. In order to compare two organizations, 4V is a useful method as it describes the structure of the organization. It gives a general idea about organizational products, their customer demands, size of the organization and visibility in the market. This model is going to help in differentiating the business performance and the overall existence of Starbucks and Greggs
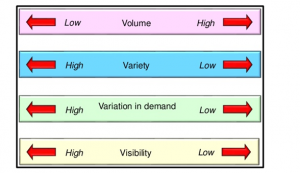
Figure 1: 4V model
(Source: Block et al. 2019)
The description of these parameters is mentioned below:
Volume
This parameter of 4V model indicates two aspects such as the size of the organization and the purchase by the organization. As discussed in the study by Tröger and Alt (2017), organizations with high volume that have many outlets and its global expansion are high. Besides, their purchasing capability should be high and they do that mainly for reducing cost. In the case of Starbucks, they have almost 80000 stores all over the world and Greggs have 2500 stores. Starbucks has these stores in almost 80 countries (Starbucks.com, 2020). However, Greggs is mainly based on the UK. Apart from that, the purchasing power of Starbucks is much higher than Greggs. Comparing these factors it can be said that the volume of Starbucks is high and the volume of Greggs is medium.
Variety
This parameter indicates the variety of products and markets from high to low. In comparison between Starbucks and Greggs, it has been seen that Greggs have more products than Starbucks. Starbucks mainly concentrate on coffee, cappuccino and similar products. As depicted by Founda et al. (2016), other products are available at Starbucks however; people prefer coffee and related products more. However, in Greggs, sandwich, sausage rolls, bakery products, soups and many more products are available (Greggs.co.uk, 2020). Variety in products is one of the core challenges faced by Starbucks. Therefore, it can be said that Starbucks has less variety and Greggs has high variety.
Variation
This segment of 4V model indicates the variation in demand by the customers. High variation indicates that customer demands vary a lot and thus the business is seasonal and low variation indicates that the organization is in demand all around the year. Starbucks and Greggs are not well-established brands and both are in the food industry. Thus, the variation in demand is low in both of these organizations.
Visibility
Visibility indicates the availability of products or stores in the market. Starbucks has plenty of offline stores and thus is visible in the market. However, they stop online deliveries which make this organization comparatively less visible in the market than before. Greggs have both offline and offline delivery stores. As mentioned in the study by Robbins and Robbins (2018), they deliver food to the customers to show their visibility in the market. However, it has fewer stores than Starbucks. Both these companies have high brand value and due to this have high visibility in the market.
| 4Vs | Starbucks | Greggs |
| Volume | High | Medium |
| Variety | Medium | High |
| variation | Low | Low |
| Visibility | High | High |
Table 1: 4V comparison between Starbucks and Greggs
(Source: Learner)
2. Performance objective analysis
It is imperative to analyse the performance of an organization to compare organization. This performance is analysed based on five parameters. The performance of Starbucks and Greggs are compared based on these parameters below:
- Cost
Cost of products is the primary parameter for analysing the performance. It is one of the biggest factors as customers are attracted towards the company which gives products at a low price and the product is value for money. As depicted by Marie (2019), the price range of Starbucks and Greggs are pretty similar. It has been seen that in the UK freshly brewed coffee from Starbucks costs around 1.85 GBP. It is the price of the tall glass size (Starbucks.com, 2020). On the other hand, the Regular Latte price of Greggs is around 1.75 GBP (Greggs.co.uk, 2020). These are branded companies therefore this price range is higher than the normal stores and thus it can be said that the cost is high.
- Quality
Customer satisfaction is the main motive of organizations and for that; they need to concentrate on quality. As mentioned in the study by Wilkins et al. (2019), Starbucks has its own quality standards and concentrate on production of coffee beans by contacting farmers. They instruct the farmers and guide them to meet their required standard and thus they can provide high-quality products. Greggs also maintain its product quality by contacting high-quality raw materials suppliers. However, the quality provided by Starbucks is better than that of Greggs. In terms of service quality Greggs is better than Starbucks.
III. Dependability
Dependability indicates the business dependency on customers and their relationship with them. As cited in the study by Giles et al. (2017), in terms of dependability with customers Starbucks has more customer trust thus customers are more dependent on Starbucks rather than Greggs. As the visibility and stores of Starbuck are more than the stores of Greggs, customer dependency is more (Greggs.co.uk, 2020). In terms of dependability towards suppliers, Starbucks is less dependable as they have their contacts with farmers and directly collect their raw materials from there. However, Greggs are more dependent on their distributors for raw materials and other services.
- Flexibility
Flexibility indicates the variety of products available in the market and it is one of the major performance indicators. As depicted in the study by Campbell and Helleloid (2016), Starbucks mainly rely upon coffee oriented products such as Fresh-brewed coffee, Frappuccino, cold coffee, coffee and non-coffee blended beverages and many more. Coffee related products are more in Starbucks and thus they can offer limited products which indicate medium flexibility. Besides, having other products than coffee people prefer to take coffee from Starbucks as it is famous for coffee oriented products. Greggs offer coffee, cheese and onion bake, sausage roll, chicken bake, veg bake and many more items (Greggs.co.uk, 2020). Therefore, their offerings are higher than Starbucks and thus the flexibility of Greggs is higher than the flexibility of Starbucks.
- Speed
Speed indicates the service and delivery speed by the organizations. As mentioned in the study by Theis and Adams (2019), it is directly associated with customer satisfaction as people want companies that give fast delivery and thus waiting time becomes less. It has been seen that the delivery speed of Starbucks is comparatively higher than that of Greggs. Average waiting time for the customers is less than Greggs. However, both of these companies need to focus on customer management and store management. Greggs have online stores and thus they need to focus on online deliveries. Their online delivery is comparatively slower than other companies.
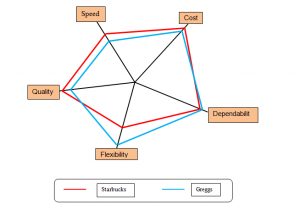
Figure 2: Performance map of Starbucks and Greggs
(Source: Learner)
Design analysis includes parameters such as customer service design and store design. As mentioned in the study by Mandzila and Zéghal (2016), both of these designs are done to create a good impression on the customer and provide them with satisfaction. Starbucks and Greggs are both in the food industry and thus customer satisfaction is their only way to reach corporate objectives. The management of these companies design the customer service process and store layout to attract customers and give them comfort.
They prepare the blueprint of the customer service process which indicates the way of dealing with customers. It includes the total procedure from the customer entering the store to when they leave the store. This procedure influences the 4V models and performance analysis parameters of the company. Overall these models indicate the customer’s satisfaction rate and performance of the companies as customer service providing organizations. Customer service procedure indicates the way to satisfying customers which can increase the volume, visibility, variation and variety of the organization.
In case the customer gets overall satisfaction then the volume of the organization and their visibility will increase (Amaral, 2019). This blueprint includes the food offering and communication with the customers and thus improving this segment of customer service process variety and variation of demand can increase by collecting feedback from the customers. Following this procedure, overall revenue generation will increase which can give organizations competitive advantage and thus their performance analysis parameters will be developed. Starbucks and Greggs have a well-planned customer service process which helps them to increase their sales rate.
Store layout indicates the design of the store and what materials will be at what place such that the overall impression of the store is good to the customers (Rahman et al. 2016). This store layout gives customers a psychological satisfaction as they feel more comfortable in a well-designed place. Therefore, their number of visits increase and thus the total sales rate of companies increase. This store layout design gives Greggs and Starbucks a competitive advantage as they plan their stores with the choice of the local people and overall people like their design of the store.
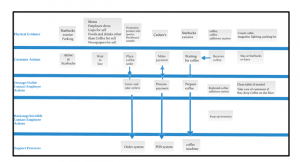
Figure 3: Customer service blueprint of Starbucks
(Source: Starbucks.com, 2020)
A. Introduction of quality management
Quality management is the process by which an organization maintains its product or service quality. It is a process of monitoring activities associated with the production of the organization to achieve a particular standard.
B. Scope of quality management
The scope of quality management states how quality management operations should be done. It defines which parameters should be excluded from production or services and defines proper justification for that. It selects elements that give the organization a competitive advantage over other companies. It is expected that proper quality management is going to increase the quality of the products which can further increase customer satisfaction.
C. Quality management of Starbucks
Starbucks gives the first priority to the quality management of their products. They believe that customers can be satisfied by giving high-quality products and constant quality maintenance. The quality management team of Starbucks concentrates on raw material production to the manufacturing procedure to check the standard.
2. Global expansion strategy and macro-environment of Starbucks
A. Global expansion strategy of Starbucks
Starbucks is one of the biggest food chains in the world. It has over 30000 retail stores throughout the world. The cardinal strategy of global expansion is addressed below:
- Starbucks uses the brand value as their main strategy for expanding globally. As they are experienced in this field higher management makes the use of brand value strategically to open more stores.
- Marketing strategy is one of the key methods for their expansion. They use a digital marketing strategy to expand in 80 countries (Jun et al. 2019).
- Market segmentation and target customer selection are one of their best global expansion strategies.
- They select locations strategically to increase the sales rate which helps in revenue generation.
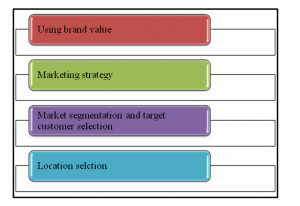
Figure 1: Global expansion strategy
(Source: Learner)
B. Importance of quality management in global business expansion
Quality management of Starbucks has an imperative role in global expansion of the company. The importance of quality management is mentioned below:
- They use their own quality standards and guidelines namely coffee sourcing guidelines. They set these standards to all of their operational units at the time of producing coffee beans. Farmers maintain this quality which helps Starbucks to expand its operation globally.
- Starbucks has a strict and well-managed quality management team which helps them in global expansion. As discussed by Alwaleed et al. (2019), the overall observe the quality of raw materials which help them to supply the same quality raw materials to every operating sector.
- Quality management indicates people management as they are the one responsible for managing the whole unit. Starbucks has distinct rules and regulations which increase the integrity of the people throughout the world. They have ethics and maintaining these ethical guidelines people can deliver their full efficiency which improves the quality management of Starbucks as well as help in expanding their units.
C. Impact of macro business environment
Macro business environments such as inflation, government rules & regulations, business policies, people behaviour, purchasing habits and many others have a great impact in global expansion of Starbucks. Starbucks analyses these factors to analyse their possible business advantages and disadvantages. They evaluate these factors and in case they think most of these factors are in the support of their company they decide to expand theirs.
3. Major requirements and challenges in quality management
Starbucks has many parameters for managing the quality of the products. Quality management also includes the overall quality of the organization that can give customer satisfaction. The major requirements of quality management of Starbucks are mentioned below:
- Maintaining the quality of raw material is required for quality management. Starbucks has a team that verifies and guide the production of raw materials. They instruct the farmers and have their Coffee and Farmers Equity (CAFE) program which leads to connecting with local farmers (Starbucks.com, 2020). This is done to maintain the quality of raw materials which is a major requirement of quality management.
- Quality management needs a good leader in every department who can guide their subordinates to achieve the organizational objectives (Elfaki et al. 2019). In all of their 80 operating countries, they have a regional head who is the leader and responsible to manage the operations in that country. Under them, many leaders are there to help in managing quality.
- Employees or especially the salesperson of Starbucks are the key requirements for Starbucks (Başaran, 2016). They are the face of the company and can give the ultimate customer satisfaction
- Franchises and distributors are the requirements as they have their own strategy of running business. Their operational strategies help in quality management of Starbucks.
Key challenges of Starbucks in quality management are addressed below:
- Due to a huge operational area and a lot of independent franchises maintaining the ultimate quality of the products is challenging (Lakshminarayanan et al. 2017). The product quality is sometimes different store to store as they independent shop owners apply their own method of running business.
- Stereotypic products are another issue faced by Starbucks globally due to quality management. Their quality management procedure is complex as it aims to give ultimate customer satisfaction. Maintaining the same quality for a lot of products is costly and needs immense effort from the organization. Thus, they cannot offer customers a variety of products.
- It is a huge organization and divided into small stores. It is challenging to maintain the integrity of the people. According to Shirdastian et al. (2019), franchises have their own rules and regulations which are applicable for their employees only and thus a clear differentiation in the employee’s behaviour is visible throughout the world.
4. Analysis of quality management of Starbucks
A. Managing resources for quality management
Resource management is important to run the global business of Starbucks. Overall business of Starbucks is based on the resources they have. These resources are mentioned below:
Quality management tools and information resources
In order to manage the overall quality of the outcome of the organization several tools are used and these tools are one of the biggest resources for quality management of Starbucks. According to Fischer and Roy (2019), tools such as flow chart, Pareto chart, co0ntrol chart, scatter diagram, histograms and many are used to plot the information for quality analysis by Starbucks. These tools are used by a quality management team of Starbucks to evaluate the quality of raw materials, final products, market records, competitive analysis and many more. Managing these tools and analysing the business scenario is imperative for quality management.
Raw material
This is one of the major resources of quality management. Verifying the quality of the raw materials and distributing them to the stores of Starbucks is essential for quality management. Therefore, Starbucks focuses on its farmers and depends on its logistics facility to maintain overall quality management.
Human resources
Human resources are the most important resources for any organization for achieving their corporate goals (Tikson, 2018). Human resources include management of Starbucks, leaders and their teams, all employees and other stakeholders, franchisees, investors and many more. These resources of Starbucks work together to achieve one single goal that is giving customer satisfaction and globalization of Starbucks
Financial resources
In order to maintain the quality management of Starbucks financial support is always essential. Investors help Starbucks to manage these resources. As discussed by Sisson and Bowen, (2017), Starbucks has much financial support and thus they can improve quality management. They take financial risks to improve their overall operation and these financial supports are managed by their investors.
B. Effect of quality management in organizational performance
The whole organization depends on customer satisfaction and overall sales rates. This is the main parameter to measure the organizational performance of Starbucks (Ahmed and Khan, 2018). It has been seen that quality management is done to improve the overall quality of the products and the employee. Improving quality of employees and products of Starbucks can increase the customer satisfaction level. Therefore, quality management is associated with the organizational performance of Starbucks.
Running the operations of a big organization such as Starbucks is pretty challenging. Employees and other stakeholders are planning to mitigate these challenges. However, Starbucks still cannot come over with these challenges. It is expected that more planning and analyses of the business dynamics are required such that quality management procedures improve by mitigating these challenges. A separate team of Starbucks is working on these issues to improve organizational performance.
D. Theory of quality management
Deming’s theory of total quality management
Deming’s total quality management theory indicates the elements that are required to control quality management (Corbacioglu, 2016). These elements are customers based and aim to give high-quality service or product quality. These elements are mentioned in the figure given below:
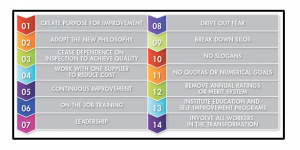
Figure 2: Deming’s elements of total quality management
(Source: Corbacioglu, 2016)
This theory also gives guidelines to the ways of achieving total quality management. This theory proposes a PDCA cycle that is plan, do, check, and act. As mentioned by Dudin et al. (2017), for achieving total quality management one should plan the aim and ways to achieve the quality goal, then execute those plans and check or monitor whether everything is running well or not. Finally, one should act to close the task and repeat the process for the next aim. Starbucks can apply this theory to improving its quality management and achieving their business goals.
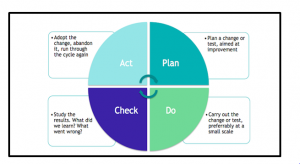
Figure 3: PDCA cycle
(Source: Dudin et al. 2017)
Situational leadership theory
As per situational leadership theory, a leader should have multiple styles of leadership and as per the situation; one should apply a style (Meier, 2016). That individual should be able to understand the situation and need to act accordingly.
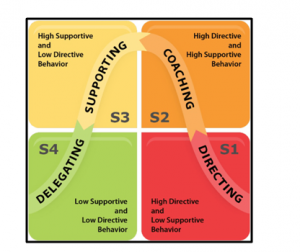
Figure 4: Situational leadership theory
(Source: Meier, 2016)
A. Description of Recommendation s
- A separate team should be allocated to observe the franchise and independent store owners. As discussed in the study by Haq and Boddu (2017), they need to visit the stores and should observe the business performance of these stores. They can discuss the major issues faced by those stores and can guide them to overcome these challenges.
- Investment in the R & D department should be more as Starbucks needs to develop new products. The product must be unique and also should be made by the raw materials they have. They can make several coffee items and can add new flavours to it which can be linked by the customers.
- In new opening stores, they can start discounts to attract customers. As depicted in the study by Dora et al. (2016), free sample testing of new products can be done by stores to let the customers be aware of the new item.
- Employee training is imperative to increase their customer handling skill. This training program can be organized by contracting with behavioural training providing institutions.
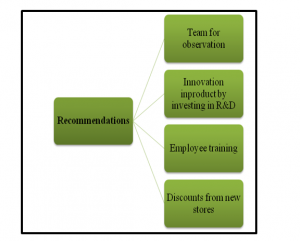
Figure 5: Recommendations
(Source: Learner)
B. Linking recommendations with challenges
- The verification by the team of Starbucks can improve the quality of the final products by Starbucks. They can set the standards of the products and help quality management. Besides, these suggestions by these experts can improve the overall sales of Starbucks.
- Investing in innovation can mitigate the issues associated with less variety of products. As mentioned in the study by Jung and Chung (2016), the addition of new flavours can attract customers which lead them to achieve business goals of Starbucks.
- Discounts can attract new customers and a free product sample is going to attract them for purchasing new products which will solve the issues of a variety of products.
- Training can increase the integrity of the employees. The customer behaviours standard is going to be the same after taking the training.
Based on the above discussion it can be said that Starbucks controls its quality management system with good approaches. Starbucks uses brand value; choose a good location, offer quality foods and many more strategies to expand its global business. Managing the quality of raw materials is the main motive behind their global expansion. Besides, it has been seen that a good quality management team, leadership skills, and standard ways of production are the key requirements. They face challenges in terms of product variety, no standard behavioural quality of employees and many more. They need resources such as quality management tools. Raw materials, human & financial resources for improving quality management are imperative resources. Besides, it has been found that providing training, allocating visiting team for franchises, innovation of new products can improve their performance.
Ahmed, B. and Khan, R.A., 2018. Influence of Quality Management Practices On Employees’ Perception of Organizational Effectiveness at Ks&E. IBT JOURNAL OF BUSINESS STUDIES (JBS), 14(2).
Alwaleed, N., Al Huwail, N.H., Singh, S. and AlMejhem, A., 2019. A Case Study on STARBUCKS. Journal of the community development in Asia, 2(2).
Amaral, V., 2019. Analysis the implementation of quality and environmental management in petrochemical industries. Envirosan: Jurnal Teknik Lingkungan, 2(1), pp.1-8.
Başaran, B., 2016. The effect of ISO quality management system standards on industrial property rights in Turkey. World Patent Information, 45, pp.33-46.
Block, C.J., Cruz, M., Bairley, M., Harel-Marian, T. and Roberson, L., 2019. Inside the prism of an invisible threat: Shining a light on the hidden work of contending with systemic stereotype threat in STEM fields. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 113, pp.33-50.
Campbell, K. and Helleloid, D., 2016. Starbucks: Social responsibility and tax avoidance. Journal of Accounting Education, 37, pp.38-60.
Corbacioglu, S., 2016. Influence of Taylorism on Deming’s Quality Management. Inquiry-Sarajevo Journal of Social Science, 2(2), pp.77-87.
Dora, M., Kumar, M. and Gellynck, X., 2016. Determinants and barriers to lean implementation in food-processing SMEs–a multiple case analysis. Production Planning & Control, 27(1), pp.1-23.
Dudin, M.N., Smirnova, O.O., Vysotskaya, N.V., Frolova, E.E. and Vilkova, N.G., 2017. The deming cycle (PDCA) concept as a tool for the transition to the innovative path of the continuous quality improvement in production processes of the agro-industrial sector. European Research Studies, 20(2), p.283.
Elfaki, T.E.M., Mustafa, A.M.A.E. and Abdalla, A.M., 2019. The Impact of Documents Review on Improving of Management System According to Requirements of ISO: IEC 17025: 2005 (A case study: NANO for Measurement and Calibration Center, Khartoum North-Sudan). organization, 3(10).
Fischer, D. and Roy, K., 2019. Market Entry in India: The Curious Case of Starbucks. Rutgers Business Review, 4(2).
Founda, D., Kazadzis, S., Mihalopoulos, N., Gerasopoulos, E., Lianou, M. and Raptis, P.I., 2016. Long-term visibility variation in Athens (1931–2013): a proxy for local and regional atmospheric aerosol loads. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(17), p.11219.
Giles, G.E., Mahoney, C.R., Brunyé, T.T., Taylor, H.A. and Kanarek, R.B., 2017. Caffeine and theanine exert opposite effects on attention under emotional arousal. Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 95(1), pp.93-100.
Greggs.co.uk, 2020. At a glance. Greggs. Available at: https://corporate.greggs.co.uk/at-a-glance [Accessed on 2nd April 2020]
Haq, A.N. and Boddu, V., 2017. Analysis of enablers for the implementation of leagile supply chain management using an integrated fuzzy QFD approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 28(1), pp.1-12.
Jun, Y., Ma, Y. and Lee, H., 2019. Empirical Study of Space Localization Approach on Brand Attitude: The Case of Starbucks in South Korea. Archives of Design Research, 32(4), pp.27-36.
Jung, H. and Chung, K., 2016. Knowledge-based dietary nutrition recommendation for obese management. Information Technology and Management, 17(1), pp.29-42.
Lakshminarayanan, S., Maggio, E. and Best, S., 2017. Kofi or Coffee-Starbucks Enters the Indian Market. Journal of Case Studies, 35(2), pp.44-55.
Mandzila, E.E.W. and Zéghal, D., 2016. Content analysis of board reports on corporate governance, internal controls and risk management: evidence from France. Journal of Applied Business Research (JABR), 32(3), pp.637-648.
Marie, A.L., 2019. The Effect of Service Quality and Servicescape Towards Customer Satisfaction, Starbucks Coffee, Jakarta. TRJ Tourism Research Journal, 3(1), pp.56-70.
Meier, D., 2016. Situational Leadership Theory as a Foundation for a Blended Learning Framework. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(10), pp.25-30.
Rahman, Z., Suberamanian, K. and Zanuddin, H.B., 2016. Social media content analysis-A study on fanpages of electronics companies. International Journal on Global Business Management & Research, 5(1), p.87.
Robbins, M.M. and Robbins, A.M., 2018. Variation in the social organization of gorillas: Life history and socioecological perspectives. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 27(5), pp.218-233.
Shirdastian, H., Laroche, M. and Richard, M.O., 2019. Using big data analytics to study brand authenticity sentiments: The case of Starbucks on Twitter. International Journal of Information Management, 48, pp.291-307.
Sisson, D.C. and Bowen, S.A., 2017. Reputation management and authenticity: A case study of Starbucks’ UK tax crisis and “# SpreadTheCheer” campaign. Journal of Communication Management, 21(3), pp.287-302.
Starbucks.com, 2020. About. Starbucks. Available at: https://www.starbucks.com/about-us/company-information/starbucks-company-profile [Accessed on 2nd April 2020]
Theis, D.R. and Adams, J., 2019. Differences in energy and nutritional content of menu items served by popular UK chain restaurants with versus without voluntary menu labelling: A cross-sectional study. PloS one, 14(10).
Tikson, S.D.S., 2018. Human Resource Policies and Work Culture: A Case of Starbucks. JBMI (Jurnal Bisnis, Manajemen, dan Informatika), 15(1), pp.1-12.
Tröger, R. and Alt, R., 2017. Design options for supply chain visibility services: learnings from three EPCIS implementations. Electronic Markets, 27(2), pp.141-156.
Wilkins, E., Morris, M., Radley, D. and Griffiths, C., 2019. Methods of measuring associations between the Retail Food Environment and weight status: importance of classifications and metrics. SSM-population health, 8, p.100404.



Thanks so much for the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
https://rylanzocp54321.wikijm.com/535548/stainless_steel_pipe_nipples
Really informative blog article. Want more.
https://johna825xgo0.develop-blog.com/profile
Muchos Gracias for your article post. Fantastic.
https://devinvrlb11108.bloggazza.com/24977822/the-benefit-of-custom-plastic-parts
Say, you got a nice post.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
https://crushon.ai/
I really enjoy the blog.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
https://crushon.ai/
Thanks-a-mundo for the article.Much thanks again. Want more.
https://www.laifentech.com/
Very neat article.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
https://www.orangenews.hk
Great blog article.Really thank you! Really Cool.
https://inspro2.com/
Im obliged for the article.Really thank you! Awesome.
https://talkietalkie.ai/
Major thankies for the blog post.Thanks Again. Will read on…
https://meencantalapinturadediamantes.es/collections/accesorios
Great article post. Great.
https://crushon.ai/
Very informative blog article.Really thank you! Great.
https://nsfw-ai.chat/
Major thankies for the post. Much obliged.
https://nsfw-ai.chat/
Thanks so much for the article post.Thanks Again. Fantastic.
https://summerseasiren.com/collections/period-underwear
Great post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
https://caidencqer65421.wikinstructions.com/525156/unleashing_the_power_of_all_in_one_99_114_121_112_116_111_your_ultimate_companion_in_the_world_of_99_114_121_112_116_111_currency
Thank you for your blog post. Want more.
https://andresgklk79023.blog2news.com/26252891/luxury-side-tables-for-living-room
Awesome blog. Much obliged.
https://cesarbpdp54219.life-wiki.com/598018/duct_cleaning_services
A round of applause for your blog.Really thank you! Fantastic.
https://masses-of-entrepreneurs.mn.co/members/22546142
Thank you for your blog article.Thanks Again. Cool.
https://jaredbpco54310.jasperwiki.com/5783626/what_is_osha_courses_online
Major thankies for the post.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
https://jasperjv3qz.blogunok.com/25431040/unveiling-romantic-escapes-maldives-honeymoon-packages
Appreciate you sharing, great blog article.Really thank you! Will read on…
https://josuearhv88754.law-wiki.com/590609/the_advantage_using_best_payroll_software
Fantastic post. Fantastic.
https://paxtonsgtf10986.cosmicwiki.com/551772/what_is_osha_courses_online
Thanks so much for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
https://arenaplus.ph/
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic article post.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
https://www.sonhungbac.com/
Muchos Gracias for your blog.Thanks Again. Will read on…
https://baixicans.com/
Appreciate you sharing, great article.Much thanks again. Great.
https://atop-education.degree/
Major thanks for the blog.Thanks Again. Fantastic.
https://gbdownload.cc/
I cannot thank you enough for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
https://fouadmods.net/
wow, awesome blog post.Thanks Again.
https://gbdownload.cc/
Really informative blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Fantastic.
https://fouadmods.net/
Major thanks for the blog.Really thank you! Want more.
https://nsfwgenerator.ai/
Muchos Gracias for your article post.Much thanks again. Cool.
http://animegenerator.ai/
Thank you for your post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
https://elliottjvhs65320.blogsvila.com/25907729/trip-package-tips
Appreciate you sharing, great blog post.Thanks Again. Awesome.
https://zionrgug21097.ourabilitywiki.com/9076207/the_advantage_using_bigcartel_ecommerce_platform
A round of applause for your article post.Thanks Again. Will read on…
https://claytonixly98764.ttblogs.com/5226234/trip-package-tips
Thank you for your article post. Really Great.
https://gracep368afj7.bloggerswise.com/profile
A big thank you for your blog.Really looking forward to read more. Keep writing.
https://ericktgug21987.blogolenta.com/22695627/all-you-need-to-know-about-satta-matka
A big thank you for your article post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
https://www.slcdunk.com/users/Bestspaandbeautyservices
I really like and appreciate your post.Much thanks again. Great.
https://sergioereq54310.wikipowell.com/5297786/tips_to_find_spa_and_beauty_services
Hey, thanks for the blog.Really thank you! Cool.
https://socialistener.com/story2227657/zenoids-leading-the-way-in-digital-solutions-across-india-and-uae
Enjoyed every bit of your blog.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
https://www.hommar.com/
A big thank you for your article.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
https://www.hkcashwebsite.com
Im thankful for the blog article.Really thank you! Want more.
https://www.kol.kim/custom-design/
Thank you for your article post.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
https://blog.huddles.app
I cannot thank you enough for the article post. Really Cool.
https://blog.huddles.app
I really like and appreciate your article. Really Cool.
https://crushon.ai/
Major thankies for the article post.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
https://www.hommar.com/products-47088
Great, thanks for sharing this article post. Will read on…
https://keeperaitest.com/
I value the blog post.Thanks Again. Great.
https://crushon.ai/character/7573a4cc-a7fc-4c3b-9b11-0f296d2bde95/details?not-for-all-audiences=true&utm_medium=home
Really enjoyed this article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
https://spicychat-ai.online/
Fantastic post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
https://crushon.ai/
I truly appreciate this article post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
https://crushon.ai/
I really like and appreciate your article post.Really thank you!
https://crushon.ai/
A round of applause for your article.Thanks Again. Want more.
https://smashorpass.app/
A round of applause for your blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
https://www.kol.kim/custom-design/
I value the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
https://www.yinraohair.com/wigs/shop-by-style/lace-wigs
A big thank you for your blog article.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
https://www.yinraohair.com/human-hair/tape-ins
Looking forward to reading more. Great blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
https://www.yinraohair.com/cosplay/shop-by-color/yellow
Im thankful for the blog article. Will read on…
https://www.metalfenceworks.com/e_productshow/?60-pedestrian-barrier-heavy-duty-and-long-lasting-60.html
Thanks again for the article post.Really thank you! Awesome.
https://blog.huddles.app
Awesome post.Much thanks again. Great.
https://blog.huddles.app
Looking forward to reading more. Great blog article.Really thank you! Want more.
https://umhom13.com
I value the article.Really thank you! Really Great.
https://umhom13.com
Major thankies for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Really Cool.
https://crushon.ai/trends/nsfw_character_ai
Major thanks for the article post.Really thank you! Great.
https://girl-friend.ai/
I loved your article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
https://honorcase.com/
Thanks so much for the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
https://blog.huddles.app
Major thanks for the blog.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
https://www.hkcashwebsite.com