The Effects of Organizational Culture on Leadership (Area of International Management)
Abstract
The key purpose of this study was to demine the impact of organizational culture on leadership performance. This study was conducted through survey over 100 managers from different retail companies.
From this study, it is identified that the organizational culture has a significant impact on the leadership performance. The organizational culture facilitates the leadership to enhance the job satisfaction level and motivation among the employees. The relationship between these two variables can be shown through the performance of the employee.
From this report, it can be analyzed that the organization managers adopt different models and theories for leading and managing the organizational work environment that is influenced from the organizational culture and brings different changes within the organization.
In addition, the leadership and culture models drive the leadership performance. At the same time, the passion and commitment, effective communication, innovation and positivity are crucial aspects of the organizational culture that also impact the leadership performance.
From this study, it can be recommended that development of different channels for the communication, transparency, reward and recognition strategy and value focus can be effective to improve the organizational culture for improving the leadership performance.
Topic: A study on the effects of organizational culture on leadership performance
After Second World War, globalization has become more advanced across the world which helps to enhance interdependence between nations economically, socially, politically and technologically.
This increased globalization formed many challenges including the needs for effective multinational organizations to be designed, to be identified and selected appropriate leaders for multinationals, and to be managed and communicated with diverse cultural workforces for organizations.
In short, Culture is a group of people’s ways of life, customs and script. According to Hofstede (1980), the definition of culture is the knowledge of beliefs, values, rules, norms, symbols and traditions which is common among a group of people.
On the other hand, leadership can be defined as a process by which an individual is influenced a group of people for achieving a common objective (Zaccaro and Horn, 2003).
They mentioned in their article that leadership can be conceptualized by five elements such as leadership is a process, leadership includes influence, leadership happens in group and leadership involves common goal. There have different leadership style being determined based on their concern, instigation and charismatic variables (Anderson and Sun, 2017).
Some of the key leadership styles are autocratic, democratic, transactional, transformational, authentic, servant, situational, laissez-faire, charismatic, and visionary.
Culture and leadership strongly influence on identifying value and people’s behaviour in a multinational company (Lord and Brown, 2001). Cultural values are important for leadership, as leadership complements subordination.
According to Gerstner and Day (1994), Except leaders are able to meet the expectations of subordinates about which leadership behaviour should be effectively conducted within the specific cultural context.
Leadership can directly impact on culture by personal styles, behaviours, thinking, leadership strategies, management approaches, and indirectly influence on culture by vision, mission and value, structures systems, job design and communication processes (Leidner, 2010).
The concept of organizational culture has been vastly research in the context of organization functioning. The continuation of a values and beliefs in an organisation forms the culture of the organisation which is known to influence the organisation activities, leadership behaviour, job attitude, behaviour and satisfaction (Neubert et al., 2009; Azanza et al., 2013).
It is a general behavioural pattern and principle that members develop in common. Also, depending on the pattern development, the culture of one organisation differs from one another.
Organisation culture is regarded to guide the workforce towards for achieve improved performance and achieve satisfaction in job. The culture has influenced thinking and action of organisational member (Azanza et al., 2013).
The organisation culture has been described by different dimensions such as innovation, risk taking, management support, leadership, reward, integrity, identity, conflict negotiation, control, communication according to the Stephen P. Robbins theory.
Also, Robbins theory indentified three the organisational culture determinants as top management actions, management selection practices and method of socialisations to sustain a culture (Arifin, 2015). The selection practice identifies the capable person with skills, traits and knowledge to get accomplish the organisation job.
The actions are the way the senior management behave, communicates, consider rewards and pays and gives freedom to other managerial level to develop a culture and socialisation refers to the coordination of the employees with other and with the prevailing organisation culture.
The effect of organisation culture are wide ranging and numerous but it is affect depends on the vigour of culture (strong or weak). The managers adjust their behaviour as per the culture to achieve the organisational goals and influence the workforce actions, and behaviour. This pointed toward the association between the culture and leadership.
Leadership is considered to be a psychosomatic as well as sociological trend based on the personality traits and effect of person or group convergence and situation needs respectively (Selznick, 2011).
It is identified that there are four factors essential to leadership these are leader, followers, situation and communication (Schein, 2010). The concept of leadership is viewed as a social process that influences the performance.
It is also recognised as a process that by which a person traits, abilities and capabilities are used to influences and direct others and interconnected them to achieve an objective. Thus, the leadership concept highlights process leadership (leader make use of their skills and knowledge) and trait leadership (leader make use of their traits like personality, beliefs, ethics and values) (Clark, 2015).
Also, the leadership style and performance is intervened the prevailing culture of the organisation (Tuan, 2010). The leadership style is defined by Yang et al. (2011) as the pattern of behaviour that a leader adopts to influence the followers. In other words, leadership style is the specific manner in which a leader guides and direct the followers to keep them motivated to achieve a common goal.
The three different types of leadership style was identified by Lewin as autocratic leadership which focuses on command and control by the leader and clear directions and expectation of the goals (Kurland et al., 2010).
Second is democratic leadership that focuses on giving guidance, involve participation of followers however, the final decision lies in the hand of the leader. The third is laissez-faire focuses on the delegation of decision making on the followers and little guidance from the leader.
Some other leadership styles are transformational leadership where the leader has abilities to motivate followers and develop positive changes in the follower group and transactional leadership style where the relationship among the leader and follower is seen as a deal where the follower obey the leader.
Among the different leadership styles, the transformational leadership and transactional leadership style has been closely linked with the organisation culture and performance.
These leadership styles along with authentic leadership style are viewed to promote the culture that is adaptable/ flexible towards changes, flexible and also known to promote an informal culture (McCleskey, 2014).
Importance of organizational culture and leadership in an organization
The relevance of organisational culture has been identified to contribute in organisation from its beliefs, principles and value system. The culture has been indentified to direct the employee interactions in the place of work and also control the way of employee behaviour (Ojokuku et al., 2012).
The culture is also recognised to promote an environment of healthy competition to improve the performance of the workforce in the workplace (Obiwuru et al., 2011). The strong and positive culture is also known to promote employee motivation to achieve business objective and keep their performances at expected level. In addition, the strong culture holds significant in developing a positive brand image in the minds of internal and external customers.
Link between organizational culture and leadership style
The culture of an organisation is related to the leadership behaviour as the core values affected the leaders and the development of the style for influencing other peoples.
Also, leaders are known to recognise their function and role in maintaining the organisational culture in relation to reducing workplace conflict, guiding high performing behaviour and developing a healthy work environment (Ojokuku et al., 2012).
The organisational together with leadership is also viewed to be incorporated with the performance measure (Schein, 2010). The culture and leadership and their relation is linked with the organisational performance.
Thus, there is a need to expand this towards the leadership performance as this study will focus on the organisation culture affect on the leadership performance to establish a link among them to gain an understanding how they are affecting each other and identify ways to establish strong and positive leadership performance outcomes from organisational culture.
Problem Discussion and Question
Organisational culture has been recognised in the employee behaviour and performers however, the culture paradigm is not well defined towards the leadership performance.
The organisation culture can have varying impact on the performance on the leader as it has potential to affect the motives and motivation level and also level of involvement in the corporate culture. The organisation culture can have potential effect on the leaders and development of the leadership style.
This is important to indentify as the culture binds with the performance of the leader to bring change, inspire, direct, and/ or guide to change the old way of doing things.
Also, considering the growing importance of leadership in facilitating organizational success, there has been little research on the area of leadership performance (Le Fevre and Robinson, 2015; Friedrich et al., 2016).
Koopman, Den Hartog and Konrad (1999) focused in their research paper how different cultural groups fluctuate in terms of what leadership should involve in organizations such as various management prototypes or culturally supported implied leadership theories.
Mittal and Dorfman (2012) mentioned the important connections between several cultural social values and servant management aspects that help to understand why nations support servant leadership.
Moreover, Ergeneli, Gohar and Temirbekova (2007) indicated in their research the linkage between the overall transformation leadership and its five aspects such as challenging the process, inspiring a shared vision, enabling others to act, modelling the way and encouraging the hearth based on Kouzes and Posner and Hofstede’s culture value dimensions.
The leadership style is linked towards the employee and organisational performances for the autocratic, democratic, and participative styles. The leadership styles have been evolving which can be more effective and can highlight a new approach in managing the performance aspects of organisation and the organisational members.
In addition, many researchers have also considered organizational culture and leadership on job satisfaction and organizational/ business performance and organisational commitment (Hartnell et al., 2016) but there is still lack of knowledge and evidence towards organizational culture consequence on the leadership performance.
There is also little research and narrow understandings towards the complex relationships among the organizational culture factors that can possibility have positive outcomes for leader performance and leadership characteristics.
The problem is that the effect of organisation culture is not directly linked to leadership performance and the relevance of its influences not recognised in relation to leader performance and can present key implications for the manager.
Thus, this presents a dynamic opportunity to full this gap and to provide a holistic view of effect of organisational culture on the performance aspect of leadership. As business and industry globalization advances, culture and leadership are critical issues.
They are also important to the growing multicultural, heterogeneous and diverse domestic workforce. Further and extended studies are necessary for the profession of human resources development to gain a more complete understanding of this major issue.
Therefore, it is identified from the discussion that the following key issue can rise to determine the impact of cultural differences on leadership performance that how organizational culture influence leadership performance.
The questions are:
- What are the effects of organizational culture and leadership performance?
- How organizational culture affects leadership performance?
The key aim of this study is to identify and comprehend the effects of organizational culture on leadership performance.
To accomplish this aim, the following contributions are identified and expected:
- To examine the relationship between organization culture and leadership
- To identify the leadership characteristics and culture models that drive leadership performance
- To provide a suggestion on ways to develop an effective organization culture for positive leadership performance outcomes.
Relationship between organizational culture and leadership
In concern of organizational culture and leadership, it is important to understand the importance of organizational culture and leadership within the organization separately.
In this way, organizational culture is defined as the combination of organizational values and beliefs that create the culture of an organization and at the same time, this organizational culture also influences the several factors under the organization (Hartnell et al., 2016).
These several factors are organizational activities, job attitude, employee’s behavior, leadership and employee’s satisfaction as well. Instead of this, leadership is referred to as an art that is used to motivate the people for performing their activities towards achieving the common goals of the organization and their own.
Leadership is an important factor that can be used in the organization in order to maximize organizational productivity and to achieve business goals (Valmohammadi and Roshanzamir, 2015).
In similar manner, after understanding the organizational culture and the leadership separately, it can be stated that leadership is an essential part of an organization for making it more profitable or successful and it is also essential to develop the organizational culture that is necessary for the employees in order to enhance their satisfaction and motivate them by influencing their behavior as well as attitude towards the organization (Demir, 2015).
In addition, the above facts disclose that there is a relationship between organizational culture and the leadership as this is supported by Bedi, A., Alpaslan and Green (2016). It is also mentioned that culture is learned by society and at the same time, transmitted by the members.
This is the main factor that provides the rules in the organization in the context of behavior. On the basis of above, it can be determined that culture defines the employees that what to do and what not to do but the leadership defines that how the employees can do the necessary things so that they get success within their tasks.
In this similar manner, Sarooghi et al. (2015) determine that leadership plays an important role in developing the organizational culture and that is why it can be declared that organizational culture is affected by the leadership directly.
In a similar manner, Schneider et al., (2017) who is one of the respected author of leadership studies determined that organizational culture cannot be developed without an effective leader as he/she helps to control the organizational tools, resources, different people, and the processes that are required to develop the culture.
Moreover, from the research of Kaya (2015), it can be claimed that leadership can be considered as the compasses that provide the direction and dimension that the organizational culture development will take. In against of this, the organizational culture helps to shape the personality of a leader and make him/her perfect to fit in along with the brand as well as the overall image of an organization.
In other words, the leadership role is important as it facilitates and fosters organizational culture development (Lee et al., 2016). In addition, leadership also provides some important points that an organizational leader needs to know in order to lead the employees effectively.
Dabke (2016) supports that leadership directly affects the organizational culture that revolves around the organizational environment, employee engagement, the atmosphere, and the foremost thing and that is the success of the organization as well as its clients.
Apart from above, Carasco-Saul et al. (2015) mention in its research study that leadership is not the small things even it can create the effect on the employee’s confidence that is important for them to see their mistakes as the opportunities, not their failures which damage employee’s self-worth.
Behalf of above, it can be mentioned that it can be depicted that leadership develops the foundation of culture in respect to empower the employees for achieving the organization’s mission and understanding that how important each of their contributions is to furthering those organizational goals (Reb et al., 2018).
Thus, it can be declared that effective leadership along with the number of skills can changes the organizational culture effectively.
Leadership characteristics and culture models that drive the leadership performance
While discussing the leadership and the organizational culture, a leader needs some important leadership characteristics and culture models that help him/her to improve and enhance the leadership performance within the organization as it is clearly defined above that there is the relation between leadership and the organizational performance (Boies et al., 2015).
In this way, in the research study of Fry et al. (2017), it is reflected that the leadership characteristics and the culture models are two different things that drive the leadership performance in their own way. Similarly, they also have a different impact on leadership.
Here, these two different things are examined differently. Furthermore, some leadership characteristics are essential for each and every leader in order to be effective within the organization (Bolman and Deal, 2017). In this way, an effective leader should have the ability to influence others with effectiveness so that they can work as per the organizational goals in order to achieve them.
In other words of Smith et al. (2016), it is identified that for influencing the others, a leader needs strong trust within their followers. In addition, an effective leader also needs to have the skill of transparency that helps the leader to build trust among its colleagues.
As per these skills, the more open a leader is about the organization’s goals as well as challenges, then it is quite easier for employees to the developing understanding of their roles and responsibilities.
In addition, as per the Behavioural Theory of leadership, Shin et al. (2016) support that the key focus area of this theory is the behavior of a leader under a situation that the person can have a particular responsibility for the specific purpose. This behavioral theory gives real marketing potential.
In a similar manner to behavioral theory, Lumpkin (2016) determined that the focus of the owner is on the specified behavior as well as actions of leaders instead of their traits as well as characteristics because these are most important for the productivity of an organization.
Moreover, effective leadership is the result of several learned skills of a person who are performing the role of the leadership. In this way, strong communication is also considered as the characteristic of a leader that is important in order to lead the performance of it in the correct direction.
Furthermore, effective communication is the greatest attribute of a strategic leader. In concern of leadership characteristics, by effective communication, the leader can communicate organizational vision and mission among the other team members as well as his/her colleagues (Cheong et al., 2016).
At the same concern, along with the effective communication, a leader can also be capable to interpret the organizational goals and objectives so that they can perform the task as per the organizational requirements.
Furthermore, passion and commitment are also the other characteristics that help the leader to enhance its performance under the organization so that the set standards can be achieved by whole the team (Laureani and Antony, 2019).
If a leader shows the passion about the organization goals in order to achieve them, the leader will get the other employees more excited because these employees or team members can see as well as feel their leader’s dedication.
In a similar manner, Al Hila and Al Shobaki (2016) describes that with the skill of passion and the commitment the leader has the ability to influence others for increasing their performance in respect to achieving the pre-decided standards of the performance.
Apart from this, the positivity and the innovative mind are also defined as the characteristics of the leadership that are helpful to drive the leadership performance under the organization.
Apart from this, Edger Schein’s model of organizational culture is also determined in context to the performance of the leaders under the organization (Ghosh, 2015).
As per this culture model, this model is proposed for the organizational culture in which the primary assumption directs the values and these values direct the practices and the behavior that is the visible part of the organizational culture.
In support to this, the culture is not adopted by the organization on a single day but in reality, learns from the past experiences and start off practicing it on regular basis hence forming the culture of the organization that is essential for the leaders in order to drive the leadership performance (Jekiel, 2016).
Thus, it can be mentioned that there are several leadership characteristics and culture models that have defined above which drive the leadership performance under the organization in order to get the benefits from it.
Suggestion on ways to develop an effective organizational culture for positive leadership performance outcomes
In the context of the organizational culture, there is a number of ways that can be adopted by the organization in concern of the positive leadership performance results for developing an effective organizational culture (Lyubovnikova et al., 2017).
In this way, it is examined by Jones et al. (2016) in its research study that as per these ways, transparency is one of the best ways of organizational culture in respect to getting positive leadership performance outcomes.
With the help of the transparency, organizations are capable to develop the trust among the top management employees who require transparency and this is the major reason that leads the effective leadership performance outcomes.
In addition, some theorist also supports that transparency helps the organizations to develop the organizational culture in which leaders can give their best while performing the operations in order to achieve the organizational objectives (Day et al., 2016). For these objectives, standards for the leader’s performance are decided on the basis of a leader’s performance or outcomes are measured.
In addition, reward in public and the coach in private techniques can also be adopted by the organization because it helps the organization to develop the workplace culture that is essential for the leaders to give their best as per the set target of the performance.
Ina similar manner, it is defined that leaders are the top level employees and if the coaching is provided to them openly, it is not good for their image. At the same time, if the rewards are given to them openly, it is best for their reputation among the employees.
Moreover, Ghobadi and Mathiassen (2016) both propose that with the support of these techniques, organizations find the way to develop the organizational culture which drives the leaders to show their full potential of their performance.
In the same concern, if the organizations develop the different channels in respect to collect the employee feedback, that can also be beneficial for the organization to create the organizational culture which is essential for the leaders to give their best in the organization so that its objectives can be achieved and its goals can also be accomplished as per its stakeholder’s requirements (Schneider et al., 2017).
At the same time, under the organization, it should stick with its core values because this helps it to improve the company culture. If the situation occurs in the organization to change the culture of it, there is a need for the organization to stay constant with its core values.
In support of it, Bird and Mendenhall (2016) mention that core values are the things that make the organization different from everyone else and the core values are the things that are considered organization’s competitive advantages.
Thus, it is quite clear that there are several ways by which organizational culture can be developed or improved which is essential to motivate the leaders to represent their leadership performance under the organization for achieving the organizational goals.
These ways are very important as it develops the workplace culture which increases the organizational efficiency and its productivity also that is most important for organizational success as well as profitability (Schneider et al., (2017).
Chapter3. Research Methodology
The research methodology is determined as the way by which several research problems are resolved in a systematic manner. It does not only provide the research techniques but it also provides the logic behind the research method application (Fletcher, 2017).
Under the research methodology, several tools are used that is why it is important for accomplishing the research. This research study also includes some methods and technologies that are crucial for the research to collect appropriate research data.
In concern of research methodology, it is determined that research philosophy is also an important part of it as it is the researcher’s thinking that provides support to develop the knowledge of research problems. In this manner, three types of research philosophy such as positivism, realism, and interpretivism, etc. are determined for the research study (Kumar, 2019).
In addition, the positivism is depended on natural science whereas interpretivism helps the researcher to interpret the research problems in order to develop a theoretical understanding of research issues. In this, as per this research topic, interpretivism was one of the best options for the researcher as it enabled the researcher for conducting in-depth analysis regarding research issues.
The research approach is explained in the research study because it provides the appropriate solution for the determined research problems by presenting reliable and effective outcomes. In this manner, two types of research approaches such as inductive and deductive are found (Gog, 2015).
In which, inductive research approach was more effective for the research study as with the help of this, the research could develop its own theory for the research topic and it was quite beneficial for the researcher because most of the issues were based on the theoretical aspects that could be analyzed by it.
It is essential for research to select the research design in order to collect and analyze the data properly. In this, there are three types of methods that are considered such as qualitative, quantitative and mix research design, etc. Apart from this, a quantitative research design has been selected under this research (Creswell & Poth, 2017).
Under the quantitative research design, the statistical data was developed that helped to analyze the situation with a more effective and understandable way with the graphs and tables.
In a research strategy, it is ensured that whether the information is available or not related to the research problem. It is also helpful to provide the right direction to the research study in an effective manner. In this way, research strategy can be used in its different manner such as survey, experiment, literature reviews, etc.
For this study, the research strategy adopted was survey-based (Cuervo‐Cazurra et al., 2017). With the survey strategy, the researcher could get collect the information from the broad target area and in-depth knowledge about the research topic.
In concern of the research, the time horizon is determined as the estimated length that reflects the time will be used for accomplishing the research study and gives the overview of the obligations to complete the research within the estimated time duration. Under the methodology, there are two types of time horizons such as cross-sectional and longitudinal.
In addition, it is examined that the cross-sectional time horizon was more efficient for the researcher to carry out the research on time. Under this, data was collected once while conducting the research and there was no requirement to collect the data again and again. It saved the researcher’s time under the research.
Data collection methods are a crucial part of the research due to the clearance of information in relation to the collection of data. In concern of collecting the data, there are two types of data collection methods such as primary data collection and secondary data collection that are determined.
In this manner, the primary data collection method is determined as the first hand that because it is collected by the first time by the researcher as per the requirements of the research study.
At the same time, the secondary data collection is the second-hand data means it has been collected by other persons for their use to accomplish their study. The study preferred to adopt both the types of data collection i.e. primary and secondary.
Here, the primary method made the use of questionnaire methodology to acquire fresh data while the secondary data collection method was used for the literature review from secondary sources like books, journals, news articles, published material from the internet, books (McCusker & Gunaydin, 2015).
In this way, for collecting the primary data, the survey respondents was identified through website traffic on survey site which based on the nature of the study hosted an invitation to managers to participate in the study on the survey website and allowed them to consider them as eligible or ineligible to take the survey (Singh, 2015).
In this manner, data collection was the important part of the research methodology to make the research more effective.
The selection of the appropriate method of collecting primary and secondary data is essential for the researcher so that the research can be conducted without any issue. As per the nature of the research study, there are two types of sampling methods such as non-probability and probability that can be adopted by the researcher as per the requirements.
In this, the researcher intended to make use of random probability sampling method so that each unit in the population has an equal chance of getting selected and the sample size of 100 was preferred. The target population included the leaders/ managers from the retail industry (McKim, 2017). As considering the sample, the researcher could reflect the actual situation as well as facts in concern of the research topic.
It is essential to analyze the collected data so that effectively and accurately the information of relevant topic can be measured. In addition, there are several data analysis methods like thematic/content analysis, statistical analysis, conversational analysis and disclosure analysis that can be applied by the researcher for making a proper and significant analysis of collected data.
Moreover, for this research study, the researcher made use of data management tool for the analysis of collected data which was used for distribution of collected data and representation of finding in the form of tables, charts, and graphs (Walliman, 2017).
This technique was quite effective as it provided reliable and trustable research outcomes that were quite beneficial for the researcher. At the same time, the use of leadership theories was effective to discuss the analyzed data in perspective of the impact of organizational culture on leadership performance.
Ethical Consideration
It is important for the researcher to consider ethics while conducting the research on the selected topic for providing the relevancy. In addition, there was a need to the researcher to be more focused at the time of collecting secondary data because plagiarism and copyright could create the ethical issues that are why researcher was more attentive in regards of reducing the ethical problems in the research (Bryman, 2016).
In addition, the researcher also gave the same respect for the past authors whose analysis reports are used by the researcher along with the references and in-text citations in the research.
Research Limitation
Under this research, it was determined that the researcher used both the data collection methods which is more time consuming for the researcher. Similarly, it also limited the researcher to more concentrate on the important aspects that were associated with the research topic.
At the same time, the quantitative research design has been selected in this study that has focused only on the numerical data instead of theoretical data (Ojua, 2016). In this way, the researcher has the more opportunity to use the qualitative data that can be more effective to enhance the effectiveness in further research.
The research methodology defines that how the researcher with the help of a methodological investigation determines the several business opportunities and challenges for leaders to develop the effective organizational culture in order to develop the positive leadership performance outcomes.
The target population was the leaders/ managers from the retail industry who play an important role to develop the organizational culture for the employees. At the same time, the selected method of research analysis was a data management tool that was quite effective to accomplish the research aims and objectives.
Question 1: Age Group
| Respondents | Frequency | Percentage |
| Below 20 | 8 | 8 |
| 20-30 | 45 | 45 |
| 30-50 | 32 | 32 |
| Above 50 | 15 | 15 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
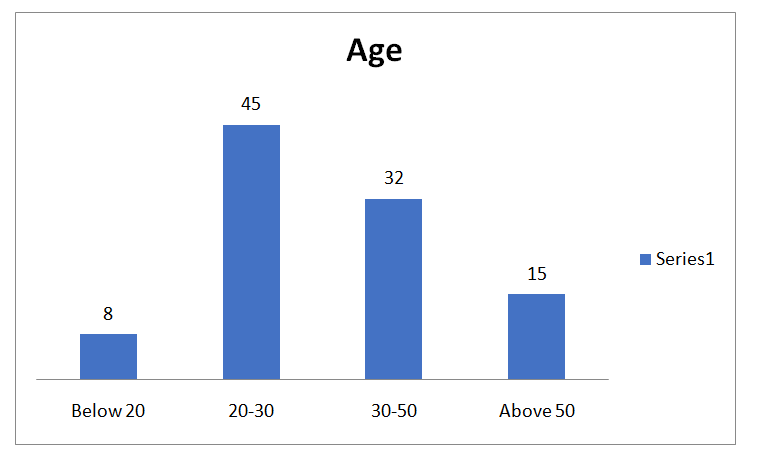
Interpretation
On the basis of above graph, it can be interpreted that most of the respondents are belong to the age group of 20-30 i.e., 45% are leaders or managers. However, the second respondent’s age group was 30-50 who are also more in numbers and included as the respondents sample size where as remaining respondents from the age group of above 50 and below 20 are few in numbers as leaders or managers.
Question 2: Gender
| Respondents | Frequency | Percentage |
| Male | 72 | 72 |
| Female | 28 | 28 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
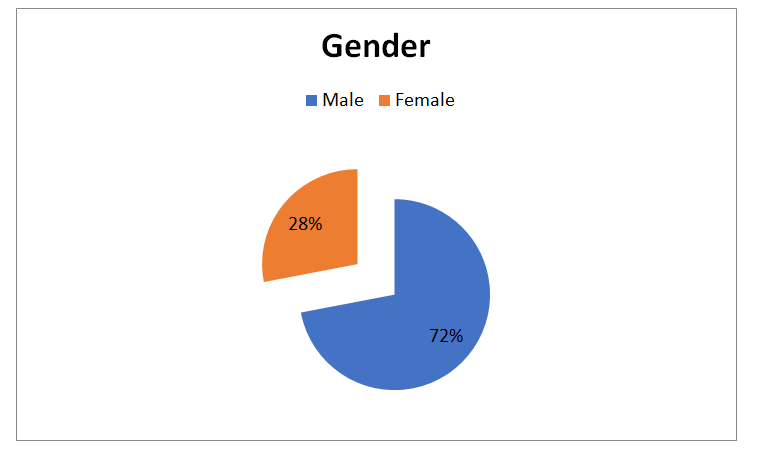
Interpretation
The above gender analysis clearly reflects that males are majority of respondents in the survey process as piece of pie reflects 72% of male respondents. At the same time, 28% are females which are included in the sample size of the survey research.
Through this, it can be interpreted that most of the organizations have engaged more number of males as their leaders or managers in comparison to female staff. However, this analysis simply signifies that still in organizations, more numbers of male managers are engaged instead of female.
Question 3: Work Experience
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Below 1 years | 10 | 10 |
| Between 2-4 years | 45 | 45 |
| 5- 9 years | 28 | 28 |
| Above 10 years | 17 | 17 |
| 100 | 100 |
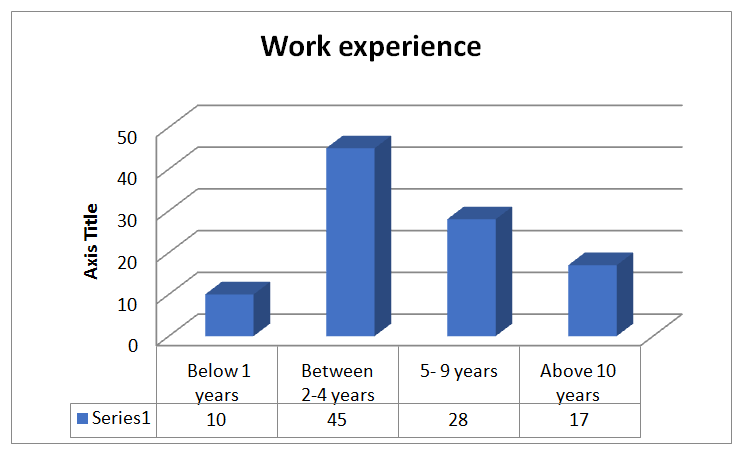
Interpretation
From the above graph, it can be determined easily that 45% of the respondents are having work experience of about 2-4 years within an organization. There are few respondents who are having below 1 years of experience and few respondents having above 10 years of experience.
On the other hand, there are only 28% of respondents who are actually having 5-9 years experiences in their field of managing and leading the other staff for enhancing the performance. However, this working experience reflects the respondent’s strengths and skill of leading the other staff by using best essential leadership style which ultimately creates the healthy organization culture respectively.
Question 4: Do you think that leadership plays important role in an organization?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 36 | 36 |
| Agree | 32 | 32 |
| Neutral | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 8 | 8 |
| Strongly disagree | 9 | 9 |
| 100 | 100 |
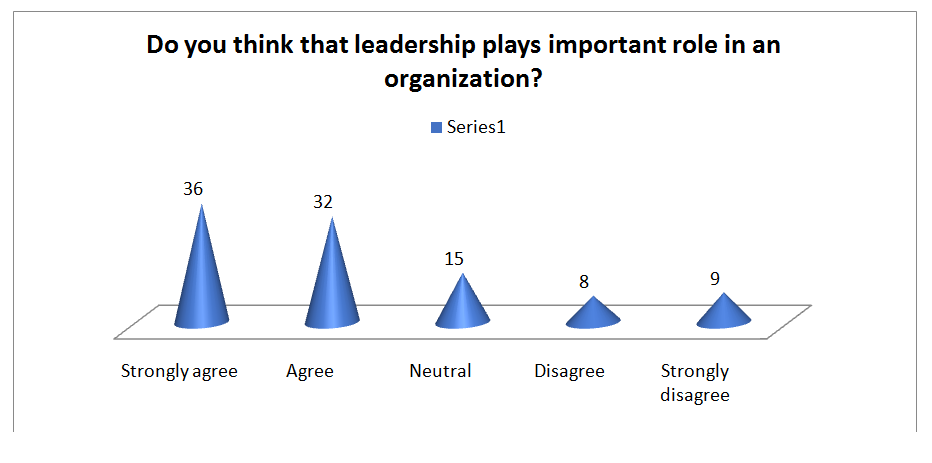
Interpretation
The above stated graph clearly presented that most of the respondents i.e., 36% have strongly agreed on the role of leadership in an organization. In support to this, there are 32% of respondents who agreed on the statement and 15% respondents have responded neutrally as they think that leadership role is somewhere important but not necessary for the organization growth and development.
Further, remaining 8% disagreed and 9% strongly disagreed on the statement that for an organization, leadership play a significant role for enhancing the performance.
Question 5: Do you agree that there is relationship between organizational culture and leadership?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 20 | 20 |
| Agree | 29 | 29 |
| Neutral | 15 | 15 |
| Disagree | 22 | 22 |
| Strongly disagree | 14 | 14 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
From the above table and graph, it can be represented that large numbers of respondents have shown positive respond on the relationship between leadership and organizational culture. There are 20% respondents who strongly agreed on the statement that organization culture and leadership share a healthy relationship.
In a similar manner 29% respondents also provided positive result but around 22% and 14% of the respondents have stated negative response i.e., disagreed and strongly disagree as they don’t found that organization culture have any kind of relationship with the leadership.
Question 6: In your concern, does organizational culture create an influence on the leadership style within an organization?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 34 | 34 |
| Agree | 26 | 26 |
| Neutral | 20 | 20 |
| Disagree | 11 | 11 |
| Strongly disagree | 9 | 9 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
While analyzing, it is identified that 34% respondents have strongly agree and 26% agree that organization culture create huge influence on the leadership style because on employee satisfaction and performance both culture and leadership tactics plays significant role.
At the same time, 20 % of respondents have shown both positive and adverse response as they think that culture of organization influences the leadership style as per the employees or organization requirements. But, remaining 20% (11% + 9%) have disagreed to the statement.
Question 7: Do you agree that leadership characteristics and culture models drives the leadership performance?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 28 | 28 |
| Agree | 35 | 35 |
| Neutral | 20 | 20 |
| Disagree | 10 | 10 |
| Strongly disagree | 7 | 7 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
During the analysis process, it is found that 35 % of the respondents agreed that there leadership characteristics efficiently drives the leadership performance because characteristics includes, ability, skills, behaviour, etc which influences indirectly to the organizational performance.
On the other hand, 28% strongly agreed that both culture models and leadership characteristics are useful for the leadership performance as this provides the benefits in making the employees or staffs work properly. After that, only 10 respondents disagree that both terms drives the performance of leader because culture model is depended on organizational environment whereas leadership characteristics motivates the employees.
Question 8: As per your point of view, do leadership characteristics and culture model support the leader/manager to enhance the organizational performance?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 32 | 32 |
| Agree | 34 | 34 |
| Neutral | 20 | 20 |
| Disagree | 11 | 11 |
| Strongly disagree | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
On the basis of above collected data, it is determined easily that 60% respondents have answered in positive manner i.e., 32 % strongly agree and 34 % agree because they understand the need for leadership characteristics for manager or leader and support of culture model in an organization.
But, 20 % respondents stated that neutrally and remaining few respondents i.e., 20 % have negative response that they are less aware regarding the use of characteristics of leader and culture model for enhancing performance of an organization.
Question 9: Do you believe that the effects of organization culture also impact on the leadership performance?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 26 | 26 |
| Agree | 30 | 30 |
| Neutral | 25 | 25 |
| Disagree | 11 | 11 |
| Strongly disagree | 8 | 8 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
The above table clearly interpreted that above 50% respondents have agreed that effects of organization culture is easily seen on the leadership performance But around 25 % respondents have shown neutral decision regarding the statement because they believe organization culture impact directly or indirectly as per circumstance on the performance of leadership.
Remaining respondents have strongly disagreed and disagreed because they believe that organization culture is totally different aspect which don’t impact on the performance of leadership as each leader only get affected from his own lack of skills or ability.
Question 10: Can you please tell which leadership characteristic found to be helpful for driving the leadership performance within an organization?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Passion and Commitment | 12 | 12 |
| Effective communication | 20 | 20 |
| Innovative mind and Positivity | 16 | 16 |
| All of the above | 52 | 52 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
Though this analysis, it is reflected that different respondents have stated different leadership characteristics for driving the performance of a leader in an organization. Most of the respondents have answered on all leadership characteristics such as effective communication, innovative mind, passion and commitment respectively.
In addition, there are few respondents who have responded on single leadership characteristics i.e., 12 responded on passion & commitment, 20 responded on effective communication and 16 responded on innovative mind & positivity.
Question 11: Would you provide suggestion that which ways can be used to develop an effective organizational culture for generating positive outcome from leadership performance?
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Open Rewards and Recognition | 20 | 20 |
| Transparency | 28 | 28 |
| Development of different channels | 30 | 30 |
| Establishment of core values | 22 | 22 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
In this analysis, respondents were asked for suggestive ways in which 30 % respondents stated that development of different channels supports in developing organization culture which ultimately generate positive result. On the other side, 28 % respondents agreed to use transparency as suggestive way for improving the organization culture and also to enhance the leadership performance.
Whereas, 20 % agreed on open reward and recognition process and 22 % agreed ion establishment of core values which indicates that respondents have different views on enhancing the organization culture and performance of leadership.
Question 12: Provide your concern about the suggested ways that can be useful for managing the organizational culture and performance in highly competitive market.
| Options | Frequency | Percentage |
| Strongly agree | 30 | 30 |
| Agree | 35 | 35 |
| Neutral | 24 | 24 |
| Disagree | 7 | 7 |
| Strongly Disagree | 4 | 4 |
| 100 | 100 |
Interpretation
As per collected response, it can be easily interpreted that organization culture and leadership performance are major concern factors on which they need to emphasis more in highly competitive market. This above graph states responses of respondents on the use of suggestive ways for managing the organization culture and leadership performance respectively.
There are more respondents that positively agreed that suggestive ways would be useful for future growth and meeting the challenges efficiently. But at the same time, on 4 respondents strongly disagree that only using suggestive ways is less effective as it creates impact on the performance and organization culture.
From the above study, it can be concluded easily that leadership performance get affected from the organization culture because leader or manager reacts on the basis of the culture and adjust the behaviour accordingly.
Within an organization, the importance of organization culture and leadership characteristics is different from each other because leader require leadership characteristics for improving the performance whereas organization culture is maintained for enhancing the job satisfaction level and motivation among the employees.
There is relationship observed between the organization culture and leadership performance which affects directly on directly to the performance of an employee to large extent because organization culture influences the use of the leadership style for enhancing the performance level.
While analyzing, it is also observed that leadership characteristic and culture models plays significant role in driving the performance for which organizational managers adopts different models and theories for leading and managing the organizational work environment.
In addition, the data analysis result clearly reveals that there is effect off organization culture on the leadership performance because organization culture This study also identified different suggestive ways such as open rewards and recognition, transparency, establishment of core values as well as development of different channels which can develop the effectiveness of organization culture in order to generate positive outcome.
Thus, overall study can be summarized that culture of an organization play a vital role in enhancing satisfactory working environment and that leads to create impact on the leadership performance efficiently.
Al Hila, A.A. and Al Shobaki, M.J., 2016. The Role of Servant Leadership in Achieving Excellence Performance in Technical Colleges-Provinces of Gaza Strip. International Journal of Management Research and Business Strategy, 6(1), pp.69-91.
Anderson, M.H. and Sun, P.Y., 2017. Reviewing leadership styles: Overlaps and the need for a new ‘full‐range’theory. International Journal of Management Reviews, 19(1), pp.76-96.
Arifin, H.M., 2015. The Influence of Competence, Motivation, and Organisational Culture to High School Teacher Job Satisfaction and Performance. International Education Studies, 8(1), pp.38-45.
Azanza, G., Moriano, J.A. and Molero, F., 2013. Authentic leadership and organizational culture as drivers of employees’ job satisfaction. Revista de Psicología del Trabajo y de las Organizaciones, 29(2), pp.45-50.
Bedi, A., Alpaslan, C.M. and Green, S., 2016. A meta-analytic review of ethical leadership outcomes and moderators. Journal of Business Ethics, 139(3), pp.517-536.
Bird, A. and Mendenhall, M.E., 2016. From cross-cultural management to global leadership: Evolution and adaptation. Journal of World Business, 51(1), pp.115-126.
Boies, K., Fiset, J. and Gill, H., 2015. Communication and trust are key: Unlocking the relationship between leadership and team performance and creativity. The Leadership Quarterly, 26(6), pp.1080-1094.
Bolman, L.G. and Deal, T.E., 2017. Reframing organizations: Artistry, choice, and leadership. US: John Wiley & Sons.
Bortolotti, T., Boscari, S. and Danese, P., 2015. Successful lean implementation: Organizational culture and soft lean practices. International Journal of Production Economics, 160, pp.182-201.
Bryman, A., 2016. Social research methods. UK: Oxford university press.
Carasco-Saul, M., Kim, W. and Kim, T., 2015. Leadership and employee engagement: Proposing research agendas through a review of literature. Human Resource Development Review, 14(1), pp.38-63.
Cheong, M., Spain, S.M., Yammarino, F.J. and Yun, S., 2016. Two faces of empowering leadership: Enabling and burdening. The Leadership Quarterly, 27(4), pp.602-616.
Choy, L.T., 2014. The strengths and weaknesses of research methodology: Comparison and complimentary between qualitative and quantitative approaches. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 19(4), pp.99-104.
Clark, D., 2015. Concepts of Leadership. [Online] Available at: http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/leadcon.html (Accessed 25 March 2019).
Creswell, J.W. and Poth, C.N., 2017. Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. California: Sage publications.
Cuervo‐Cazurra, A., Mudambi, R., Pedersen, T. and Piscitello, L., 2017. Research methodology in global strategy research. Global Strategy Journal, 7(3), pp.233-240.
Dabke, D., 2016. Impact of leader’s emotional intelligence and transformational behavior on perceived leadership effectiveness: A multiple source view. Business Perspectives and Research, 4(1), pp.27-40.
Day, C., Gu, Q. and Sammons, P., 2016. The impact of leadership on student outcomes: How successful school leaders use transformational and instructional strategies to make a difference. Educational Administration Quarterly, 52(2), pp.221-258.
Demir, K., 2015. The Effect of Organizational Trust on the Culture of Teacher Leadership in Primary Schools. Educational Sciences: Theory and Practice, 15(3), pp.621-634.
Ergeneli, A., Gohar, R. and Temirbekova, Z., 2007. Transformational leadership: Its relationship to culture value dimensions. International journal of intercultural relations, 31(6), pp.703-724.
Fletcher, A.J., 2017. Applying critical realism in qualitative research: methodology meets method. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 20(2), pp.181-194.
Friedrich, T.L., Griffith, J.A. and Mumford, M.D., 2016. Collective leadership behaviors: Evaluating the leader, team network, and problem situation characteristics that influence their use. The Leadership Quarterly, 27(2), pp.312-333.
Fry, L.W., Latham, J.R., Clinebell, S.K. and Krahnke, K., 2017. Spiritual leadership as a model for performance excellence: a study of Baldrige award recipients. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion, 14(1), pp.22-47.
Gerstner, C.R. and Day, D.V., 1994. Cross-cultural comparison of leadership prototypes. The Leadership Quarterly, 5(2), pp.121-134.
Ghobadi, S. and Mathiassen, L., 2016. Perceived barriers to effective knowledge sharing in agile software teams. Information Systems Journal, 26(2), pp.95-125.
Ghosh, K., 2015. Developing organizational creativity and innovation: toward a model of self-leadership, employee creativity, creativity climate and workplace innovative orientation. Management Research Review, 38(11), pp.1126-1148.
Gog, M., 2015. Case study research. International Journal of Sales, Retailing & Marketing, 4(9), pp.33-41.
Hartnell, C.A., Kinicki, A.J., Lambert, L.S., Fugate, M. and Doyle Corner, P., 2016. Do similarities or differences between CEO leadership and organizational culture have a more positive effect on firm performance? A test of competing predictions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 101(6), p.846.
Hofstede, G., 1980. Culture and organizations. International Studies of Management & Organization, 10(4), pp.15-41.
Jekiel, C.M., 2016. Lean human resources: redesigning HR processes for a culture of continuous improvement. Productivity Press.
Jones, R.J., Woods, S.A. and Guillaume, Y.R., 2016. The effectiveness of workplace coaching: A meta‐analysis of learning and performance outcomes from coaching. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 89(2), pp.249-277.
Kaya, A., 2015. The Relationship between Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors: A Research on School Principals’ Behaviors. Educational Sciences: Theory and Practice, 15(3), pp.597-606.
Koopman, P.L., Den Hartog, D.N. and Konrad, E., 1999. National culture and leadership profiles in Europe: Some results from the GLOBE study. European journal of work and organizational psychology, 8(4), pp.503-520.
Kumar, R., 2019. Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. California: Sage Publications Limited.
Kurland, H., Peretz, H. and Hertz-Lazarowitz, R., 2010. Leadership style and organizational learning: The mediate effect of school vision. Journal of Educational Administration, 48(1), pp.7-30.
Laureani, A. and Antony, J., 2019. Leadership and Lean Six Sigma: a systematic literature review. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(1-2), pp.53-81.
Le Fevre, D.M. and Robinson, V.M., 2015. The interpersonal challenges of instructional leadership: Principals’ effectiveness in conversations about performance issues. Educational Administration Quarterly, 51(1), pp.58-95.
Lee, J.C., Shiue, Y.C. and Chen, C.Y., 2016. Examining the impacts of organizational culture and top management support of knowledge sharing on the success of software process improvement. Computers in Human Behavior, 54, pp.462-474.
Leidner, D.E., 2010. Globalization, culture, and information: Towards global knowledge transparency. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 19(2), pp.69-77.
Lord, R.G. and Brown, D.J., 2001. Leadership, values, and subordinate self-concepts. The Leadership Quarterly, 12(2), pp.133-152.
Lumpkin, A., 2016. Key characteristics of teacher leaders in schools. Administrative Issues Journal: Connecting Education, Practice, and Research, 4(2), p.14.
Lyubovnikova, J., Legood, A., Turner, N. and Mamakouka, A., 2017. How authentic leadership influences team performance: The mediating role of team reflexivity. Journal of Business Ethics, 141(1), pp.59-70.
McCusker, K. and Gunaydin, S., 2015. Research using qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods and choice based on the research. Perfusion, 30(7), pp.537-542.
McKim, C.A., 2017. The value of mixed methods research: A mixed methods study. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 11(2), pp.202-222.
McNabb, D.E., 2015. Research methods for political science: Quantitative and qualitative methods. UK: Routledge.
Mittal, R. and Dorfman, P.W., 2012. Servant leadership across cultures. Journal of World Business, 47(4), pp.555-570.
Neubert, M.J., Carlson, D.S., Kacmar, K.M., Roberts, J.A. and Chonko, L.B., 2009. The virtuous influence of ethical leadership behavior: Evidence from the field. Journal of Business Ethics, 90(2), pp.157-170.
Noe, R.A., Hollenbeck, J.R., Gerhart, B. and Wright, P.M., 2017. Human resource management: Gaining a competitive advantage. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Obiwuru, T.C., Okwu, A.T., Akpa, V.O. and Nwankwere, I.A., 2011. Effects of leadership style on organizational performance: A survey of selected small scale enterprises in Ikosi-Ketu council development area of Lagos State, Nigeria. Australian journal of business and management research, 1(7), p.100.
Ojokuku, R.M., Odetayo, T.A. and Sajuyigbe, A.S., 2012. Impact of leadership style on organizational performance: a case study of Nigerian banks. American Journal of Business and Management, 1(4), pp.202-207.
Ojua, M.O., 2016. Strategic management accounting practices among indigenous Nigerian manufacturing enterprises. Open Science Journal, 1(2).
Reb, J., Chaturvedi, S., Narayanan, J. and Kudesia, R.S., 2018. Leader mindfulness and employee performance: A sequential mediation model of LMX quality, interpersonal justice, and employee stress. Journal of Business Ethics, pp.1-19.
Sarooghi, H., Libaers, D. and Burkemper, A., 2015. Examining the relationship between creativity and innovation: A meta-analysis of organizational, cultural, and environmental factors. Journal of business venturing, 30(5), pp.714-731.
Schein, E.H., 2010. Organizational culture and leadership (Vol. 2). US: John Wiley & Sons.
Schneider, B., González-Romá, V., Ostroff, C. and West, M.A., 2017. Organizational climate and culture: Reflections on the history of the constructs in the Journal of Applied Psychology. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(3), p.468.
Selznick, P., 2011. Leadership in administration: A sociological interpretation. New Orleans: Quid Pro Books.
Shin, Y., Kim, M., Choi, J.N. and Lee, S.H., 2016. Does team culture matter? Roles of team culture and collective regulatory focus in team task and creative performance. Group & Organization Management, 41(2), pp.232-265.
Singh, K.D., 2015. Creating your own qualitative research approach: Selecting, integrating and operationalizing philosophy, methodology and methods. Vision, 19(2), pp.132-146.
Smith, J.E., Gavrilets, S., Mulder, M.B., Hooper, P.L., El Mouden, C., Nettle, D., Hauert, C., Hill, K., Perry, S., Pusey, A.E. and van Vugt, M., 2016. Leadership in mammalian societies: Emergence, distribution, power, and payoff. Trends in ecology & evolution, 31(1), pp.54-66.
Tuan, L.T., 2010. Organisational culture, leadership and performance measurement integratedness. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, 9(3), pp.251-275.
Valmohammadi, C. and Roshanzamir, S., 2015. The guidelines of improvement: Relations among organizational culture, TQM and performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 164, pp.167-178.
Walliman, N., 2017. Research methods: The basics. UK: Routledge.
Yang, L.R., Huang, C.F. and Wu, K.S., 2011. The association among project manager’s leadership style, teamwork and project success. International journal of project management, 29(3), pp.258-267.
Zaccaro, S.J. and Horn, Z.N., 2003. Leadership theory and practice: Fostering an effective symbiosis. The Leadership Quarterly, 14(6), pp.769-806.
Survey Questionnaire form
Question 1: Age Group
- Below 20
- 20-30
- 30-50
- Above 50
Question 2: Gender
- Male
- Female
Question 3: Work Experience
- Below 1 years
- Between 2-4 years
- 5-9 years
- Above 10 years
Question 4: Do you think that leadership plays important role in an organization?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 5: Do you agree that there is relationship between organizational culture and leadership?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 6: In your concern, does organizational culture create an influence on the leadership style within an organization?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 7: Do you agree that leadership characteristics and culture models drives the leadership performance?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 8: As per your point of view, do leadership characteristics and culture model support the leader/manager to enhance the organizational performance?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 9: Do you believe that the effects of organization culture also impact on the leadership performance?
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree
Question 10: Can you please tell which leadership characteristic found to be helpful for driving the leadership performance within an organization?
- Passion and Commitment
- Effective communication
- Innovative mind and positivity
- All of the above
Question 11: Would you provide suggestion that which ways can be used to develop an effective organizational culture for generating positive outcome from leadership performance?
- Open Rewards and Recognition
- Transparency
- Development of different channels
- Establishment of core values
Question 12: Provide your concern about the suggested ways that can be useful for managing the organizational culture and performance in highly competitive market.
- Strongly Agree
- Agree
- Neural
- Disagree
- Strongly Disagree


