Principles And Practices Of Product Costing And Pricing Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of Principles And Practices Of Product Costing And Pricing Assignment, written by the expert.
Introduction
Product costing and practices, an integral part of the cost accounting provides information to operate the business activities. This process differs from accounting or financial practices, as it concentrates on costs, generation of costs, and on reducing the expenses. In this essay, the cost accounting principles and practices followed in Australia and Singapore is presented. The industrial standards and the plans made to control the costs to specific products in accordance with the industrial standards are examined in the practice part. Costs of the products influence the buyer’s willingness, and thus the practices in different countries to control the production costs are examined (Hoozée & Hansen, 2018).
Principles of product costing
Schmidt & Nakajima (2013) outlined the principles of product costing as a process to examine and systematically indulge in the product cost management process. The product life cycle includes important cost control factors that contribute towards the development. Costs analysis process has to be measurable, manageable, and defined. With this the companies could launch new products and constantly regularise the costs of the products on the market.
In Australia, the manufacturing units preferably follow the standard costing method, where the costs are controlled by examining the variances. Under section 102 of the inventory management, the type of costs to be included in the production processes is outlined. The variances are used to compare the actual costs to the pre-defined standards and this facilitates the actions. In a standard for cost analysis and revenue generation, the reason to implement the control of expenses through the variance evaluation and standard settings are outlined.
A standardised technique to measure the inventory cost, including the standard expenses are outlined. This allows getting the approximate expenses, where the standard expenses takes into the account the normal material levels and product supplies. A constant evaluation is done to increase the labour efficiency and the product costs. An example of the retail cost analysis is being presented. As per the price regulation process, an accurate method to price the services and products is done through the stated policy method (Tsai et al., 2010).
As per the competition and consumer act of 2010, the retail store in Australia can follow a comparative pricing method were the sale price of the services can be easily compared with the former price. The previous price valuation method could be “the recommended retail price” method. This costing technique is applied to stop misleading the customs or provide improper information.
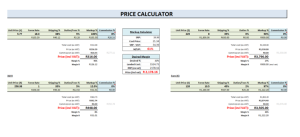
Cost product practices in Singapore
In 2016-17, the production and sales of the retail manufacturing unit in Singapore had increased by 15% van Triest & Fathy (2007). This increase resulted due to the improvement in the unit service or price cost components like royalty, utilities charges, and a decline in the labour charges. The business cost unit from 2012-2017 for the retail stores and the manufacturing sector had increased by 1.1% p.a. different companies also experienced a downfall in the production and the retail industrial performances, which impact the product costs in the country.
The companies operating in Singapore follow a marginal costing method, where the products are charged at a marginal value. In the marginal costing method, the variable expenses and direct costs are included in the cost data analysis. These charges are differently reflected in the costing statement, and is using used at the time of decision-making to improve the sales and the value of the products. This costing principle is preferred by the companies to make short-term decisions like make r buy the products in the given period of time.
Labour costs spent by a company in the manufacturing sector are usually quite high, and it contributes to a major portion of the production expenses. The other charges are the loyalty costs, royalty payment, and others. These expenses contribute a larger part of the production cost. With the help of the marginal costing process, the companies finely distribute the expenses and evaluate the costs associated with different production process. It assists in evaluating the reason for the cost increase and develops and introduce new processes top control the expenses (Hoozée & Hansen, 2018).
The IASC and IFRS standards are followed for the costing process, and to determine the best practices that would be used in different production and sales unit in Singapore. Most of the manufacturing and retail industries preferable use the marginal costing standards, while the small sellers follow cost based process.
Practices of product costing
During 1980’s and 1990, companies operating in different countries experienced a gap between the costing process and practices followed and the method followed to charge the expenses. It was realised that a single costing system designed to value the inventory didn’t meet the need of the information requirement to make managerial decisions. The cost structure followed in the companies had to be changed, and it needed to include the direct labour based cost and overhead allocation method, which had to be related to the production process.
The traditional method followed to record and analyse the cost information based on the direct labour cost evaluation was not effective, as it restricted the management from making the useful and accurate decisions. Accurate costing or cost valuation process was not recommended in case of multiple product manufacturing process. In Australia, the standardised process and methods to record the production costs were highly evaluated. It enabled the management to manufacture products and sell it to the clients in the local and international markets (Schmidt & Nakajima, 2013).
A marginal costing process was followed in Singapore, so as to closely monitor the cost variations incurring in the production department. With the stated process, it was possible for the companies operating in different countries to regularise the costs and increase the value for the services. A change in the cost standards and principles were also needed to meet with the international standards needed to export the products to a foreign country. With the standardised process, the companies could regularise the price and approach the customers from different markets.
Critical evaluation
Tsai et al., (2010) analysed the need to adopt and followed the standardised process to cost management. The costing methods and standards followed in various countries differ from each other, and it is done in accordance to the accounting policies of the country. A process to evaluate the costs for the product might not be suitable for the other one, due to the labour cost, raw material availability, and others. However, a standardised process and practices are followed to value the overhead charges that include the direct labour costs, machine hours, and other incidental charges that are included in the production process.
The labour costs in Australia are marginal as compared to the charges levied in Singapore. Part from the labour charges the other costs of eh raw materials, taxes, and others has to be proper accommodated by the manufacturing units. This is done so to valley or calculates the right cost of the products from the clients. Competition in the respective market regularise the price for the products, and thus it has to be constantly monitored by the management. A standardised cost valuation process enables the management to charge the customers the exact price and improve the cost valuation process.
A costing analysis practice followed in a country might have to be upgraded or changed in the other. In Singapore the companies highly concentrate on the recovery of the direct labour and the marginal expenses incurred in the production process. Australian companies concentrate on recovering eh overall expenses incurred on the production of different units. This is an essential factor that differentiates the product value and the costs incurred by the companies on valuing the actual costs of the products on the company. The accepting standards clearly specify the process that is adopted to charge the clients for the products.
The valuation process is also important for the companies to determine the actual costs incurred on the product valuation and in charging the clients for the costs. These are quite an important factor that is included at the time of calculating the product value. Full product costs intend to reflect the approximate average long run expenses incurred by the company on the production works. In the normal capacity, the overhead valuations and its dispersion is examined in an accurate manner. These aspects are done in accordance with the cost standardised process, where the costs and other charges are equally charged and valued by the company.
Conclusion
The cost practices and the policies differ for the companies and the countries. Policies are implemented in accordance to the standardised policies that is followed in the country. The cost bifurcation and its valuation are done in accordance with the policies stated by the companies. In a standardised process, the reason for the product variations and its impact on the operational works and in the sales are examined by the management. By doing this the managers could easily examine the changes to be implemented to increase the sales and the product value for the clients.
References
Hoozée, S., & Hansen, S. (2018). A Comparison of Activity-Based Costing and Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing. Journal Of Management Accounting Research, 30(1), 143-167. doi: 10.2308/jmar-51686
Tsai, W., Lin, T., & Chou, W. (2010). Integrating activity-based costing and environmental cost accounting systems: a case study. International Journal Of Business And Systems Research, 4(2), 186. doi: 10.1504/ijbsr.2010.030774
van Triest, S., & Fathy Elshahat, M. (2007). The use of costing information in Egypt: a research note. Journal Of Accounting & Organizational Change, 3(3), 329-343. doi: 10.1108/18325910710820328
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

