SM4022 Globalisation Innovation and Sustainability
Introduction
Globalisation, Innovation, and Sustainability are the most essential aspects of the modern corporate era (Cramer, 2017). Companies and business houses largely aim at mastering these three principal factors or aspects driving towards the path of success. The present report sheds light on the strategies and action plans of Nike concerning globalisation, innovation, and sustainability.

Nike is a multinational company engaged in design, development, production, and global marketing and sales of apparel, footwear, accessories, equipment, and services. The report includes a systematic review of available scholarly publications and the opportunities and challenges faced by Nike.
Globalisation
Literature Review
According to Cherunilam, (2020) globalisation refers to the approaches and ways by which people across the globe have become more connected and interacted economically, politically, and socially. Globalisation in the corporate world is the change in the business model of a company associated with a single nation to the one that operates in multiple nations. It offers immense opportunities to enhance prosperity and ensure better jobs. In the context of consumers, globalisation provides a huge variety of products to choose from available at affordable prices. For companies and business houses, globalisation provides great opportunities concerning gains of higher efficiency as well as productivity growth.
Thrift, (2020) claims that the processes of globalisation are inseparably secured with competitiveness. In a global economy, the quest for national competitiveness increases in line with the international systems. Globalisation is mainly associated with integration and liberalisation of the country, borderless movements of investment and capital, the flow of information, mobilisation of the workforce, and many other aspects. Multinational businesses grow in scope to size and to a certain point where the global economy is now dominated by international companies from all the nations in the world. As different economies enhance, trade and related activities continue to grow as well as technological advancements and increased tourism contribute to making the gap among nations become smaller and enhanced understanding of several legal aspects of internationalisation.
Rasche et. al. (2017) observed that globalisation offers immense opportunities and benefits which include the opening of large and diverse markets, shared technology, and enhanced flow of information, capital, trade, and people, sharing expertise and knowledge, and promotion of diversified workforce. The other advantages of globalisation include collaboration and sharing of resources, availability of varied products at affordable prices, cross-cultural exchanges, and increased household income. However, with the benefits and opportunities, globalisation also offers some issues and challenges. The major issues and challenges faced by multinational corporations as well as the ecological environment include political, technological, dynamic socio-cultural aspects, legal compliances, and economic concerns, in which they operate. Additionally, the other challenges include exploitation, high costs of investments, confusing local systems, challenges related to immigration, loss of localised jobs, and weak regulation.
Integration/Responsiveness framework concerning Nike
The Integration/Responsiveness framework describes the features or characteristics of a corporation and focuses on deriving feasible strategies from the gained insights. The characteristics or aspects of a business or a company are developed by a set of relevant political, economic, and organisational imperatives that contribute to shaping strategy-making (Meckling & Hughes, 2018). The degree up to which a company is capable to use the same methods and products in other economies is referred to as Global Integration. Additionally, the degree or the extent up to which a company should customise or alter its products and the applied methods to meet the conditions in other concerned nations.
Nike is a multinational corporation operating on a large scale and in a huge number of countries. The leading apparel company maintains a high level of global integration but then it witnesses a significantly poor level of local responsiveness. Nike has determined the importance of international customers concerning higher sales and presence of global competitors in developing nations like India and China. Moreover, the fashion company has also identified the need for capital and investment intensity in the concerned international fashion industry concerning promotional strategies. Nike also spotted the degree and the extent of technology intensity in the global fashion industry, the universality of wants and requirements in the customer base, and the prevailing competitive pressures concerning cost reduction. The leading apparel company, Nike lacks local responsiveness in relation to differences in certain needs of the local customers, urgency, and requirements to adapt itself to the global product considering local needs, and the buying behaviour patterns of the locals in the Indian market structure (Ortiz-Villajos & Sotoca, 2018). This analysis and assessment place the apparel company, Nike in the Global segment of the Integration/Responsiveness framework.
Expansion strategies of Nike
The strategies of globalisation and expansion adopted by Nike include Joint Ventures, Licensing, Exporting, and Wholly-owned subsidiaries. The adopted strategies and action plans focusing on international expansion have immensely supported the company in achieving its goals and objectives that cater to a large customer base, improved competitive advantages, and immense success across the globe (Shakeel et. al. 2020). The company undertakes different expansion strategies in different nations based on several factors and aspects in the external environment. Joint Ventures, Licensing, Exporting, and Wholly-owned subsidiaries are proved to be effective in the case of Nike. The expansion strategies offered benefits to the company in terms of economies of scale, access to new markets and distribution channels, enhanced brand name, lowered the cost of production, innovation, and shared expenses as well as risks. Moreover, these strategies enable the company to establish and operate within a short time frame.
However, with the benefits, the expansion also offers some great challenges to Nike. The major issues and challenges faced by the company include the frequently changing business environment. Every country differs in the external environment offered to business houses and companies. Any changes in factors like legal compliances, political conditions, socio-cultural aspects, technological advancements, and environmental considerations are the major source of challenges to Nike. The other key challenges include lack of capital or finance required in the expansion process, space limitations, communication issues, designation of authorities and responsibilities, the requirement of new employees, old and outdated business practices, and poor expansion plans and strategies (Lüdeke‐Freund, 2020). Hence, the company should consider all the challenges and issues prior to making decisions concerning business expansion into new nations.
Innovation
Literature Review
According to Karno & Purwanto, (2017) innovation refers to the design, development, and implementation of unique ideas which enhance the ways things and operations are undertaken or the ways to accomplish set goals and objectives. Innovation and creative techniques support an organisation to improve levels of efficiency and productivity. Abilities and skills to introduce innovation help an organisation to gain competitiveness and adapt as well as respond to changes in the business environment. Innovation is the principal source of enhancing economic growth as well as creating opportunities for new employment. Moreover, innovation holds the potential for realising and gaining environmental benefits. Several authors and writers highlight different categories of innovation based on its type, competence, degree, ownership, and impact. It is considered and can be demonstrated in both services as well as manufacturing sectors operating on a different scale (small, medium, and large). Although, the two sectors highlight many differences but the general process and definition of innovation remain unchanged. The service sector depicts its unique characteristics distinguished from the manufacturing sector. The differentiating elements which characterise the service sector are perish ability, heterogeneity, and intangibility.
Basova, (2017) claims that innovation is not only about opening up or entering into new marketplaces; it can also be highlighted in new ways of catering to older and established ones. Innovation is further classified into four categories which include Product, Process, Position, and Paradigm. Each of the four categories can take place along an axis, running from incremental through radical change. Innovation offers many benefits to a business in terms of enhanced growth potential, keeps an organisation relevant and profitable, helps corporations to differentiate themselves, and gain strong competitive advantages in the concerned industry. Moreover, it simplifies each process and operation, thereby, ensuring enhanced effectiveness and efficiency. Such strategies and techniques of implementing innovation drive an organisation towards the path of success and development in the long run.
However, with the benefits and merits, innovation also offers great challenges and issues to an organisation. Hahn et. al. (2018) observes that innovation requires much time and is very costly. Many companies experience negative financial status due to higher investments in the adoption and implementation of innovative techniques. Innovation is also criticised due to the organisations ending up wasting valuable resources by designing and developing something that doesn’t contribute to selling. Hence, with the pros, innovation also offers some cons to the companies and business houses. However, it stills holds utmost importance in driving a company towards the path of gaining strong and exceptional competitive advantages as well as long-term growth.
Innovation strategies in Nike
Nike is a well-established fashion brand operating across the globe and enjoying a strong brand name in the industry. The company is known for its effective innovative strategies and techniques in the market (Wijethilake, 2017). In the year 2019, the company developed a new strategy known as “Consumer Direct Offense” which takes a page from direct to customer start-ups by increasing the pace of product innovation as well as speed-to-market, thereby, enhancing direct engagement with the company’s customers. Moreover, digital innovation has resulted in accelerating help in differentiating between winners and losers in the B2C retail industry. The company is also focusing on digitising its end-to-end supply chain. The implementation of a unique strategy called Express Lane enables the company regarding product updates including colours for famous models depending on real-time insights, materials, and restocking stores in as fast as two days.
Nike is also known to highly focus on continued product innovation to meet customer needs and expectations based on the concepts of personalisation and customisation. Nike initiated the acquisition of a consumer data and analytics company, named, Zodiac. The leading product innovation introduced by the brand is Adopt BB (BB is an acronym for Basket Ball). The product can actively change its shape and connects to a Smartphone via Bluetooth. It is vital in collecting the extraordinary amount of information and data related to human movements, analogous to what the company gathers in its internal Performance Lab, outstanding anything close to Nike+ did (Meuer et. al. 2020). Hence, Nike is well-known for its unique innovative approaches in various categories including Product, Process, Position, and Paradigm.
Sustainability
Literature Review
In the opinion of Abbas, (2020) sustainability refers to the abilities and ways adopted by corporations for utilising resources to fulfil their present needs and requirements without compromising the needs and requirements of future generations. Corporate sustainability is a triple bottom line concept which analyses and demonstrates the process through which an organisation obtains and fulfils its obligations, responsibilities, opportunities, and the associated risk factors from social, environmental, and economical areas. The triple bottom line concept demonstrates the management of people, planet, and money consisting of people (which means social), environment (planet), and profit (refers to financial and economic aspects). Corporate sustainability is largely influenced by the time dimension as it impacts an organisation both in the short as well as long term.
According to Bansal & Song, (2017) sustainability in organisations refers to the impact businesses have on society as well as on the environment. Sustainability strategies and action plans focus on positively affecting either one or both of these areas, hence, supporting addressing some of the global issues and problems. Sustainability strategies help businesses to address issues including income inequality, racial injustice, and depletion of natural resources, climate change, human rights issues, pollution, fair working conditions, and other environmental or societal aspects. Sustainability offers immense benefits to corporations including brand protection, mitigation or elimination of risk factors, gaining strong and unique competitive advantages, being purpose-driven, and caters to the growing market for sustainable products. Additionally, it also helps corporations in becoming more effective and efficient, gain a platform for innovation, enhance brand value and image, achieve better growth aspects, attract and retain competent and talented staff, and cut costs and strengthen relations with different stakeholders groups.
Several authors argued that sustainability in business is a major source of increasing overall expenses and costs of undertaking business operations. It includes costs related to labour, capital extension, getting certifications, and implementation of quality and assurance checks. The combination of all these costs leads to a significant increase in overall business costs. Moreover, sustainable business strategies hold the potential to increase risks in certain ways when a company invests a huge amount in the introduction of a new sustainable product or service or a new sustainable technology (Bansal & Song, 2017). The introduction or implementation of any of these sustainable products or technology doesn’t provide any guarantee related to the demand of the introduced product or service or related to the return on the cost of the newly implemented technology.
Sustainability strategies in Nike
Nike is a leading multinational apparel and footwear brand. The company enjoys a strong brand name and reputation in the international market due to its unique strategies focusing on sustainability (NIKE: Is it the Sustainability Transformation of the Decade? 2017). The strategies implemented by Nike include Power Nike facilities which focus on a set target of using 100% renewable energy by the year 2025 and reduce carbon emissions across the entire global supply chain of the company by the year 2030. The company aims at the concept of Circular Economy as well as equipping the world with the brightest thinking approaches through the platform of NikeCircularDesign.com. Nike manufacturers of footwear have significantly cut the use of energy per unit by approximately 50% which means that the company takes half the energy as well as generates approximately half the emissions to develop Nike footwear.
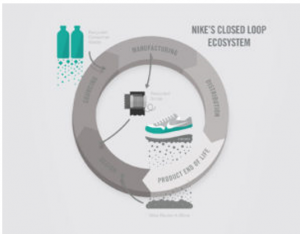
Figure 1 Sustainable product lifecycle at Nike
(Source: NIKE: Is it the Sustainability Transformation of the Decade? 2017)
Nike initiated working with better contract factories that are committed and dedicated to transforming their companies beyond a base or a foundation of compliances to be green, lean, equitable, and encouraging for the workforce (Cramer, 2017). The apparel and footwear company strives to generate zero waste from contracted shoe manufacturing sent to incineration and landfill without recovery of energy. In addition to this, the company also works to reduce the generation of waste and get close to the model of closed-loop which is Nike Grind. Nike Grind refers to the palette of high-end regenerated and recycled materials built and developed from original products and materials. Hence, the adoption and implementation of effective and strong strategies leading towards sustainability and green concepts have made Nike gain exceptional competitive advantages and be successful in the global fashion industry.
Conclusion
Hence, it can be concluded from the above report that globalisation, innovation, and sustainability are the key factors which determine the growth, development, and success of an organisation in the industry. An organisation should develop and implement exceptional and promising plans towards the adoption and application of the above-mentioned three aspects as they offer immense benefits to the corporations. The report included a systematic review of literature obtained from various scholarly sources including journals, articles, books, and other related sources. It highlighted the case of Nike which is a leading multinational fashion company operating across the globe. Moreover, the report included the application of strategies focusing on globalisation, innovation, and sustainability by the concerned organisation. Therefore, it can be concluded that globalisation, innovation, and sustainability are the principal success driving factors in the modern corporate world and hold utmost importance to influence and attract customers across the globe.
References
Abbas, J. (2020). Impact of total quality management on corporate sustainability through the mediating effect of knowledge management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, 118806. Retrieved from: <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652619336765>
Bansal, P., & Song, H. C. (2017). Similar but not the same: Differentiating corporate sustainability from corporate responsibility. Academy of Management Annals, 11(1), 105-149. Retrieved from: <https://journals.aom.org/doi/abs/10.5465/annals.2015.0095>
Basova, A. (2017, June). Accounting-analytical model of innovation-active business entities. In International Conference on Trends of Technologies and Innovations in Economic and Social Studies 2017 (pp. 40-46). Atlantis Press. Retrieved from: <https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/ttiess-17/25885409>
Cherunilam, F. (2020). International business. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. Retrieved from: <https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=bbDrDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=globalisation+in+business&ots=leZ4u9qMb3&sig=-qAjF57yot7trPXZun42nFXOwZg&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=globalisation%20in%20business&f=false>
Cramer, J. (2017). Corporate Social Responsibility and Globalisation: an action plan for business. Routledge. Retrieved from: <https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=TGRQDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=globalisation+in+business&ots=VNDqMAN4eL&sig=ia-1ttTlWBYUpnTuhEC44rySjqU&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=globalisation%20in%20business&f=false>
Hahn, T., Figge, F., Pinkse, J., & Preuss, L. (2018). A paradox perspective on corporate sustainability: Descriptive, instrumental, and normative aspects. Journal of Business Ethics, 148(2), 235-248.Retrieved from: <https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10551-017-3587-2>
Karno, C. G., &Purwanto, E. (2017). The effect of cooperation and innovation on business performance. Calitatea, 18(158), 123. Retrieved from: <https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Edi-Purwanto-3/publication/317385734_The_Effect_of_Cooperation_and_Innovation_on_Business_Performance/links/59380afaaca272bcd17707ca/The-Effect-of-Cooperation-and-Innovation-on-Business-Performance.pdf>
Lüdeke‐Freund, F. (2020). Sustainable entrepreneurship, innovation, and business models: Integrative framework and propositions for future research. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(2), 665-681. Retrieved from: <https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bse.2396>
Meckling, J., & Hughes, L. (2018). Protecting solar: global supply chains and business power. New Political Economy, 23(1), 88-104. Retrieved from: <https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13563467.2017.1330878>
Meuer, J., Koelbel, J., & Hoffmann, V. H. (2020). On the nature of corporate sustainability. Organization & Environment, 33(3), 319-341. Retrieved from: <https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1086026619850180>
Ortiz-Villajos, J. M., &Sotoca, S. (2018). Innovation and business survival: A long-term approach. Research Policy, 47(8), 1418-1436. Retrieved from:<https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048733318301094>
Rasche, A. N. D. R. E. A. S., Morsing, M. E. T. T. E., & Moon, J. E. R. E. M. Y. (2017). The changing role of business in global society: CSR and beyond. Corporate social responsibility: Strategy, communication, governance, 1-30. Retrieved from:<https://www.cambridge.org/highereducation/api/resources/C485294F3F1601F2120ED2C8E70B0BB6>
Shakeel, J., Mardani, A., Chofreh, A. G., Goni, F. A., &Klemeš, J. J. (2020). Anatomy of sustainable business model innovation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 261, 121201. Retrieved from: <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652620312488>
Thrift, N. (2020). Virtual capitalism: the globalisation of reflexive business knowledge (pp. 161-186). Routledge. Retrieved from: <https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003135807-8/virtual-capitalism-globalisation-reflexive-business-knowledge-nigel-thrift>
Wijethilake, C. (2017). Proactive sustainability strategy and corporate sustainability performance: The mediating effect of sustainability control systems. Journal of environmental management, 196, 569-582. Retrieved from: <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479717302724>
Online:
NIKE: Is it the Sustainability Transformation of the Decade? 2017. [Online:]. Accessed through:<https://digital.hbs.edu/platform-rctom/submission/nike-is-it-the-sustainability-transformation-of-the-decade/
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

