STRATEGY MAKING
Part 1: Starbucks Business Report
Starbucks is currently one of the biggest giants in the coffee making industry as well as in the worldwide business industry. Spanning over 6 continents and 77 countries and it has covered over 30,000 locations (as of early 2020) and with nearly 291,000 employees (as of 2018) Starbucks is expanding around the world in a very short amount of time. Starbucks was established as a high quality whole beans coffee seller by three local businessmen in 1971. However, in 1981 Howard Schultz visited the store and he had an idea to build a strong company by the name of Starbucks and expand high quality coffee business across the United Kingdom. Starbucks opened their first store in the UK in 1998. Starbucks’ target audience was 18 to 24 years old. Starbucks’ annual profit grew from $21.3 billion (2016) to $24.7 billion (2018) and as of 2019 they reached over $27.4 billion in overall revenue. Starbucks achieved revenue growth of 14.17% and improved market to approximate 26.48%. Starbucks had tough competitors in the UK since 1998 but as of 2020 the number of their strong competitors in the United Kingdom is 11. Here is a list of their top 7 competitors. The first company is Caffe Nero. A brand that was established in London in 1997 is now one of the leading independent coffeehouses in Europe. Gerry Ford has an idea to create traditional Italian coffee shops around the continent. Caffe Nero has over 1000 stores across Europe and Asia. They have almost 9000 employees and revenue reached over $532 million as of May 2019. The second big competitor in the UK for Starbucks is Costa Coffee. Costa Coffee is a multinational coffeehouse with more than 3800 stores in 32 markets and is the leading coffee brand in the United Kingdom and worldwide second after Starbucks. They have 18,000 employees working under them as of 2018 and their revenue reached over $1.5 billion and Coca Cola the chain for $5.1 billion. The next brand is McDonald’s coffee shop McCafe. They have over 1.7 million employees and $22 billion annual revenue but by 2003 McCafe generated 15% more revenue than a regular McDonald’s. McCafe has 15,000 inn store coffee outlets globally. The next one in the list is Dunkin’ Donuts. They are the fourth largest coffee chain in the world. Since Bill Rosenberg opened his first outlet in Quincy in 1950, the company grew worldwide over the years.They have 18,000 employees and have expanded over 33 countries. Their annual revenue is $1.2 billion. The next company is Caffe Ritazza. Founded in 1995 in London has over 37,000 employees worldwide and expanded over 30 countries. They generate overall $3.4 billion as of 2018. The next coffee shop is a coffee and tea manufacturer and online retailer of coffee and tea products. The company is Peet’s Coffee. They have almost 5000 employees and generate overall estimated $800 million annual revenue. The last one on the list is Tim Hortons. They covered nearly 5000 locations in 14 countries. They have 4,800 employees and generate an overall estimated $2.2 billion annual revenue.
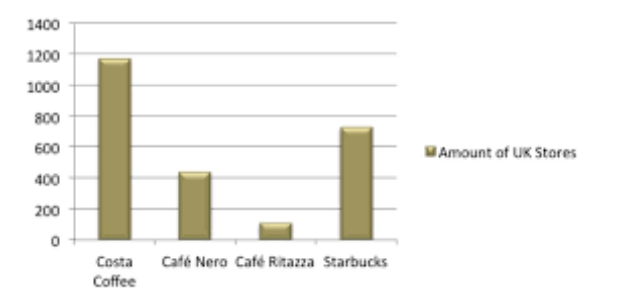
Figure 1: Market position of Starbucks in UK
(Source: Hendra et al)
- Political Factors
To import the coffee beans and other materials in the UK the trade relationship plays a big part. There are a lot of trade relationship regulations and agreements that help the coffee industry but the uncertain regulations and agreements like the United Kingdom’s one are unlikely to affect the coffee industry. As stated by Hendra et al. (2019) the government of the United Kingdom decides where to import from as a way to support international peace. The good part about this is the coffee beans have to pass a minimum test to be allowed in the country and it has to be free from pests and diseases. The involvement with the government has a good side but it rejects the fact that the coffee making company cannot import coffee beans from any country other than the countries that have trade sanctions.
- Economic Factors
As stated by Roland et al. (2019) as of March 2020 the coffee industry contributes 17.7 billion GBP in the United Kingdom’s economy. The UK boosted the consumption rate daily, now the number is 95 million cups daily and the percentages are 65% consumed at home, 25% at work or while studying and 10% is drunk in coffee shops, bars or restaurants. The coffee industry is helping the UK’s economy steadily and it does not look like that the percentage or the revenue is going down from that.
- Social Factors
As stated by Jennifer and Carlos (2020) in 2003 the hot drinks market decreased by 2.3% as the young people were becoming health conscious but now after several researches over this topic happened over the past few years it is clear that coffee does not have any ingredients which are bad for health and now for social media it is a trend. Another social trade that helps the coffee industry is fair trade and the coffee industry is the main target for this movement. This is an international movement which seeks better opportunities for farmers behind the production. Technological Factors
Technically the biggest trend in the food and beverages industry is Genetic Engineering. Genetic engineering modifies the drink in the genetic level which ultimately improves the taste, yield and more and it carries the label ‘GMO’. Genetic engineering is quickly growing across the food and beverages industry and it is helping the producers to earn more. Genetic engineering is contributing a lot in the coffee making industry in general across the UK and all over the world. As stated by Viachaslau et al. (2019) another technical aspect that changes the coffee making industry across the globe is coffee machines. Now coffee machines have different varieties and that is helping the producers to give customers their orders very fast.
Environmental Factors
The world is facing numerous environmental issues and most of these issues are unrelated to the food and beverages industry in general. In environmental aspect there are certain concerns over the farming with the usage of pesticides and fertilisers on water consumption but the coffee making industry is making sure that they can support the environment with a little contribution from their part and that is the reason why every coffee making company across UK and over the world rejected plastic cups and started using paper cups even high quality fiver cups. As stated by Chinglik and Flavio (2019), the coffee making industry in the UK takes every precaution to help the environment with a little consideration and even some outlets contain banners and posters about their supporting the environment.
Legal Factors
Legally the coffee making industry has certain barriers. As stated by Fernando et al. (2019) coffee falls under food and drinks regulations and the subject has a range of laws on how it should be stored, brewed and even transported. Coffee contains a large amount of caffeine and there are certain standards for that in some countries. These legal standards are getting strict day by day but coffee handling is quite safe so it should not affect the industry after all.
Threat of new entrants: Moderate
The threat of new entrants have been considered to be moderate in the case of Starbucks as it has been evidenced that the entry barriers are not that high for new organisations to enter. As commented by Chinglik and Flavio (2019), the business has a monopolistic structure of rivalry in the case of new entrants. The new entrants can easily rent places and additional infrastructure. Even any local cafes could also replace the organisation at a localized level.
Threat of substitution: High
There are various products available in the market which could easily substitute new products. These products include juices, caffeinated drinks or soft drinks. Even the pubs and bars which provide non alcoholic drinks could provide the customers with the similar atmosphere and social experience that Starbucks promise. As commented by Fernando et al, (2019), individuals also could prepare coffee back at their home which would cost them a lot less. Moreover, the switching cost for buyers is very low and they could easily switch to substitutes.
Bargaining power of buyers: Moderate to low
As the industry has various buyers, it is difficult for any individual buyer to bargain with the organisation. Moreover, the organisation offers various kinds of products and each has a specific customer base. Thus, every kind has low volume purchase. This reduces the capacity of the buyer.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Low
The organisation has its own supply chain and that provides the coffee beans and these coffee beans are developed in specific locations. These have their own sources of information. This has reduced the cost incurred by the organisation in terms of shifting between suppliers. Thus, the bargaining power of suppliers is low.
Competitive rivalry: Moderate to high
It has been considered that the organisation faces a monopolistic rivalry. Its competitors also possess a significant amount of market share which impacts the competitive situation of Starbucks. Moreover, buyers do not have to incur any switching cost in terms of providing switching to any of its rivals. Thus, competitive rivalry is high for Starbucks.
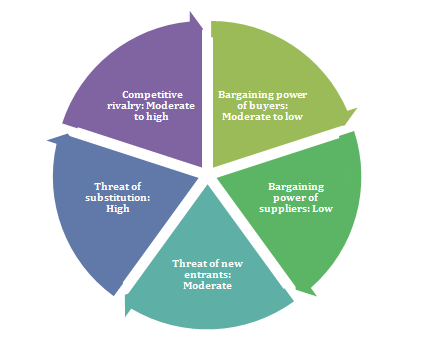
Figure 2: Porter’s five forces
(Source: Created by the author)
Industry lifecycle models
It has been evidenced in the research conducted by Ahmed, 2020 that Starbucks is now in its third stage of its industry lifecycle. This model includes four stages. The first stage is the introduction stage. The second stage is the growth stage. The third stage is the maturity stage and the fourth stage is the decline stage. Starbucks have passed the first two stages and now is in the maturity stage.
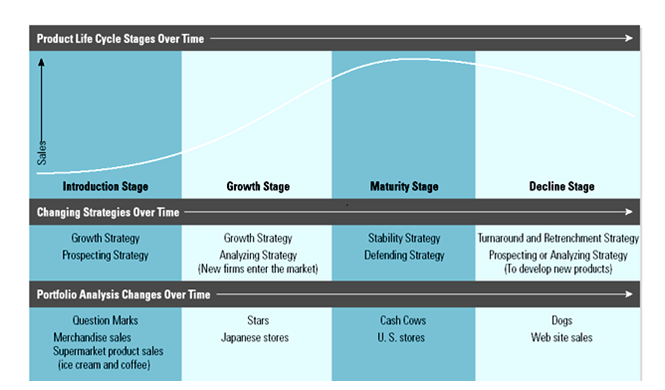
Figure 3: Industry Life Cycle of Starbucks
(Source: Ahmed, 2020)
V (Value)-
Brand Image-When one considers Starbucks, they ordinarily think morals, noble cause, and so on. Starbucks picture depends on morals and quality and it does in reality make the organization increasingly important.
Production network- Starbucks’ store network is the fundamental motivation behind why it can keep up the incredible quality.
Quality-Starbucks is known for its superb nature of espresso got from different pieces of the world.
Pleasing Environment-Starbucks has become a spot for gatherings, bunch work, dates and so on.
R (Rarity)
Brand Image-All of the contenders has this also, yet Starbucks rules with their image picture, so it’s a test for contenders.
Store network– Starbucks has the high ground here. Contenders would have an extremely hard time since this requires both speculation and system.
Quality – Starbucks is one of a kind with this, and a ton of speculation and time goes into this.
Worldwide nearness: It would be difficult for contenders to extend universally since it would require a great deal of speculation.
Pleasant Environment-Competitors can accomplish this however it would require interest in inside of stores, preparing and centre.
I (Imitability)
Brand Image-This would be difficult to do, however it could occur later on.
Inventory network: This would be difficult to do, yet it could occur later on.
Quality – Not generally ready to mimic.
Worldwide nearness: Not generally ready to mimic.
Pleasing Environment-Not generally ready to emulate.
O (Organization)
Brand Image-Yes, Starbucks, has an outstanding picture.
Production network: Yes, Starbucks sources 99% of its espresso morally. Top notch beans are sourced from around the globe.
Quality – Starbucks drinks are notable and clients are energized when occasion and strength drinks job around.
Worldwide nearness: Yes, and it helps Starbucks produce high income and acclimates individuals with the organization around the globe.
Pleasing Environment-Yes, gives Starbucks an edge as a gathering/venture place.
Inbound logistics- Starbucks has coffee buyers which specifically have been appointed by the company. As commented by Lucas and Maria (2019), the unroasted beans are produced by these buyers directly.
Operations- It has been evidenced that the organisation has its reach to more than 75 markets which is either a franchise or a direct store. Thus, in total the brand owns 24000 stores all over the world.
Outbound logistics- There is next to no items are sold in outbound process. Most of the items are sold in their own or in authorized stores.
Marketing and sales- Starbucks does not engage in marketing procedures extensively. They engage more in providing quality to their customers. Moreover, they provide customer support in a higher level. However, there is a system of need based advertising which is used in the time of product launches. It is also used for entering new markets (Mesfin and Woon, 2019).
Technology- The organisation is famous for its technological advances. It is often witnessed that customers make the outlets into their office spaces or meeting spaces as they can use the high speed Wi Fi. Moreover, the application which has been launched in 2008 creates a network of all the customers (Dongyun et al. 2019). Here, they can review products and provide recommendations. In addition, the organisation also uses the framework of iBeacon. This is used so that customers can order for products through apps and notice its status as well.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
| ● Strong position in the market
● Globally established brand ● High quality products ● Customer Loyalty ● Aesthetic approach ● Brand value |
● High price range
● European tax avoidance ● Overall same products ● General standards of products ● Negative corporate image ● American coffee culture clashes with European coffee culture |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| ● Global brand value
● Try out different marketplace ● Brand extension ● Reaching out to the target audience ● Contributing to countries economy ● Partnerships with other firms |
● Increasing competition
● High price range ● Independent coffee houses ● Cost of raw materials increasing ● Price fluctuation in the coffee industry ● Store closures and higher wages |
- Strength –
Strong position in the market – Starbucks covered 6 continents and 77 countries in their small span of time.
Globally established brand – Starbucks have covered over 30,000 locations globally. This is a successful brand which generates overall $27.4 billion yearly as of 2019.
High quality products – As commented by Ahmed (2020) the main reason Starbucks is so popular today globally is that they produce high quality products across the world.
Customer Loyalty – As stated by Dongyun et al. (2019) the customers of Starbucks are very loyal because Starbucks has a set target audience and it varies from country to country but mostly their age range is youth customers and due to social media and their well branding the customers are always going back to Starbucks again and again
Aesthetic approach – The Starbucks outlets across the world have a beautiful aesthetic approach and friendly and cosy ambience with light music and portraits on the wall.
Brand value – As stated by Mesfin and Woon (2019) anybody can tell that this is Starbucks’ logo by sharing a glance at it. Starbucks is one the biggest names in the business world in general.
Weaknesses –
High price range – Starbucks has a high quality range of products but they are quite expensive for most of the customers and that is the reason most of the people want to enjoy their coffee but they cannot do that so they avoid it.
European tax avoidance – Due to their tax avoidance in the UK they faced a lot of criticism and it was announced that Starbucks did not pay tax on their 1.3 billion GBP sales for three years in 2012.
Overall same products – Starbucks has a range of products but mostly the same one with other companies like Caffe Nero, Costa Coffee etc.
General standards of products – Generally some of their products offerings are not quite going with the cultural standards of some countries.
Negative corporate image – Like any big companies, Starbucks does come under a lot of scrutiny and like any other big company they are investing in corporate social responsibility activities.
American coffee culture clashes with European coffee culture – Starbucks does contain a particular culture in their stores and some people do not like that while enjoying their coffee. Some people do like their own culture but now Starbucks is changing that.
Opportunities –
Global brand value – Starbucks is globally acknowledged brand and that helps them to open certain opportunities for them.
Try out different marketplace – As stated by Lucas and Maria (2019) Starbucks has a wide range of following and customers that are loyal to them and give them confidence to try out different marketplace.
Brand extension – Starbucks have extended their brand to 77 countries and they can plan more as well. They have that opportunity to explore different cultures and bring them into sharing a coffee (Adriana, 2019).
Reaching out to the target audience – Starbucks has their own sets of target audience mainly reaching out to the youth.
Contributing to countries economy – Their contribution to the country’s economy helps the foods and beverages contribution to that country’s economy grow. Starbucks’ contribution including all of their outlets in that particular country helps then generate a lot of revenue and their taxation helps the country’s economy to grow.
Partnership with other firms/artists – As stated by Marina (2019) now Starbucks is in a higher position where they can reach out to any other firm in the world with collaborative ideas and even reach out to bigger artists for advertisement or being their brand ambassador and they will accept the offer and that will be beneficial for the company.
Threats –
Increasing competition – Increasing competition around the UK will be their biggest threat. They will have to make a strategy that will tell them how to handle this situation carefully.
High price range – As stated by Patrizia et al. (2020) the other companies growth will cause Starbucks harm as their price is high and the products are high quality but general like other stores so that will cause trouble.
Independent coffee houses – Independent coffee houses in the UK are growing fast as they are cheap with good ambience and culture. People are taking this movement seriously as it saves them a lot of money.
Cost of raw materials increasing – The cost of raw materials and ingredients can cause Starbucks in terms of profitability and may force the company to raise the prices.
Price fluctuation in the coffee industry – There has been a significant market price fluctuation of high quality coffee beans.
Store closures and higher wages – Starbucks lost $22 million in 2018 as the store closures cost was high as well as the wages.
It has been evidenced throughout the study that the biggest growth prospect for the organization lays in the international market. As per the research conducted by Patrizia et al. (2020), several emerging markets such as India, Brazil, South Africa and China have a growing population of the middle income group which is the key target group of the organization. These markets could provide the company with the opportunity of opening new stores and adding more customers bringing more profitability to the organization. It is also important that the company adapts its marketing strategies with the needs of the local markets which would be culturally different from each other. These are some recommendations which would help the organization to build an international presence. These recommendations have been developed in regard with the components of SMART plans.
- Organic expansion-The core competencies and capabilities of the organization should be different in each country. Thus, it would result in a gradual building for drivers of profits. As commented in the studies of Marina (2019), this helps in an organic global expansion for an organisation.
- Product variety- It has been evidenced in the report that one of the major weaknesses of the organisation is that it has a limited range of products. As per the research of Mesfin and Woon (2019), there is a huge market of tea and juice products. Thus, it might be recommended to the organisation that it expands their range of products in order to gain maximum profitability.
- Socio-cultural aspects- This report has presented a macro environmental analysis of how the preferences of customers are shifting towards healthier products with less sugar content. Thus, it can be advised to the organisation that they include a healthy range of snacks and beverages as well in order to expand their market segment.
- Fluctuation of the coffee beans prices- Due to the volatility in the price of coffee beans, there could be an issue with the organisation’s price range as well. Thus, they could use the help of specific hedging techniques in order to mitigate this risk.
- Growth strategy- It has been advised that the organisation should tap into the emerging markets of the country area which is yet to be tapped by such giant coffee chains.
- Retail strategy- Starbucks has a product range of packaged coffees and other beverages. It might strike a deal with the retail chains in order to gain a longer shelf life which could provide the organisation with much profitability.
- Marketing- It has been evidenced in this study that the expenditure of the organisation in terms of its branding and marketing is considerably less than its competitors. Thus, it could be advised to the organisation that it should focus more on marketing campaigns to increase its brand recognition in newly entered markets.
- Technological aspects- It has been evidenced that there have been a 10% increase in the sales of Starbucks due to its mobile application. Thus the organisation is further advised to develop its application in terms of its ease of use. It should also increase its mobile payment options. Moreover, an integrated loyalty program could be established with the help of this application.
Part 2: Starbucks’ Stakeholder Report
List of internal and external stakeholder list
(Refer to appendix 1)
One priority Starbucks’ Stakeholder group (Customer)
Starbucks has specific segments of customers in terms of its approach and target market. The key segments are discussed here.
High income group- As determined by the price range of the products, most outlets of the organisation are around affluent neighbourhoods. However, mid income neighbourhoods with high disposable income is also the target customer of this coffee chain.
On the go, urban customers- Most of the Starbucks outlets are situated in urban areas. This is due to the outlook and the cultural association of the ideology that is associated with the organisation.
Technology driven- As the organisation comes up with the recent mobile application, it caters to the technology driven youth who are the main target of this application.
Health conscious individuals- Due to the newly developed healthy beverages and snacks, the new niche of health conscious individuals are also the target market of the organisation.
Power of customers on Starbucks (Mendelow’s matrix)
Customers are one of the key external stakeholders in terms of an organisation in the food and beverage industry. It has been commented in the studies of Mariana (2019), customers determine the profitability of this industry and it depends on the subjective choices of the customers. Thus, this report has identified the customers as the priority stakeholder in order to analyse its power over the organisation. The Mendelow matrix suggests that there are four kinds of stakeholders for an organisation. First kind are the key players which are the investigators and the customers of an organisation. As per the matrix, this section of stakeholders is the high power and high interest section. It has also been evidenced in Porter’s analysis in this report that customers have immense power on this organisation in terms of low switching cost.
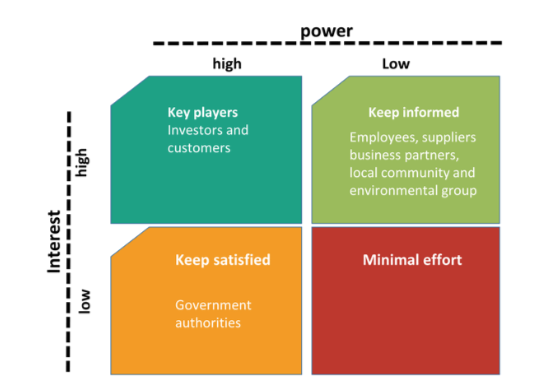
Figure 4: Mendelow’s Matrix
(Source: Patrizia et al.)
Appropriate communication strategy
The first section of the report has provided a recommendation of increasing the organisation’s social media presence and streamlining its mobile application. Similarly, in terms of stakeholder analysis as well, it will be advised to the organisation that appropriate communication strategy for the organisation would be social media. As per the evidence provided by Patrizia et al. (2020), social media campaigns increase brand equity. It also increases a sense of belonging amongst the customers.
Atabani, A.E., (2019). Valorization of spent coffee grounds into biofuels and value-added products: Pathway towards integrated bio-refinery. Fuel, 254, p.115640.
Barros Jr, F., (2019). Coffee exports and industrialization in Brazil. Applied Economics Letters, 26(9), pp.712-716.
de Luca, P., (2020). Customer Experience in the Coffee World: Qualitative Research on the US Market. In Handbook of Research on Retailing Techniques for Optimal Consumer Engagement and Experiences (pp. 257-283). IGI Global.
Farah, A. ed., (2019). Coffee: Production, Quality and Chemistry. Royal society of chemistry.
Ferreira, J., ( 2020). From the grounds up: the coffee shop industry and the circular economy _.
Filimonau, V., ( 2019). An exploratory study of managerial approaches to food waste mitigation in coffee shops. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 76, pp.48-57.
Haile, M., (2019). The role of microbes in coffee fermentation and their impact on coffee quality. Journal of food quality, 2019.
Hii, C.L., (2019). An Overview of Cocoa and the Coffee Industry. Drying and Roasting of Cocoa and Coffee, pp.1-20.
Justi, M., (2019). Fulvic acid in foliar spray is more effective than humic acid via soil in improving coffee seedlings growth. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 65(14), pp.1969-1983.
Maamoun, A., 2020. Coca-Cola brews a hot acquisition: Costa coffee.
Oh, D., (2019). A holistic view of the service experience at coffee franchises: A cross-cultural study. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 82, pp.68-81.
Raza, H., (2019). Social Sustainability Assessment of the Organic Gayo Coffee Industry in Aceh Province, Indonesia.
Sousa, L.M., (2019). Spent coffee grounds as a renewable source of energy: An analysis of bulk powder flowability. Particuology, 43, pp.92-100.
Urwin, R., (2019). The rise of specialty coffee: An investigation into the consumers of specialty coffee in Gauteng.
Uwizeye, O., (2019). Influence of Strategic Management Drivers on The Growth of Coffee Export Processing Firms in Rwanda (Doctoral dissertation, JKUAT-COHRED).
Appendix 1: Internal and external stakeholders of Starbucks