To analyze the effect of implementing MCSR on the economy growth of India
The growing environment problems and increasing business environment give rise to the up-gradation of CSR strategy. It is found that previously companies in India performed the CSR activities in the form of construct the temple or provide funds to some needy once. But such areas do not support the social community, environment and economy factors. It results in improper development and growth in India (Waagstein, 2011).
In regards to this, India initiated the new policy under the India’s company’s act within the section of 135 and it makes mandatory for companies to invest at least two percent of firm net profit in terms to the betterment of society, environment and economy. This practice allows companies to determine the CSR needs and develop plan for implementing the CSR activities.
However, this act considered as one of the main step of government in regards to made it compulsion for firm to use the CSR strategy and this practice also helps in transforming the CSR programs from tradition into new one. Likewise, initially, firms involved in philanthropic activities like to building temple, performing charity work and providing food to poor people etc.
But with the changes in business environment, firm comes with innovative CSR activities (Afsharipour and Rana, 2013). The best example of this is the big organisations like Mahindra and TATA and many more. Companies majorly include CSR programs in the form of supporting the education of particular group. Besides that, environment, health care and women empowerment is another focus point under current CSR programs. However, the selection of CSR areas are largely depend on a host of factors like nature of business, relevancy of community issue and availability of finances within the company (Dhaliwal et al., 2011). Thus, these areas influence the CSR program implementation. Likewise, big companies have more scope to earn profit so it more involves in the development of CSR but it is not easy for small firm whose profit margin is not at much. In such case, the mandatory CSR act proved to be adverse.
Additionally, current scenario signifies that there are various companies that used the CSR strategy with the aim to make a profit because this practice is the best areas to directly connect with the society and influences them (Mukherjee et al., 2018). However, the mandatory CSR law is quite beneficial approach by the side of Indian government in regards to realise the firm their responsibility towards the society, environment and economy. But, its effectiveness can only be examined with the analysis of implementation process of government. This is because there are various policies which are developed by Indian people but citizens never get benefit of such policies due to poor implementation of policy (Van Zile, 2011). In respect to this, the study will focus on evaluation the effect of implementation of MCSR on the economic growth of India. This means that the paper helps to identify whether MCSR implementation proved to be useful for the economic growth of India.
The consideration of this research study provides a better understanding about the implementation of mandatory CSR at the India companies. This study will also guide in terms to analyse the significances of such implementation over the economy growth. Based on this, it becomes easy to better ways to implement the CSR activities into the business. However, this study is quite important for companies as well as country to analyse the impact of MCSR policy (Singh and Kaur, 2016). This way study would be effective for government in regards to identify the problem behind of poor implementation and offer new strategies to design the CSR activities. However, in professional viewpoint, this study contributes for increasing researcher knowledge and understanding about the MCSR policy and impact of implementation over the economy growth. Similarly, the study will also help the researcher to fill the research gap in regards to lack of focus on MCSR policy as there are various researcher which address the study of CSR and ignore the MCSR which is the important initiative which Indian government has taken in 2014 and it also indicated the strong impact on the economic growth (Okoye, 2012). However, this study proves to be useful for future research as well as for the development of skill and knowledge also. Similarly, the research would support more the existing literature study related to CSR implementation by firms.
However, this research is also significant in regards to examine the role of government in regards to push the CSR concept into reality. Likewise, it is found that initially when CSR activities come into practice, there are only few firms that applied into its business. These types of organisations are also only big firms which have a capability to implement it. But it ignores largely by the SMEs firm (Manesca, 2010). Thus after the amendment of company act, this law proved to be useful for realising the firm about their responsibility towards the society, environment and economy etc. That’s why this study proved to be beneficial in regards to identify the role of Indian government in regards to implement the Mandatory CSR policy into the businesses. Hence, it can be stated that this study will help in many aspects like for developing further research or to solve the problem which faced by the firms with the policy of mandatory CSR.
This section addresses the layout of the research report in order to provide brief about the areas which will perform in the research study. This structure presents the systematic way to perform the research work.
Introduction: This is first chapter of dissertation and it provides background facts about research topic in order to make a better understanding about the problem areas. Besides that, the chapter also provide aims and objectives in order to conduct the research work properly (Gopalan and Kamalnath, 2015). Based on research objectives, the questions are prepared so that study can be addressed. Basically, this chapter develop the base to gain knowledge about the problem area and define the scope of research through provide proper justification.
Literature Review: – This chapter consider as a theoretical explanation of research study with proper justification or examples. It offers views of different authors, researchers upon the research topic. Basically, it undertakes the research question in order to address best solutions. For this, chapter review the research of existing information which is extracted from journal articles and e-books, news and government websites etc (Afsharipour and Rana, 2013). This is done through provide a theoretical understanding about the research issue and research gap in this study.
Research Methodology: – This is the important section in regards to conduct the research work. It allows to converting the theoretical knowledge into practical manner. It offer the design research, research philosophy, research approach and strategy etc. along with this, data collection method and sampling techniques will be discussed for carrying out the study in a appropriate way. The chapter also addresses sample size, method of analysis etc. However, this chapter allows the researcher to investigate the research question related to the effect of implementation of Mandatory corporate social responsibility (Lam et al., 2017).
Finding and Data analysis: – This above chapter constitutes the chapter fourth which helps to present the findings of research study. However, researcher analyse the data and present the finding in a systematic manner. Based on such discussion, the research result will be identified. Basically, this section includes tables, charts and graphs to present the data and interpretation. Thus, it can be depicted that this section is critical for the researcher because it shows the practical understanding about the research topic (Bihari and Pradhan, 2011). In case researcher makes any mistake in analysing the data then it directly influences the entire research study.
Conclusion and Recommendation: – The chapter consider as the final one in the research study and it present summary of above study in an appropriate form. It includes key points, findings and addresses the research question (Öberseder et al., 2013). However, the section indicates the recommendation based on the analysis for the effect of Mandatory CSR over the India economy growth.
In today’s corporate world, social responsibility is creating a huge influence over the business entity and shareholders as well as towards the welfare of the society. According to Okoye (2012), CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) is an effective area that needed to be considered by every registered large company as a mandatory law every year. The corporate social responsibility is a complex and best responsibility which creates an impact over the decision of the business and activities in terms of society and environment development. In an organization, such type of social responsibility practices develops a healthy environment and also consistent achieving the sustainable development practices.
While studying, it is also identified that government made mandatory for the organization to make 2% of the profit contributed for the social responsibility in order to develop an economy as whole. The Companies Act 2013 made it mandatory for the registered company which having an income of approx. INR 1000 crores and more than one who have net worth of INR 500 crores or more, similarly net profit of Rs 5 crores or more etc are liable to contribute into CSR practice. At the same time, Dhaliwal et al., (2011) also added his point of view that such kind of social responsibility is mandatory for the betterment of the economy in terms of establishing best firm practices, creating wealth as well as improve in the society culture and environment.
But on the other side, Mukherjee et al., (2018) also stated that corporate social responsibility also creates issues for the business that become increase in integration in the modern developing business practices. In addition, Van Zile (2011) also demonstrated that corporate social responsibility is clearly understood as a way for the firm which integrate the economic, social and environment concerns in terms of customs, values, strategy, etc. The use of corporate social responsibility as mandatory restricted the companies to save their profit as reserves but allowed to use it for society welfare by undertaking the expectation of shareholders respectively (Stomberg, 2016).
In concern to this, every registered company are required to develop an effective CSR policy and committee who focus on developing social responsibility program which contributes towards the economy and society through sufficient funds. The development of CSR policy creates a huge influence over the company that need to be undertaken while performing any list of projects and this policy should have a disclosure in the report of Board of Directors of the company. Moreover, Wiese and Toporowski (2013) also elaborated that in India, there are approx. 8000 companies which fall under the range of CSR provision which is mandatory for all.
In year 2014, India became first nation across the globe for making the CSR mandatory as a new rule in Companies Act 2013 for the businesses. In India, the concept of making corporate social responsibility mandatory is quite different from the other developed and developing countries. In regards to this, Singh and Kaur (2016) clearly stated that corporate responsibility for businesses is important activity to contribute towards the social, economic and environmental development for creating a positive influence over the society. Apart from this, this mandate also made businesses more committed towards the social clauses and making more engaged with the local communities for ensuring their development in long run.
In regards to this policy, it can be stated that Mandatory CSR activities is the crucial step which is taken by the Indian government as it makes realise the firm about their responsibility towards the environment, society and economy (Raub and Blunschi, 2014). But at the same time, poor implementation of MCSR strategy and improper regulatory body could be also considered as a major limitation in regards to achieve the maximum benefits of MCSR activities. Thus, it is quite difficult to conclude that Mandatory CSR activities contributed efficiency for the economic growth of India.
Steps taken by Indian government to make CSR programs mandatory for every organisation
For an organization, it is important to develop its company image and reputation in high competitive market for which timely social welfare program required to be conducted. Visser and Tolhurst, (2017) determined that only India is a country around the world where CSR is mandatory legislated. This step of actions by the Indian government found to have an effective impact or effect on the business decisions and practices which directly or indirectly connected with the economy growth and development. Additionally, Singh and Kaur (2016) also explained that for making the CSR practices as mandatory for that government of India decided to make a new legislative law which will make the Indian companies to adopt or implement that practices in their respective firm.
While undertaking this action, in 2012, government first analyzed the annual reports and CSR reports of companies before they passed this CSR law as mandatory. Further, it is also examined that Indian government also identified that need of CSR activities for the society and also its overall effect on the economy as a whole (India Briefing, 2017). In Companies Act 2013, three different dimensions or fiscal conditions are provided by the government in terms of net worth, net profit and net turnover of the company. However, if any company meet these conditions then they required to develop a CSR committee and proper CSR policy which enforce the CSR mandatory and also make ensure that it is followed by the company and its staff members respectively.
The step of adding CSR law in Companies Act 2013 is found suitable idea for the development of the Indian economy and that affected the condition of poor people and society as whole in positive way. As per Arora (2016), this mandatory CSR decision somewhere promoted the transparency and disclosure of the company actual image in terms of turnover or profit in global competitive market. On the other side, company relationship with the internal as well as external stakeholders and the integration of CSR to its core operations is discussed for determining the CSR needs which require to be addressed for the well being of the shareholders as well as society also.
Moreover, Ni and Van Wart (2015) also stated that Section VII of companies Act 2013 also added the list of CSR activities which involves activities like promotion of education and employment, eradicating the poverty and hunger, promoting the equality among the gender, empowerment of women, old age homes facilities, contribution for the flora and fauna and also for the sport promotion and development of project to a large extent (Sharma, 2009). These all activities getting small contribution from the companies of 2% is also huge in development and encouragement of people of the Indian society to get educated and aware.
According to Indian government, this action of CSR law is fruitful and useful for both companies and economy as this practice will encourage the firms to initiate for achieving the sustainable position in today’s developing competition market. In concern to this, Grayson and Hodges (2017) also elaborated that CSR practices efforts by an organization is an win-win situation because this practices helps in developing sustainability as well as company reputation among the customers. In addition, the other measure taken by the government that if there is any company which don’t meet the three fiscal conditions then they are provided with the exemption for the three consecutive years respectively.
In support to this study, Haar and Keune, (2014) found that Indian government has taken initiative in regards to help the firm for making proper planning about the CSR activities. In regards to this, government appoint the authorities for helping the firm regards to how CSR practice can be performed. Besides that, Indian government organise training sessions for the organisation in terms to make them understand about the way of CSR execution. This contributes towards the development of CSR in a proper manner (Resmi et al., 2018). But still the CSR activities are not implemented properly and the main reason is the lack of government focus towards the SMEs due to which these enterprises tend to be not success to adopt the CSR. Thus, these areas restrict the Indian government to successfully implement the MCSR policy into the country.
According to Valmohammadi and Ahmadi, (2015), the development of scorecard is another step which government has included for the implementation of policy. This is because scorecard method helped the firm to evaluate or track the current status of firm and accordingly it provide assistant to firm for creating a CSR activities. Besides that, Indian government also encouraged the NGOs to collaborate with the firms in order to execute the CSR practices into the reality. For this, it is found that government push pressure on firm to make an alliance with the NGOs and serve the society. This is done in such a way that Firm ask the NGOs about the current issues which need to address such as poor education infrastructure and accordingly provide aid to society. Thus, this way the CSR activities get established. Lastly, government also made it compulsion for the firm to develop the CSR report of every year whether it is big or small firm. This practice also helped the government to implement this policy into the Indian business (Shuaibu, 2017). Thus, these are the steps or strategies that contribute efficiency for the Indian government for implementing the Mandatory CSR policy.
Effect of implementation MCSR over the economic growth in India
The implementation of mandatory CSR (corporate social responsibility) creates a huge effect on the economic growth of an India in both most positive and negative manner. The research study of Wiese and Toporowski (2013), clearly stated that a corporate social responsibility affected society in a positive manner in the Indian economy and that brought a huge improvement in terms of developing country. There are various areas that can easily justify that Mandatory CSR policy proved to be effective for Indian government (Krishnan, 2012). Likewise, as per the associated chambers of commerce and Industry, it is recorded that around 67% of domestic firms in India have select non-government organisations as partners to undertake their CSR projects.
Besides that, IICA (The Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs) has developed CSR implementing hub. In this, it present database of agencies through conduct baseline surveys and evaluate the impact assessment and social audits etc. but at the same time, there are various challenges that firms faced in regards to perfectly implemented of CSR activities. This is to identify right NGOs to work with as with so many NGOs in India which extensively involved in CSR practices. In that case, it is must to engaged with right one and implement it successfully through provide help to needy once (McHale et al., 2013). Thus, such areas contribute towards the improving standard of living which turns into economic growth and development.
In favour to this study, Dutta and Singh (2013) stated that Mandatory CSR has a positive response over the society because previously, there are various companies which do not follow this concept as CSR practice include high cost investment. So that’s why organisation does not show support or concern towards the community, environment and economy. Thus, in such case, mandatory CSR policy is the best one to make firm realise about their responsibility towards the society and increasing environmental problems. At the same time, Taneja et al. (2011) mentioned that this policy is good for making organisation responsible but it positive effects are not reflected properly due to lack of monitor or implementation of CSR mandate.
Likewise, it is stated in Clause 135(5) of the act that if in case firm be unsuccessful to spend 2% of its 3 years average profit over the CSR then the top management are needed to show such information in the report with the specific or prompt reason. But such areas are absent in current scenario (Bafna, 2018). Likewise, there are few companies who follow this law otherwise firms ignore the reporting action. The reason behind of this is the poor role of government in the monitoring process. There is lack of a separate entity which is unbiased in nature and due to which there is failure of companies are recorded to undertake the CSR as per the section 135 (Menezes et al., 2012). Thus, such areas clearly present the reason why the Mandatory CSR policy benefits are not gained by the society. It can be stated that the development of MCSR tend to be ethical but its improper implementation and monitoring area are not contribute towards achieving the positive end results. On the other side, Grayson and Hodges (2017) also stated that once the CSR became mandatory and implemented by the Indian government that created positive effect over the proposed taxation system which hold the promise in terms of sustainability growth and development in an Indian economy. This implementation effect also reflected on the India GDP growth rate which found to be raise by 8.2% respectively.
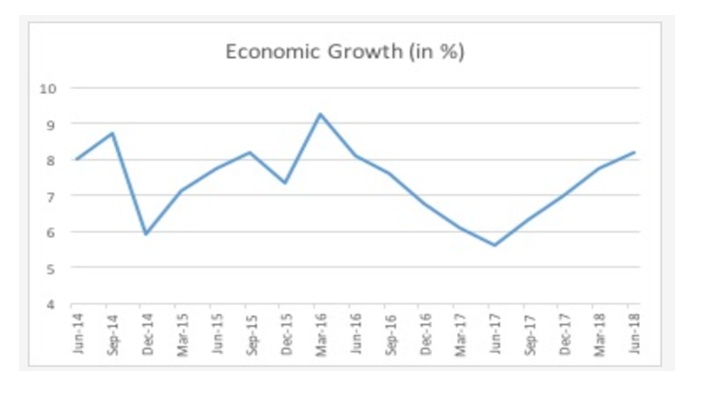
(Source: AsiaTimes, 2018)
The above graph of economic growth clearly reflects the change in the growth level of India in previous and current financial years 2014-2018. However, this growth in economy reflects the contribution level of business towards the development of the society in terms of livelihood and healthy environment respectively.
In contrary to this study, Rangan et al. (2015) stated that the implementation of MCSR is not proved to be effective completely due to improper monitoring system within which Indian government fails to monitor and evaluate that organisation implement the CSR activities properly with ethical manner. It is found that when companies fail to contribute 2% for the development of society and environment then board of directors is not provided any valid reason for failing to report related to CSR as per the clause 134(3) (Mezzadri, 2014). In regards to this, there is no strict action is imposed by the government and this happened due to non-presences of independent agency that evaluate the failure of companies to incorporate expenditure for the betterment of society (Susruth, 2017). Besides that, there is no provision available related to scrutinize the company actions regards to CSR activities. Thus, these limitations may present that implementation of MCSR policy does not contribute such benefits which is expected to create. In support to this study, Dhanesh (2014) discussed that nature of increasing competition could be another area that makes the implementation of MCSR adverse. It is because growing competition develops a sense of perception to generate more profit. It is found that since people have more conscious about the environmental issues and society development, they engage into the CSR activities just for grabbing the attention of consumers and increase the profit. In respect to this, the firm primary objective is to earn maximum money rather than serve to society. Thus such intension never supports the firm to implement properly CSR programmes.
In a similar manner, Nunes et al. (2013) found that small firm like SMEs faced main challenges to execute the CSR activities and this is because of less availability of resources like talent workforces, technical equipments and adequate capital etc. these areas limits the small firms to successfully implement the CSR activities. At the same time, lack of support by the government is also considered as an important aspect due to which small business houses faced problem to serve society and community in an effective manner. Thus, it can be stated that poor execution process of the government could be the cause of achieving low benefits with this policy. But at the same time, Marquina Feldman and Vasquez-Parraga (2013) illustrated that Mandatory CSR Policy not proved to be effective for all areas but it support the main objective of society which is to focus on the critical issues like poverty, malnutrition and hunger problems. It is found that the reason behind to start the MCSR policy is to help the people to gain basic necessity through realise the firm responsibility towards the society. This aim is successfully achieved with the implementation of Mandatory CSR activities as every organisation is involved in designing CSR activities with good or bad intension. Thus, this area contributes to address the basic or major problems of society. This can be justified with the instances like it is recorded that there is an enhancement of craftsmanship by promoting the works of art and setting up facilities for the creative people in order to increase more skills. Besides that, Mandatory CSR policy also assisted in regards to raising the education standard and women empowerment (Muhajid and Abdullah, 2014). It is depicted that big organisation like HUL and ITC are more involved into the promotion of education campaign through saving 1 Rs over the product selling for the girl child education. Thu, these areas clearly signify the initiatives of firms towards the improving education system.
However, mandatory CSR also contributed towards the promotion of gender equality among the Indian citizens where inequality is the major concern area. In the study of Malik (2015), it is discussed that India have high problem related to gender inequality as this problem occurred at every area like women are getting their rights at home even at workplace. Thus, such areas are addressed properly by the CSR activities. For example, organisations like Reliance’s and TATA promotion gender equality through empower women in the form of providing accommodation like homes and hostels for girls. Moreover, it also engages in development of old age homes and day care centres. Thus, such areas encouraged the women’s to pursue their professional career (Navjeet, 2018). It can be analysed that CSR initiatives proved to be effective for the Indian women’s to eliminate the inequality not completely but push the women’s to pursue their careers.
In favour to this study, El Ghoul et al. (2017) analysed that other than education and gender equality, CSR implementation is emphasised more on the environmental and healthcare facilities. It is found that company like Ultratech Cement are involved on social work across 407 villages by providing the healthcare facilities. This is done through develop campaign which create an awareness about the healthy life and supply the necessary treatment to the peoples. In a similar manner, firms like Tata group also engaged into the resolving of environmental related problems. However, there are various problems are occurring with changing environment such as growing pollution and frequent change in climate etc. In regards to this, the organisation moves towards the sustainability practice by adopting the method like recycle, reuse and reduce (Kanwal et al., 2013). Thus, such areas help the firm to reduce the maximum emission of carbon and result in elimination of negative effect over the environment. This way, the implementation of mandatory CSR policy implementation proved to be effective in regards to address the major areas such as society, environment and economic development.
In the research of Karam and Jamali (2013), it is identified that the implementation of Mandatory CSR does not gain that much popularity among the companies. This is because this law limits the activities in CSR like this policy includes that spending need to be included related to social causes rather than those activities which benefit the stakeholder of firm. This legislation creates a problem for firm to successfully implement the CSR activities. However, organisation are developed with the aim to achieve profit so in that case if they do not gain benefit with the execution of CSR then take less interest in the implementation of CSR activities. Thus, this area clearly reflect that government initiative is correct but its policy is not appropriate for the welfare of organisation MCSR policy focus more towards the betterment of society, environment and economy. That’s why organisation fails to successfully report or implement the CSR into its business operations (Dhingra and Mittal, 2014). On the basis of this study, it can be depicted that implementation of mandatory CSR proved to be positive as well as negative for the economic growth of India.
Approaches to improve the MCSR for the economic development of India
In regards to above study, it can be stated that MCSR not fully contributed well for the economic growth of country. This is because of existences of various limitations in the implementation and monitoring process. In regards to this, there is need to include various approaches and recommendations in order to bring improvement in the MCSR policy so that economic growth can be obtained. In the views of Grohmann and Kauffeld (2013), firstly, there is need to address the problem of absence of monitoring body under the company act. In regards to this, Indian government need to develop a panel and require to making them responsible for the review the CSR report of firms and recording the reasons for not submitting the CSR documents. Such areas may help to realise the firm about their responsibility and this practice also provide benefit to government in regards to make a control over the organisations. In a similar manner, Bond and Goldstein (2015) believed that both parties such as government and organisation divert their intension towards the optimally utilisation of available resources to a greatest extent so that economy can move towards the development. However, Indian government should shift their CSR investment towards the ongoing improvements through making proper interaction among the companies with government departments. This help to developing managerial capabilities of the public service delivery and it also result in introducing the continuous innovations. Thus, this practice is far better on simply make CSR investment in regards to uplift the society. The interaction of both the parties not only provide benefit to firm but it also support the government in regards to asses and list programmes and activities of private sectors and this participation may also contribute towards the improving standards of living. Hence, the equal involvement of both the parties can proves to be more beneficial as compare to make a high investment in CSR activities.
As per the above study, it is found that CSR practice is preferred by the firms in India as a stakeholder approach followed by the profit motive. Besides that, firm faced lots of problem in the implementation of CSR due to lack of resources availability and less support of government in regards to take participate with the organisation for implementing any social activity. In respect to such issues, Bargain et al. (2013) suggested that government should facilitate the proper infrastructure which support the firm in respect to timely use the resources and perform the actions. Such act would not be possible without the support of government. Besides that, government body should conduct proper training session through appoint trainers for the organisation so that they can understand such aspect and execute the CSR in a proper manner.
According to Sutherland and Figari (2013), the Indian government need to focus on new approaches under the companies act. Likewise, initially tax related treatment for all CSR practices are come under MCSR policy and it includes as a uniform in nature. But such practice does not contribute towards the encouragement of companies towards the implementing of CSR. In that case, it is suggested that separate tax strategy for expenditure on various CSR programmes may create more advantage to both government and firm. It is found that differential tax policy encourages the firm to more involve into the CSR activities with the aim to gain more tax benefits. Thus, this exercise could support the policy of MCSR in a more effective manner.
Research Aim and Objective, Research questions
In order to conduct the research work successfully, the researcher aim is to analyse effect of implementation of MCSR on the economic growth of India (Tewari, 2011). In regards to achieve the aims, here are the study objectives:-
- To study about the Concept of MCSR
- To discuss the steps which Indian government has taken to make CSR programs mandatory in every organisation (Van Zile, 2011).
- To examine the effect of implementing MCSR over the economic growth in India.
- To define the approaches to improve the MCSR for the economic growth of India
On the basis of such activities, the researcher pursues its study and collects resources for accomplishing the research result.
For the accomplishment of research objective, here is the research question which is addressed in regards to gain better understanding about the research topic and it will result in attaining positive research outcome.
- What is the reason behind to make MCSR Mandatory among the organisation by the side of Indian government?
- Do you think that the MCSR policy proved to be successful?
- What are the steps which Indian government have taken for execute the MCSR initiatives?
The main purpose of this report is to analysis the effect of implementation of Mandatory CSR on the economic growth of India. In concern to this, Scheurich (2014) also stated that qualitative and quantitative method is two different types of the research methods which are useful for the researcher in accomplishing the research aim efficiently. For this research study, research used qualitative research method for completing the research study on time as well as addresses all research questions efficiently and effectively. In regards to this, discussion and finding is used to present the data and based on this researcher achieved the research outcome.
The first major part of research methodology is research philosophy which hep he researcher in developing in-depth knowledge and understanding related to research topic efficiently. In regards to this study, the researcher is used the interpretivism philosophy in a way to develop both subjective and theoretical understanding related to research topic. The use of this philosophy contributes towards conduct of overall study related to evaluate whether MCSR proves to be effective for the Indian economy or not.
Research strategy is effective process that provides right direction for conducting systematic information related to research topic. According to Farrington et al., (2012), it is clearly stated that research strategy help the researcher in solving the research problem efficiently and effectively by following proper and right direction respectively. For doing research, researcher conducts several studies which include literature review, survey, experiment, case study, focus group and much more. This available study helps the researcher in selecting best study as a research strategy which support in achieving the best suitable research outcome. In context to it, the researcher decided to use the literature review as research strategy for collecting required data or information and analyzing them by using the best research data analysis method. This research strategy will help the researcher to make a knowledge related to the execution effect of mandatory CSR in India for economic growth.
Sultan and Yin Wong (2013) defined as a plan or procedure that consists of set of step which is based on the assumption for addressing the research problem respectively. The use of research approach is quite helpful for the researcher in generating and presenting the reliable outcome for the research. There are different types of research approach are included i.e., inductive approach and deductive approach. For this study, researcher decided to use the inductive research approach instead of using the deductive research approach. The inductive research approach helped researcher in developing its own theory as appropriate for the research. In concern to this, Stacciarini et al., (2011) also determined that use of deductive approach might create the problem in accomplishing the research aim that might result into the research issues. However, for this research study, researcher used deductive research approach for solving the problems or issues as research is related to the theoretical aspects.
Neuman (2013) defined that collection of data is an effective way or process through which large amount of data is collected from different sources which provides new and existing information related to research topic. The data collection methods are primary data collection and secondary data collection which supports the researcher in gathering a large and relevant amount of data respectively (Kumar, 2018). For this research, researcher used secondary data collection method for collecting the data which reflects the implementation effects of corporate social responsibility over the economic growth in India.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is undertaken as major section of research methodology that helps the researcher in examining the data which is gathered from different sources (Walliman, 2011). It is very important part of any research. It interprets the data collected through various methods and it helps to know that which tools and technique needs to be used further for the research. It supports the researcher in decision making and find out some useful information regarding research. Basically it is a procedure of conversion of raw data into useful data through some tests, Interviews and fact findings. In context to this study, researcher is used qualitative technique for analysing the data (Kumar, 2011). Qualitative technique aims at describing the situation, also identify the expected outcome in advance. It is based on observations, hypothesis and different patterns and theory. Researcher analyse the data through group discussions, brain storming sessions etc. In this study, content analysis has been used to represent the data (India CSR Network, 2018). It helps the researcher to achieve the desired results, also enables the readers to understand the results easily.
Ethical Considerations
It is very much important to run any research on ethical grounds. It helps the researcher in collecting right information from the respondents. It eliminates the manipulation and runs the research effectively (Carroll and Shabana, 2010). Ethical considerations ensure that rules and regulation related to copyright and Plagiarism are followed during research. Also, researcher must verify that data source from which data has been collected before using them in research and must do citation for the data collected. To avoid Plagiarism and copyright related issued researcher should write the content in his own language instead of copy paste the data. It is the core responsibility of researcher to maintain the confidentiality of the respondents who provided the data so that they can share their valuable opinion without any fear and hesitation (Tripathi and Singh, 2014). In this research researcher has followed all the ethical values and collected the data without and biasness and prejudice (Anlensiya et al., 2014). Thus it plays a signification role in research and makes the research much smoother.
Research Limitations
Every research has certain limitations. In this research researcher has faced the limited time and high cost related issues. It was very time consuming such practices affects the authenticity of its results. As researcher has limited period of time to conduct this research, it was very challenging to collect appropriate and authentic data in stipulated time period and faced issues to interpret the data (Fooks et al., 2012). There were some weakness related to the scope of the research, collection of data and objectives of research. Apart from that staff was not supportive, this is also a reason that research crossed the time and research could not conduct in a proper manner
Data Analysis/Results and Discussion
The data analysis and finding is the important section of the dissertation as it guides the researcher about the finding about the research topic. It also helps the people to gain an understanding about the effectiveness of Mandatory CSR and its consequences. This study presents data which is gathered from the secondary sources such as e-books, online journal articles and different researchers study (Grbich, 2012). It is the appropriate manner to converse the data to the readers and interpret the finding to them which is gained from the objectives and Literature review. Therefore, this section proves to be effective in terms to analyse and present the important facts to the reader.
On the basis of above discussion, it is found that Mandatory CSR policy is enacted in 2013 under the Indian companies act and after implementation of Mandatory CSR policy, the impact of such policy can be justified with the analyse of Indian economy (CNBC, 2018).
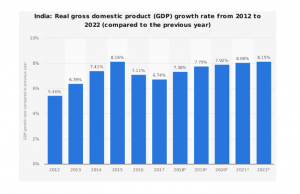
(Sources: Statista., 2018 )
This figure clearly present the impact of Mandatory CSR acts over the Indian economy growth (Dixit and Kumar Pandey, 2011). It can be illustrated that before execution of MCSR policy, the India GDP falls down. Likewise, in 2012-13, the GDP rate of India is recorded only 5 to 6% which is not effective for the country economy growth. But with the introduction of MCSR policy, it is found that the GDP start increasing in rapid manner like 7 to 8% till 2016 and then GDP become stable till 2018, now it is supposed that GDP will increase in future. This upliftment would be expecting due to continuous improvement and innovations in the Indian market. Such area enhances the standard of living and high demand attracts the FDIs in a rapid way.
In regards to such study, it can be discussed that the policy of Mandatory CSR is responsible for achievement of high GDP rate of country. This can be stated that before enactment of policy, the growth rate of Indian economy do not get push. This is because of lack of less involvement of firms in regards to improve people standard of living. But with the execution of Mandatory CSR policy, companies become responsible for the society welfare and start contributing efficiency for the development of community, environment and economy etc. This occurs in the form of company focuses more towards the sustainability practice through involve recycle, reuse and reduce method etc. It results in reduction of environmental problem, besides that, firms also engaged towards the women’s empowerment and promotion of girl education in society (Govindaraju and Tang, 2013). Therefore, these practices result in development of society and move the economy towards the growth.
The impact of Mandatory CSR policy can be analysed with the help of companies. Likewise, Mahindra and Mahindra is the one which is extensively involved in the CSR areas. Firm is concentration majorly on the young girl, farmers in a way through programmes in the domain of education, public health and environment etc. Moreover, Mahindra develop a campaign with pride school with the aim to provide livelihood training to youth who belong to socially and economically poor communities. In a similar manner, TATA Power involved in CSR areas related to environment and health aspects. Firms spend on CSR in year 2015 at INR 31.1 Crore as against the 2% of PAT requirements of Rs 29.8 Crore. Besides that, firm spends on joint ventures of the firm with Rs 18.2 Crore as against the need of INR 17.2 Crore (The Economic Times, 2015). Thus, this study clearly reflects that TATA performs exceptionally well as it invested more than 2% in the CSR activities. Furthermore, Bharat petroleum is also take part into the CSR activities and contributed maximum support in the areas like quality education, skill development and solving basic problems of general public like drainage problem. For this, firm developed the project called BOOND which emphasis on the development of rain water harvesting structures to make a village drought-free. This initiative starts with the four villages in Maharashtra and now it is extended to over 140 villages in Karnataka, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra etc. therefore, these campaigns or projects of firm under CSR strategy proved to be healthy for the economy growth. On the basis of such initiatives, it is found that local people of India able to improve their standard of living and able to access basic necessity (The CSR Journal, 2018). Due to which, India structure pursue towards the growth rate.
This result in attracting of FDIs as it is estimated that FDIs is increased more after the implementation of policy in India (Chandra, 2018). This occurs in the form of increasing investment in automotive sector after April 2014 to February 2015 by 89% (Aminu et al., 2013). This makes India the largest producer of vehicles in across the globe with 17.5 million vehicles annually (Tata and Prasad, 2015). However, it is investigated that the local firms get maximum benefit of CSR activities in the form of inflow of FDIs through knowledge transfer. It is found that with the incorporation in CSR activities, the firm get benefit in the form of achieving the high goodwill in market and this recognition provide advantage to firm in terms to get the offer of partnership with foreign agency. It is found that foreign companies enter into the new market by making partnership with that firm which has high goodwill in local market (Rana, 2018). This is because new firm can attain high recognition in the new area. Thus, in such manner, firm gets maximum benefits with the implementation of CSR activities (Hoi et al., 2013). Other than that, CSR activities also support the local firm in terms to expand the firm as with the engagement of ethical practice, every stakeholder wants to work with the organisation. So in that case, firm has a high chance to gain competitive advantage. Thus, this policy proved to be effective in terms to attract FDIs and expansion of local business outside the boundaries.
However, there is one more important affect is recognised which gained from the Mandatory CSR policy is that with the companies start investing more than 2% of its profit into the CSR activities. This practice contributes efficiency for both organisation as well as social community. Business gains the benefit in the way of getting high recognition in market while society achieves the upliftment in terms to fulfil basic needs and enhance their standard of living. This can be justified with the example of ITC group as it is observed that firm in its initially level earn recognition based on its product feature and quality. It always pursue towards the new product range for enhancing goodwill and recognition. But after development of Mandatory CSR activity, it become easy for the firm to interact directly with the general public and identify the needs and wants of them. This way firm able to fulfil the needs of different customers (Arora and Dharwadkar, 2011).
Moreover, the CSR policy also helps ITC in its business also like firm introduce e-Choupal program which objectives is to connect the rural farmers with the internet for obtaining agricultural product covers 40,000 villages and four million farmers. This practice helps the organisation in regards to directly take agricultural product from the farmers. On the other hand, farmers gain advantage in terms to earn enough money directly from the firm without exploiting by the intermediaries.

(Sources: Mukherjee, 2015)
This e-Choupal program helps ITC in regards to provide quality product at affordable price. It results in increase in sales and revenue. Thus, it can be depicted that CSR activities proved to be effective in terms to attain the competitive advantage and market share.
The effect of CSR is not limited to just helping society or earning profit but with the increasing business competition, the CSR strategy become a trend in India. However, listed firms in India spent approx. US$1.23 billion in several programs such as educational programs, skill development, social welfare, environment conservation and healthcare etc. Moreover, it is recorded that there is an increment in the education sector funding with US$300 million followed by healthcare with US$240.88 million (The Indian Express, 2018). Furthermore, currently, there is great impact of Mandatory CSR policy is found out with the implementation of CSR practices in the form of introduce new government program such as Swachh Bharat and Digital India. This CSR practice proved to be successful especially in India as this initiative allows the country to be clean and safe (Kuada and Hinson, 2012). Such practice attracts various tourists which in short benefit the economy growth.
However, there are different journal articles stated that most SMEs Indian firms are showed less interest in the adaptation of CSR activity. Firstly, the SMEs do not have enough money to invest; secondly they do not get that much benefit with the implementation of CSR like investment in charitable activities. Besides that, small firm are not able to achieve high returns from the CSR activity. It is found that the first announcement of the policy of MCSR caused a decline in firm value about 2.6% to 3.3% (Lanis and Richardson, 2012). This is because firm initially earn loss with the investment in CSR programs like child education campaign as they do not have any effective return. So the magnitude effect of this policy is low at the initial level. But after a time CSR activities proved to be effective for the firm when Indian government takes important steps in regards to implement the Mandatory CSR policy in an actual manner. Likewise, government announced about the tax benefit to the organisation as the firm who invest more share in CSR activities tend to receive redemption in the tax. This opportunity generates an interest among the big or small firms to grab chances of get reduction on tax. Thus, such practice results in the implementation of CSR activities into the businesses. Moreover, the Indian government another step is the assignment of NGO to the companies as this practice helps the organisation to plan and design the CSR activities with the NGO and able to execute it into the reality. Furthermore, the participation of NGO guides the firm in respect to identify the issues which exist in society so that such problems are addressed by the organisations (Watson, 2015). Thus, this area also supports the firms to implement the CSR activity into the business operations.
On the other hand, there are various researchers which investigated that the impact of Mandatory CSR policy do not contribute that much efficiency as there are various limitations exist with the execution of policy. Likewise, there is no proper monitoring body is established for regulating the MCSR process. Because of this, various problems occurred in the form of no mention of the report to be submitted to the government or monitoring body. It is also identified that there is no official body who take responsibility to ask the firm about the reason of not submitting the CSR report. Such areas limit the benefit of MCSR policy over the economic growth (Reddy, 2015). Additionally, it is found that there are various firms which not involve with the positive intension to serve society but firms engage with the CSR activities for just earning more and more capital. This practice of firm does not contribute towards the welfare of society. Thus, this study present that the implementation process of Mandatory CSR do not contribute much efficiency for the Indian economy growth. In regards to this, lack of government supports is considered as a major reason for the poor result of policy. It is identified that government develop the policy but at the time of implementation, there is absence in the participation by the side of government (Jeffrey, 2015). Thus, this areas influences both organisation as well as government in a way that policy do not work properly and firm fails to successfully execute the CSR activities. However, the improper availability of resources for performing a CSR activity tends to be considered as another fault from the government side. Likewise, small firm are asked to implement a CSR project when firms need help for develop, design the CSR. Then in that case, government neither provide capital assistance to small firms nor help the firm in regards to provide direction. That’s why there are many firms which fail to adopt the policy and implement it successfully.
Furthermore, the Mandatory CSR policy consist of legislation which depicted that CSR program do not include the betterments of organisation employees or any internal stakeholders (Van Zile, 2011). This area creates dissatisfaction among the firm since business run for making revenue. In that case, firm faced problem in regards to attain the profit over the expenses as CSR programs demands for the huge investment of both money and time. Thus, such areas restrict the firm towards the implementing of CSR practice in an effective manner. Additionally, the study also investigated that political interferences is another weakness of this policy. Different opinions of political leader are occurred in which some individuals support the policy and many of them criticized. However, the practice of CSR always consider as a controversial topic and it has attracted strong viewpoint from different sides like academics, executives and social activist etc. The arguments arise on the action that companies should be legally required to report CSR activities. In regards to the MCSR policy, the lower house of the Indian Parliament passed bill that mentioned that companies to ensure that they are required to spend at least 2% of annual profits on CSR exercise. However, the parliament upper house is likely to pass new bill in future. This legislation covers around 3000 companies in India and $2 billion expenditure is spending on CSR activities (Sheehy, 2015). In respect to this bill, some politicians illustrated that proposed law is to encourage firm for undertaking social welfare while some people stated that this proposed bill may only increase the burden over the organisation and it can affect the economy in an adverse manner. This aspect also plays an important role to consider in regards to identify the reason behind of improper implementation of Mandatory CSR activities.
In respect to such problems, the government of India requires to incorporate new approaches for bringing efficiency. Likewise, for CSR to be sustainable and effective, it is important for the government to include growth of different stakeholders like employees, suppliers, banks etc. This practice encouraged small or large organisations to incorporate CSR programs into business operations (Singh and Kaur, 2016). Moreover, the Mandatory CSR policy needs to include a separate entity that evaluates the failure of firms towards the reporting of CSR activities. In respect to this, there is need to develop a legislation related to penalties in order to create a strictly applied the policy. However, differential tax treatment is another aspect that requires to addressing by developing legislation through mention that those organisations who have contributed more than 2% on CSR activities are liable for receiving tax benefit. Furthermore, integration between the government and organisation is other recommendation that need to include as government active participation allows the firm to properly design the layout of CSR program and it result in the development of CSR activities in an effective way. Thus, these approaches may assist the Indian government to attain the benefits of Mandatory CSR policy (Gupta, 2014). The above analysis defines that Mandatory CSR policy need to be revised as this practice have a positive impact over the economy but it also includes various limitations due to which benefits are not gained properly.
From the above discussion, it is summarized that Govt has introduced MCSR policy in 2013 in India. It is successful to the some extend to create awareness in companies regarding CSR programmes. Now businesses are following this seriously and taking initiatives for it. Such CSR programmes also creating a healthy environment in corporate and also inspires corporate world to contribute for the society. Government carefully studied the economy of the country before announcing it compulsory. Firstly Government has studied the annual reports and CSR reports of companies and formulated the terms and conditions that which companies are bound to implement this policy mandatorily and how it will impact the economy of the country. In addition to this government is taking initiatives to help the companies in implementing the CSR programmes, also conducting training sessions to educate the companies that how to conduct CSR programmes effectively. It is supporting to create better understanding for the execution of these programmes. All such efforts are helpful in implementing this policy effectively on ground level. Some of the occasions State government acts as coordinator between NGO’s and organisations and provide them the information regarding CSR programmes and activities to be held. However government is facing challenges while implementing the CSR programmes smoothly. There is lack of public participation in CSR programmes. It is also observed that sometimes the intended beneficiaries do not cooperate much as they show a very little interest which effects their participation and contribution in the activity. There is also need to build local capacities as non-governmental organisations are not adequately trained and well equipped and these in- capabilities impacts the succession rate of CSR activity. In addition to this there is lack of transparency and consensus. Lack of the transparencies creates a lot of discomfort between companies and local agencies. They do not share the important details regarding CSR programmes. It is also found that due to lack of proper framework of work there are chances of duplicity. NGO’s and companies do not prioritize the CSR programmes that which activity needs to be performed first. It also shows the lack of coordination between NGO and Local agencies. It affects the relationship of companies and NGO’s. These challenges decrease the growth of CSR programmes in the country. It has been revealed that now trends are changing the country regarding CSR programmes. It has now become essential part for corporate to perform. They are also realizing that if they are receiving so much from the society now it is their turn to give them back and this circle must to be completed. CSR programmes affect the growth of the economy both in positively and negatively. CSR programmes help the companies to create a good image in the market and good reputation with its clients. It brings the lost of positivity in terms of values and ethic in corporate as no organisation can run without following ethics. Now organisations tend to think more seriously regarding CSR programmes and taking initiatives at different levels. Now organisations are much concerns regarding environment and promoting GO Green initiative and motivating employees to use eco-friendly things. Company like Infosys contributes a lot for the betterment of the society. It organise charity work like donation of money, note books and computers for the NGO’s and especially for unprivileged children. It also uses the eco friendly techniques like solar panel to create energy in its campus. CSR activities also help companies to create a good brand image in the market. It builds the reputation of being responsible business organisations and differentiates from other organisation in the market; it helps in taking lead in the respective industry. It increases the clients for the business. By using echo friendly techniques business are saving cost and becoming self independent in area of energy which is also an initiative of CSR activity. When the organisation starts contributing towards society then it created good relationships with stakeholders and client and it also attracts the potential clients and it enables the organisation to get more business. It boosts the employee morale and inspire for doing something good for society as their end. Some of the organizations establish schools and hospitals especially for their employees and their children which contributes the society indirectly. A good image and brand name helps the organisation establishing good relationship with local authorities which helps to reduce some legal burden and run the business much smoother. Thus it can be summarize that CSR activities brings a lot of positive changes in the country, organisations are more sincere for the betterment of the society and helps the government to fight against serious some issues like Education, energy and in promoting echo friendly environment.
On the contrary, there are some disadvantages of CSR programmes, not all the consequences are favourable. Banerjee 2007 notes that not all the CSR work done truly social and companies are using this platform for improving the financial performance for future. Some organisations are inspired by hypocrisy to do CSR activity. Companies showcase that they follow the CSR Idea however in reality they indulge with corporate abuses like environmental destruction, hazardous labour conditions, improper focus on product and safety standards, relocations of polluting sectors to regions and week environmental safety measures. They only pretend the compliance of social responsibility whereas in reality they develop only their goodwill in market and establish relationship with client and customers while abusing their corporate power. There is also lack of a supervision body to measure the performance of CSR activities. There are no such rules and regulations are formulated by the government by which improvement in society can be measured. As per the Johnson 1958 companies can use their ‘Socially responsible’ philosophy in their general interest and it can lead to centralization of power into their hands so they can interfere into so many non business areas. Thus, CSR programmes have negative impact too on society.
As per the above analysis it is concluded that CSR programmes significantly contributed in economic growth of country. Organisations are seriously taking initiatives towards it and realizing the value of it. Mandatory CSR activity is introduced into India in 2013 and before that economy of India was falling down but if the result of its implementation impacted it and it boosts the economy. In 2013 the GDP growth rate was 5 to 6 % which was not so impressive, but later in 2016 it increased to 7 to 8 % and after that economy gets more stable. It is projected that there is chances of increase in GDP rate. This is the result of continuous improvement in CSR activities which helps the economy to grow faster. It also supports to enhance the living standards and quality of life, empowering the basic requirements of life of needy section of society. Most important of CSR initiatives is it invites the Foreign Direct investments in the country. It attracts the foreign brands into Indian Market to business. It helps the economy to earn the foreign currency. By implementing the MCSR policy corporate world is becoming very much responsible towards social betterment. They are showing interests towards the social, economical and environmental development. They are also involved in women empowerment and girls’ education. They are offering employment opportunities to women. Hence these efforts support the growth of economy.
There are many companies which are engaged in corporate social responsibility likewise, Mahindra & Mahindra is widely involved in CSR programmes. It majorly pays attention towards girl’s education, farmers, environment and public health. They arrange the trainings sessions to train people for their bread and butter. There is one more company TATA power works in health and environment area. It spends for CSR Rs 31.1 Crore in year 2015, apart from that it invests 18.2 Crore on subsidiaries and joint ventures. There is also an organisation named Bharat Petroleum. It contributes in area of public interest like quality education and skill development and water drainage. It started a project called BOOND related to water harvesting. It promotes to rain water harvesting and establish the entire structure for making village’s drought free. Initially it was started in Maharashtra covering four villages not it has been expanded to 140 villages of Rajasthan, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra. Thus CSR programmes supports the economy to grow faster and resolving the issues related to public interest. It is also helpful to invite the foreign investments in the country; it is found that the parentage of FDIs has increased after the implementation of the MCSR policy. FDI is increased in automobile sector after April 2014 to February 2015 by 89 %. Due to which India has become largest producer in the globe with 17.5 million vehicles annually.
There is an example of ITC Group, MCSR programmes a new platform to launch new products and these programmes are quite useful to gain recognition in based on its product feature and quality. Now it is easy for this organisation to interact directly with general public in order to find their necessities. With the support of this policy ITC group started E-Choupal which cover 40,000 villages. The purpose of this initiative is to connect the farmers with internet and educate them how to procure the products using internet. This is beneficial for the farmers and the organisations as well as. Firm can purchase the agricultural product directly from the farmers and farmers can sell their goods without interference of intermediaries. It supports the eliminated the role of intermediaries in the market and farmers get fair rates for their products. Thus, this practice supports the elimination of corruption in the system and increases the sales and revenue. Swachha Bharat Abhiyaan is the great initiative of CSR initiative taken by the government. This is not regarding the cleanliness only but also it is creating awareness about the environment and health. It is motivating people to keep to their cities and ultimately country clean which helps to attract more tourism in the country. Thus, these areas concluded that the policy of Mandatory CSR proved to be effective for realising the firm about its responsibility but it fails to contribute major benefits due to poor implementation of policy.
Limitation/ Future Recommendation
There are certain limitations that occur in the conduct of study. This includes cost and time. It is found that there is high time invested in the performing of each chapter due to which cost of the overall project get increased. Such area influences the result of research study. In regards to above study, there are some recommendations for addressing some major issues which government faced during the implementation of CSR programmes. The most critical issue is there is not supervisory body in the system to keep track of CSR practices. It is very important to have proper governance around it for measuring the effectiveness CSR programmes so that these practices can be executed properly. There is also lack of government side in the participation side hence government should take some serious steps to make more awareness among the organisations. In addition to this, many small firms are able to participate in this practice because of funding issues so government must help them in financial aspect. Government should also help the smaller firms to formulate the entire framework for designing and implementing CSR practices so that they can also contribute towards it. These steps will help the government to implement the CSR activities effectively and widen the area of such programmes.
Afsharipour, A., and Rana, S. (2013) ‘The emergence of new corporate social responsibility regimes in China and India’, UC Davis Bus. LJ, 14, pp. 175.
Aminu, S. A., Salau, T. J., and Pearse, O. E. (2013) ‘Attracting more foreign direct investment (FDIs) to alleviate poverty in Nigeria’, International Journal of Management Sciences and Humanities, 1(1), pp. 65.
Anlensiya, A., Ahinsah, J.,Fatimatu, B. and Bukrari, Z. (2014) ‘The effect of corporate of social responsibility on Financial Performances on MTN Ghana Limited’, International Journal of Thesis Projects and Dissertations. 2, (2), pp. (62-69)
Arora, P., and Dharwadkar, R. (2011) ‘Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility (CSR): The moderating roles of attainment discrepancy and organization slack’, Corporate governance: an international review, 19(2), 136-152.
Arora, R. (2016) ‘Enhancement in employee skills and benefits to employees and organization with respect to CSR Initiatives’, JIM Quest, 12(2), p.39.
Asia Times (2018) Why Indian economic growth is back at 8%. [Online] Available at: http://www.atimes.com/why-indian-economic-growth-is-back-at-8/. (Accessed on: 20th September, 2018)
Bafna, A. (2018) A Study on the Impact of CSR on Financial Performance of Companies in India. International Journal of Engineering technology Science and Research. [Online] Available at: http://www.ijetsr.com/images/short_pdf/1512892686_325-331-ietech842_word_etsr.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Bargain, O., Dolls, M., Fuest, C., Neumann, D., Peichl, A., Pestel, N., and Siegloch, S. (2013) ‘Fiscal union in Europe? Redistributive and stabilizing effects of a European tax-benefit system and fiscal equalization mechanism’, Economic Policy, 28(75), pp.375-422.
Bihari, S. C., and Pradhan, S. (2011) ‘CSR and Performance: The story of banks in India’, Journal of Transnational Management, 16(1), pp.20-35.
Bond, P., and Goldstein, I. (2015) ‘Government intervention and information aggregation by prices’, The Journal of Finance, 70(6), pp. 2777-2812.
Carroll. A. B. and Shabana, K. M. (2010) ‘The Business Case for Corporate Social Responsibility: A Review of Concepts, Research and Practice’, Internal Journal of management Reviews, 2 (1), pp. 85-105
Chandra, S. (2018) Analysis of Corporate social responsibility with special references to India. [Online] available at: https://www.livelaw.in/analysis-of-corporate-social-responsibility-with-special-reference-to-india/ (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
CNBC. (2018) Measuring the impact of CSR spends. [Online] Available at: https://www.cnbctv18.com/economy/measuring-the-impact-of-csr-spend-1400431.htm (Accessed: 20thSeptember, 2018)
Dhaliwal, D. S., Li, O. Z., Tsang, A., and Yang, Y. G. (2011) ‘Voluntary nonfinancial disclosure and the cost of equity capital: The initiation of corporate social responsibility reporting’, The accounting review, 86(1), pp.59-100.
Dhanesh, G. S. (2014) ‘CSR as organization–employee relationship management strategy: A case study of socially responsible information technology companies in India’, Management Communication Quarterly, 28(1), pp.130-149.
Dhingra, D. and Mittal, R. (2014) ‘CSR practices in Indian banking sector’, Global Journal of Finance and Management, 6(9), pp.853-862.
Dixit, A. and Kumar Pandey, A. (2011) ‘SMEs and Economic Growth in India: Co-integration Analysis’, IUP Journal of Financial Economics, 9(2).
Dutta, K. and Singh, S. (2013) ‘Customer perception of CSR and its impact on retailer evaluation and purchase intention in India’, Journal of Services Research, 13(1).
El Ghoul, S., Guedhami, O. and Kim, Y. (2017) ‘Country-level institutions, firm value, and the role of corporate social responsibility initiatives’, Journal of International Business Studies, 48(3), pp.360-385.
Elwyn, G., Frosch, D., Thomson, R., Joseph-Williams, N., Lloyd, A., Kinnersley, P., Cording, E., Tomson, D., Dodd, C., Rollnick, S. and Edwards, A., (2012) ‘Shared decision making: a model for clinical practice’, Journal of general internal medicine, 27(10), pp.1361-1367.
Farrington, D. P., Ohlin, L. E. and Wilson, J. Q. (2012) Understanding and controlling crime: Toward a new research strategy. USA: Springer Science & Business Media.
Fooks, G., Gilmore, A., Collin, J., Holden,C. and Lee, K. (2012) ‘The Limits of Corporate Social Responsibility: techniques of Neutralization, Stakeholder Management and Political CSR’, Journal of Business Ethics.112,(2),pp-283-299
Gopalan, S. and Kamalnath, A. (2015) ‘Mandatory corporate social responsibility as a vehicle for reducing inequality: an Indian solution for Piketty and the millennials’ Nw. JL & Soc Pol’y’, 10, pp. 34.
Govindaraju, V. C. and Tang, C. F. (2013) ‘The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, economic growth and coal consumption in China and India’, Applied Energy, 104, pp.310-318.
Grayson, D., and Hodges, A. (2017) Corporate social opportunity!: Seven steps to make corporate social responsibility work for your business. UK: Routledge.
Grbich, C. 2012. Qualitative data analysis: An introduction. UK: Sage.
Grohmann, A. and Kauffeld, S. (2013) ‘Evaluating training programs: development and correlates of the Q uestionnaire for P rofessional T raining E valuation’, International Journal of Training and Development, 17(2), pp-135-155.
Gupta, A. D. (2014) ‘Implementing corporate social responsibility in India: issues and the beyond. In Implementing Corporate Social Responsibility’, pp. 19-29. New Delhi: Springer.
Haar, B. T. and Keune, M. (2014) ‘One step forward or more window-dressing? A legal analysis of recent CSR initiatives in the garment industry in Bangladesh’, International Journal of Comparative Labour Law and Industrial Relations, 30(1), pp.5-25.
Hart, M., (2013) ‘The matization of power, the search for common interests, and self-reflection: Towards a comprehensive concept of emancipatory education In From Adult Education to the Learning Society’, pp. 45-63. UK: Routledge.
Hoi, C. K., Wu, Q. and Zhang, H. (2013) ‘Is corporate social responsibility (CSR) associated with tax avoidance? Evidence from irresponsible CSR activities’, The Accounting Review, 88(6), pp.2025-2059.
Hwang, G.J., Wu, P.H. and Chen, C.C., (2012) ‘An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities’, Computers & Education, 59(4), pp.1246-1256.
India Briefing (2017) Corporate Social Responsibility in India. [Online] Available at: https://www.india-briefing.com/news/corporate-social-responsibility-india-5511.html (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
India CSR Network. (2018) “The Hilton Effect” Defines the Ongoing Influence of the First Global Hotel Company Around the World and in Asia Pacific. [Online] Available at: http://indiacsr.in/the-hilton-effect-defines-the-ongoing-influence-of-the-first-global-hotel-company-around-the-world-and-in-asia-pacific/ (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Jeffrey, R. (2015) ‘Clean India! Symbols, policies and tensions’, South Asia: Journal of South Asian Studies, 38(4), pp.807-819.
Kanwal, M., Khanam, F., Nasreen, S. and Hameed, S. (2013) Impact of corporate responsibility on the firm’s financial performance. Journal of Business and Management [Online] Available at: http://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol14-issue5/I01456774.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Karam, C. M. and Jamali, D. (2013) ‘Gendering CSR in the Arab Middle East: an institutional perspective’, Business Ethics Quarterly, 23(1), pp.31-68.
Krishnan, N. (2012) Impact of Corporate Social Response Responsibility on the Performance of Select BSE Listed Companies. [Online] Available at: http://www.dypatil.edu/schools/management/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Impact-of-Corporate-Social-Responsibility-on-the-financial-and-non-financial-performance-of-select-BSE-listed-companies-NALINI-KRISHNAN.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Kuada, J. and Hinson, R. E. (2012) ‘Corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices of foreign and local companies in Ghana’, Thunderbird International Business Review, 54(4), pp.521-536.
Kumar, A. (2018) Does CSR makes economic sense? [Online] Available at: http://indiacsr.in/csr-make-economic-sense/ (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Kumar, R. (2011) Research Methodology. SAGE Publications Ltd, [Online]: Available at: http://www.sociology.kpi.ua/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/Ranjit_Kumar-Research_Methodology_A_Step-by-Step_G.pdf (Accessed on 20th November, 2018)
Lam, J. Y., Sethuraman, K., and Singh, P. J. (2017) Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility Dimensions on Firm Value : Some Evidence from Honh Kong and China. [Online] Available at: file:///C:/Users/User/Downloads/sustainability-09-01532.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Lanis, R. and Richardson, G. (2012) ‘corporate social responsibility and tax aggressiveness: a test of legitimacy theory’, Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 26(1),pp. 75-100.
Malik, M. (2015) ‘Value-enhancing capabilities of CSR: A brief review of contemporary literature’, Journal of Business Ethics, 127(2), pp.419-438.
Manesca, C. (2010) Economic Implications of Corporate Social Responsibility and Responsible Investments. University of Gothenburg. [Online] Available at: https://mail.google.com/mail/u/0/#inbox/FMfcgxvzLXKsXcFhCMcqfRfKrdVQBXnJ?projector=1&messagePartId=0.1 (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Marquina Feldman, P. and Vasquez-Parraga, A. Z. (2013) ‘Consumer social responses to CSR initiatives versus corporate abilities’, Journal of Consumer Marketing, 30(2),pp.100-111.
McHale, P., Wood, S., Hughes, K., Bellis, M. A., Demnitz, U., and Wyke, S. (2013) ‘Who uses emergency departments inappropriately and when-a national cross-sectional study using a monitoring data system’, BMC medicine, 11(1),p.258.
Menezes, A. C., Cripps, A., Bouchlaghem, D. and Buswell, R. (2012) ‘Predicted vs. actual energy performance of non-domestic buildings: Using post-occupancy evaluation data to reduce the performance gap’, Applied energy, 97, pp.355-364.
Mezzadri, A. (2014) ‘Indian garment clusters and CSR norms: Incompatible agendas at the bottom of the garment commodity chain’, Oxford Development Studies, 42(2), pp.238-258.
Muhajid, M and Abdullah, A. (2014) Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Firms Financial Performance and Shareholder wealth. European Journal of Business and Management [Online] Available at: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.685.5627&rep=rep1&type=pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Mukherjee, A., Bird, R. and Duppati, G. (2018) ‘Mandatory Corporate Social Responsibility: The Indian experience’, Journal of Contemporary Accounting & Economics, 14(3), pp.254-265.
Mukherjee, W. (2015) India’s Best Companies for CSR 2014: Here’s how ITC’s social outreach programme works. [Online] Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/indias-best-companies-for-csr-2014-heres-how-itcs-social-outreach-programme-works/articleshow/45372587.cms (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Navjeet, (2018) India’s Mandatory CSR Law: Issues and Challenges. [Online] Available at: http://vips.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Mandatory.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Neuman, W. L. (2013) Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. USA: Pearson education.
Ni, A. and Van Wart, M. (2015) ‘Corporate Social Responsibility: Doing Well and Doing Good. In Building Business-Government Relations’, pp. 175-196. UK: Routledge.
Nunes, P. M., Gonçalves, M. and Serrasqueiro, Z. (2013) ‘The influence of age on SMEs’ growth determinants: empirical evidence’, Small business economics, 40(2), pp. 249-272.
Öberseder, M., Schlegelmilch, B. B. and Murphy, P. E. (2013) ‘CSR practices and consumer perceptions’, Journal of Business Research, 66(10), pp.1839-1851.
Okoye, A. (2012) ‘Exploring the relationship between corporate social responsibility, law and development in an African context: Should government be responsible for ensuring corporate responsibility?’, International Journal of Law and Management, 54(5),pp. 364-378.
Rana, S. (2018) India: Corporate Social Responsibilities Enforcement Review. [Online] Available at: http://www.mondaq.com/india/x/755280/Corporate+Governance/Corporate+Social+Responsibilities+Enforcement+Review (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Rangan, K., Chase, L. and Karim, S. (2015) ‘The truth about CSR’, Harvard Business Review, 93(1/2), pp.40-49.
Raub, S. and Blunschi, S. (2014) ‘The power of meaningful work: How awareness of CSR initiatives fosters task significance and positive work outcomes in service employees’, Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 55(1), pp.10-18.
Reddy, K. S. (2015) ‘India’s aspirations for universal health coverage’, New England Journal of Medicine, 373(1), pp.1-5.
Resmi, S. I., Begum, N. N and Hassan, M. M. (2018) Impact of CSR on Firm’s Financial Performance: A study on some selected agribusiness Industries of Bangladesh. Published by American Institute of Science. [Online] Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327135497_Impact_of_CSR_on_Firm’s_Financial_Performance_A_Study_on_Some_Selected_Agribusiness_Industries_of_Bangladesh (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Scheurich, J. (2014) Research method in the postmodern. UK: Routledge.
Sharma, S. G. (2009) Corporate Responsibility in India : An overview. The International lawyer. [Online] Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40708084?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Sheehy, B. (2015) ‘Defining CSR: Problems and solutions’, Journal of Business Ethics, 131(3), pp.625-648.
Shuaibu, M. A. (2017) The Effect of Social Responsibility on Financial Performance: Evidence from the Banking Industry in Emerging Economics. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly.[Online] Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321964143_The_Effect_of_Corporate_Social_Responsibility_on_Financial_Performance_Evidence_from_the_Banking_Industry_in_Emerging_Economies (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Singh, B. J. R. and Kaur, M. P. (2016) ‘Corporate social responsibility in India’, International Journal of Higher Education Research & Development, 1(1).
Singh, B. J. R.,and Kaur, M. P. (2016) ‘Corporate social responsibility in India’, International Journal of Higher Education Research & Development, 1(1).
Stacciarini, J. M. R., Shattell, M. M., Coady, M. and Wiens, B. (2011) ‘Community-based participatory research approach to address mental health in minority populations’, Community mental health journal, 47(5), pp.489-497.
Statista., (2018) India: Real gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate from 2012 to 2022 (compared to the previous year). [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/263617/gross-domestic-product-gdp-growth-rate-in-india/) (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Stomberg, A. (2016) CSR Sustainable Economic, Environmental and Social Aspects. Centria University of applied Sciences. [Online] Available at: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/122202/Annika%20Stromberg_thesis.pdf?sequence=1 (Accessed: 20th September, 2018 )
Sultan, P. and Yin Wong, H. (2013) ‘Antecedents and consequences of service quality in a higher education context: a qualitative research approach’, Quality assurance in education, 21(1), pp.70-95.
Susruth, M (2017) A Study on corporate social responsibility and financial performance in the Indian Context. International Journal of Commerce and Management Research. [Online] Available at: file:///C:/Users/User/Downloads/3-3-91-594.pdf (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Sutherland, H and Figari, F. (2013) ‘EUROMOD: the European Union tax-benefit microsimulation model’, International Journal of Microsimulation, 6(1), pp.4-26.
Taneja, S. S., Taneja, P. K. and Gupta, R. K. (2011) ‘Researches in corporate social responsibility: A review of shifting focus, paradigms, and methodologies’, Journal of Business Ethics, 101(3), pp.343-364.
Tata, J., and Prasad, S. (2015) ‘CSR communication: An impression management perspective’, Journal of business ethics, 132(4), pp.765-778.
Tatli, A., (2012) ‘On the power and poverty of critical (self) reflection in critical management studies: a comment on Ford, Harding and Learmonth’, British Journal of Management, 23(1), pp.22-30.
Tewari, R. (2011) ‘Communicating corporate social responsibility in annual reports: A comparative study of Indian companies & multi-national corporations’, Journal of Management & Public Policy, 2(2).
The CSR Journal (2018) CSR Spends: What the data Tells Us. [Online] Available at: https://thecsrjournal.in/csr-spends-what-the-data-tells/ (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
The Economic Times., (2015) Mahindra & Mahindra tops CSR list in India even as companies scale up operations. [Online] available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/company/corporate-trends/mahindra-mahindra-tops-csr-list-in-india-even-as-companies-scale-up-operations/articleshow/49330470.cms) (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
The Indian Express. (2018) CSR spending requirement: Notice to firms for not complying with norms. [Online] Available at: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/csr-spending-requirement-notice-to-firms-for-not-complying-with-norms-5436507/ (Accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Tripathi, R and Singh,V.P. (2014) ‘Corporate Social Responsibility and Ethical Issues in Marketing’, International Journal of Management and International Business Studies. 4,(3),pp.297-308
Valmohammadi, C. and Ahmadi, M. (2015) ‘The impact of knowledge management practices on organizational performance: A balanced scorecard approach’, Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28(1), pp.131-159.
Van Zile, C. (2011) ‘India’s mandatory corporate social responsibility proposal: Creative capitalism meets creative regulation in the global market’, APLPJ, 13, p.269.
Visser, W. and Tolhurst, N. (2017) The world guide to CSR: A country-by-country analysis of corporate sustainability and responsibility. UK: Routledge.
Waagstein, P. R. (2011) ‘The mandatory corporate social responsibility in Indonesia: Problems and implications’, Journal of business ethics, 98(3), pp.455-466.
Walliman, N. (2011) Research Methods: The Basics. Taylor & Francis e-Library, [online] available at :https://edisciplinas.usp.br/pluginfile.php/2317618/mod_resource/content/1/BLOCO%202_Research%20Methods%20The%20Basics.pdf (accessed: 20th September, 2018)
Watson, L. (2015) ‘Corporate social responsibility, tax avoidance, and earnings performance’, The Journal of the American Taxation Association, 37(2), pp.1-21.
Wiese, A and Toporowski, W. (2013) ‘CSR failures in food supply chains–an agency perspective’, British Food Journal, 115(1), pp.92-107.


